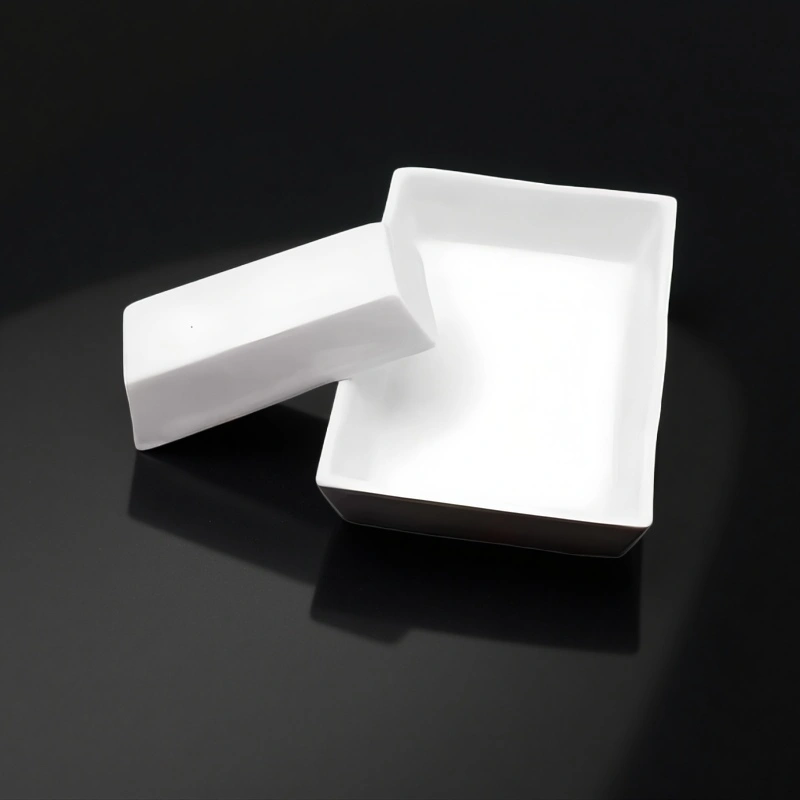
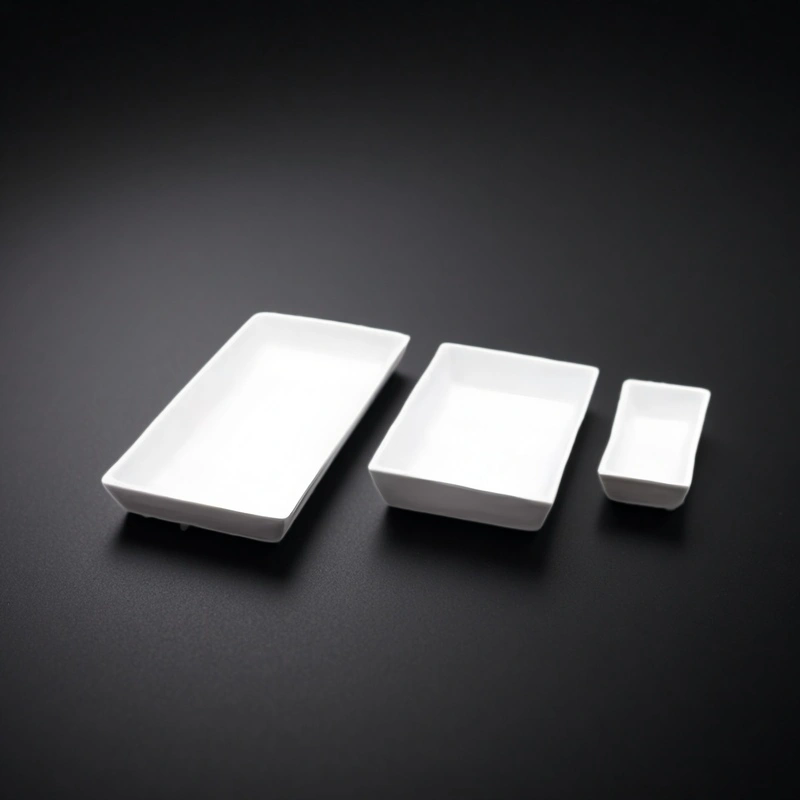
Trapezoid alumina crucibles are trapezoid-shaped ceramic crucibles made from alumina (Al₂O₃), used as high-temperature sample holders in laboratory and industrial thermal processes such as ashing, calcination, combustion tests, and high-temperature pre-treatment.
Advantages of Trapezoid Alumina Crucibles
-
Trapezoid geometry improves placement stability and prevents rolling or shifting in furnaces, keeping each crucible seated in a fixed position on trays and holders during loading, firing and unloading.
