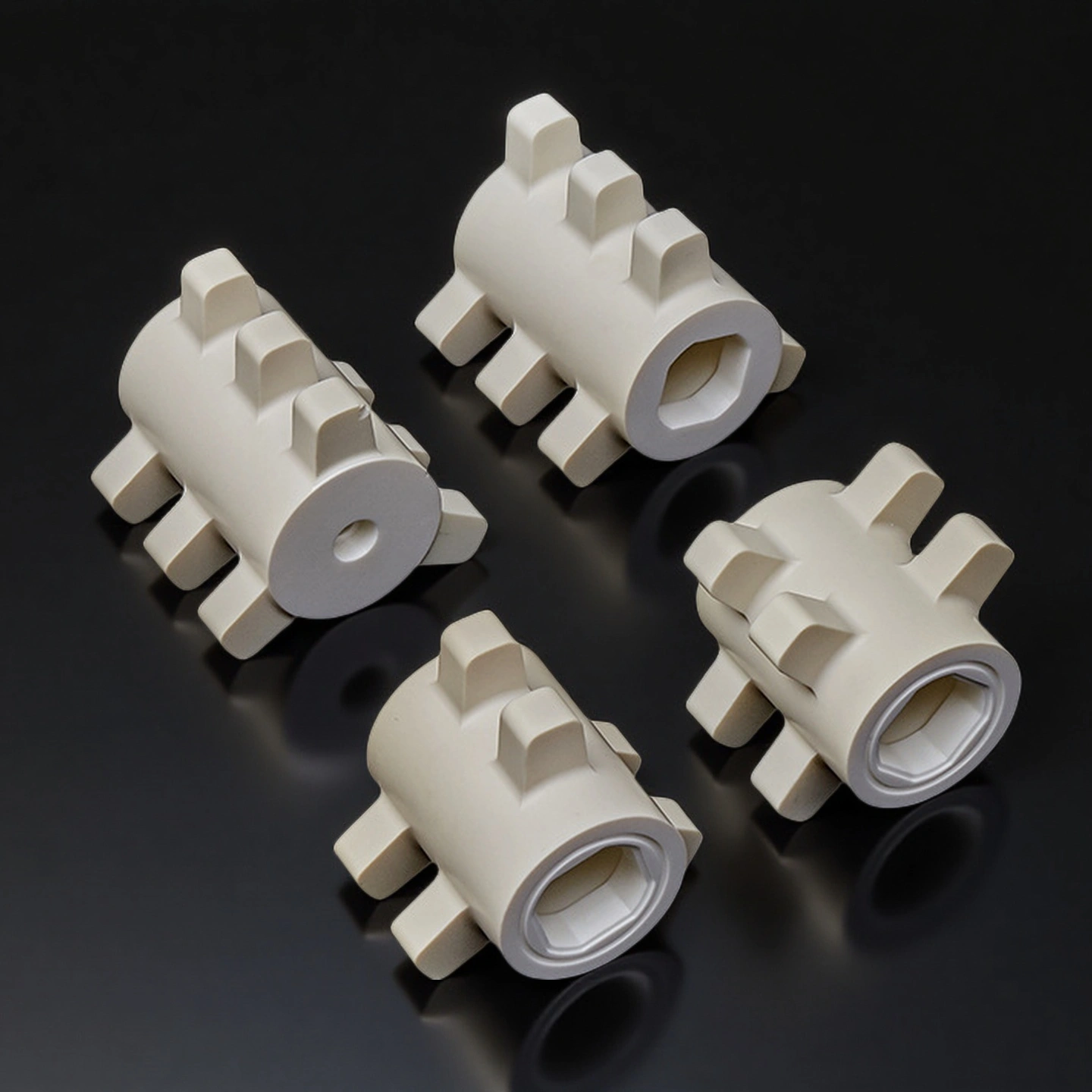
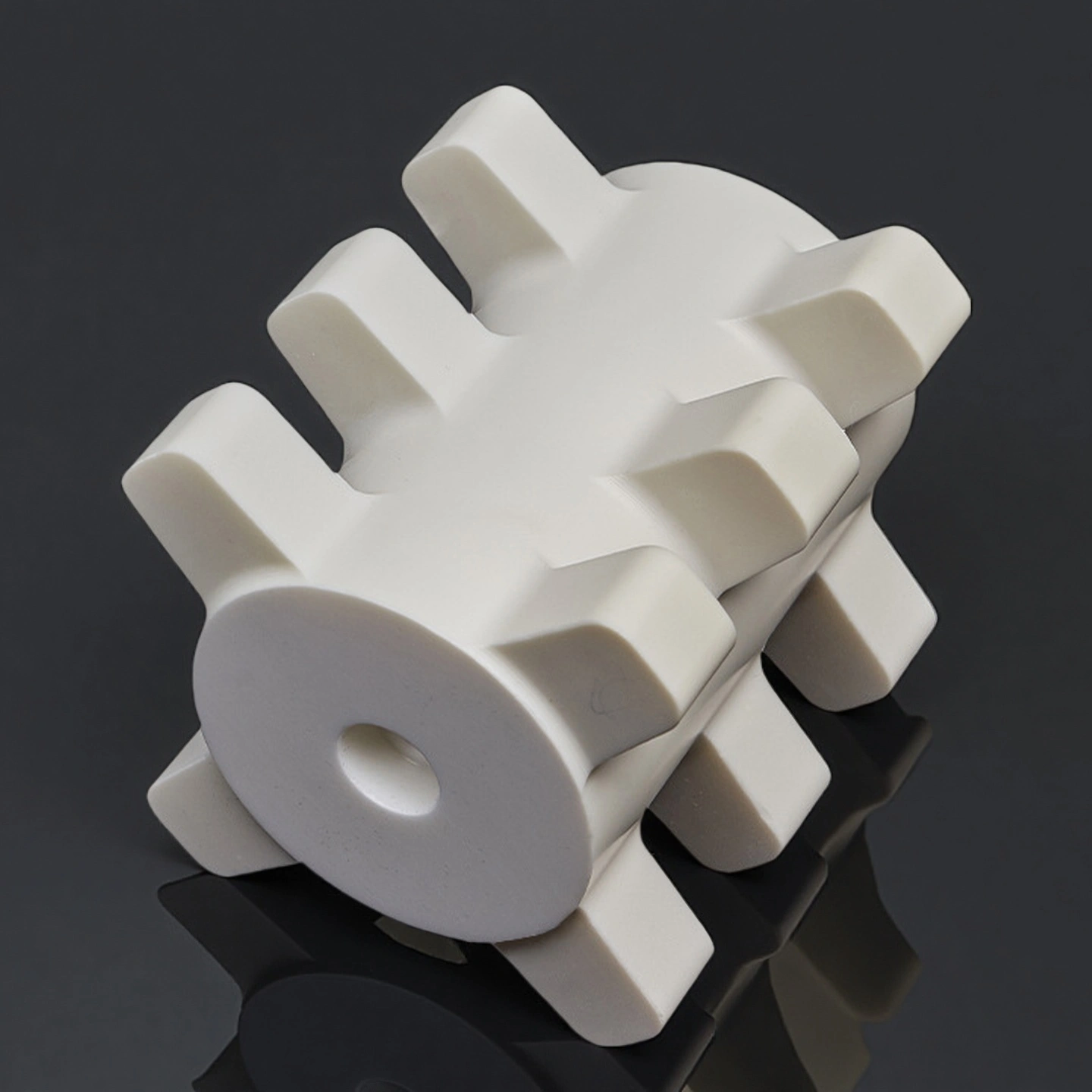