-
Uniform wall thickness and a flat base support consistent heat distribution across the sample bed, helping laboratories obtain repeatable ash and combustion results from batch to batch.
-
High-density alumina with low porosity reduces micro-cracking and edge chipping under repeated heating and cooling cycles, extending crucible service life in routine quality control work.
-
Angled sides and flat base allow close packing on furnace shelves and in racks, improving chamber utilization and making it easier to organize, label and transfer multiple samples at once.
-
Controlled dimensional tolerance between crucibles helps them fit reliably into standard frames or automated testing systems, simplifying replacement and reducing setup adjustments when switching batches.
Trapezoid Alumina Crucibles Properties
| Property | Unit | 99.5% Al₂O₃ | 99.6% Al₂O₃ | 99.7% Al₂O₃ | 99.8% Al₂O₃ | 99.9% Al₂O₃ | 99.99% Al₂O₃ |
| Alumina content | % | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.99 |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.89 | 3.91 | 3.92 | 3.93 | 3.94 | 3.98 |
| Open porosity | % | 0 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Color | – | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory |
| Water absorption | % | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Young’s modulus (Elastic modulus) | GPa | 375 | 356 | 357 | 358 | 359 | 362 |
| Shear modulus | GPa | 152 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bulk modulus | GPa | 228 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Poisson’s ratio | – | 0.22 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Compressive strength | MPa | 2600 | 2552 | 2554 | 2556 | 2558 | 2570 |
| Flexural strength | MPa | 379 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 320 |
| Fracture toughness | MPa·m¹ᐟ² | 4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hardness | GPa | 14.1 (≈1440 kg/mm²) | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 35 | 32–37 | 33–38 | 34–39 | 35–40 | 36–42 |
| Thermal shock resistance ΔT | °C | – | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 228 |
| Maximum use temperature (no load) | °C | ≤1750 | 1755 | 1760 | 1765 | 1770 | 1800 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 10⁻⁶/°C | 8.4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Specific heat | J/kg·K | 880 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Volume resistivity | Ω·cm | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ |
| Dielectric constant (relative permittivity) | – | 9.8 | 9.83 | 9.84 | 9.85 | 9.86 | 9.92 |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 16.9 | 23.2 | 23.4 | 23.6 | 23.8 | 24 |
| Dissipation factor (loss factor @ 1 kHz) | – | 0.0002 | – | – | – | – | – |
Trapezoid Alumina Crucibles Specifications
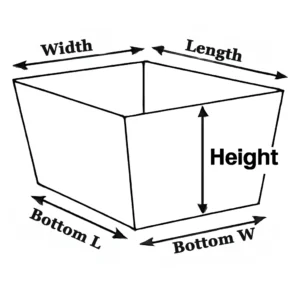
| Item NO. | length (mm) | width (mm) | height (mm) |
| TE-AS-071 | 100 | 84 | 35 |
| TE-AS-072 | 100 | 56 | 35 |
| TE-AS-073 | 100 | 43 | 26 |
| TE-AS-074 | 100 | 27 | 27 |
| TE-AS-075 | 100 | 24 | 17 |
| TE-AS-075-1 | 100 | 20 | 20 |
| TE-AS-075-2 | 100 | 27 | 27 |
| TE-AS-075-3 | 103 | 28 | 30 |
| TE-AS-075-4 | 100 | 43 | 25 |
| TE-AS-075-5 | 100 | 24 | 17 |
| TE-AS-075-6 | 100 | 27 | 25 |
| TE-AS-075-7 | 100 | 43 | 26 |
| TE-AS-075-8 | 100 | 56 | 35 |
| TE-AS-075-9 | 100 | 50 | 35 |
| TE-AS-075-10 | 100 | 56 | 35 |
| TE-AS-076 | 73 | 30 | 22 |
| TE-AS-076-1 | 73 | 30 | 22 |
| TE-AS-076-2 | 70 | 30 | 22 |
| TE-FA-001 | 300 | 70 | 30 |
| TE-FA-002 | 200 | 80 | 35 |
| TE-FA-003 | 200 | 11 | 12 |
| TE-FA-004 | 105 | 23 | 20 |
| TE-FA-005 | 100 | 30 | 25 |
| TE-FA-006 | 90 | 10 | 10 |
| TE-FA-007 | 80 | 30 | 20 |
| TE-FA-008 | 88 | 12 | 10 |
Trapezoid Ceramic Alumina Crucibles Packaging
- Individual protective ceramic separators to prevent edge damage
- Batch packaging with shock-absorbing inserts for transport stability










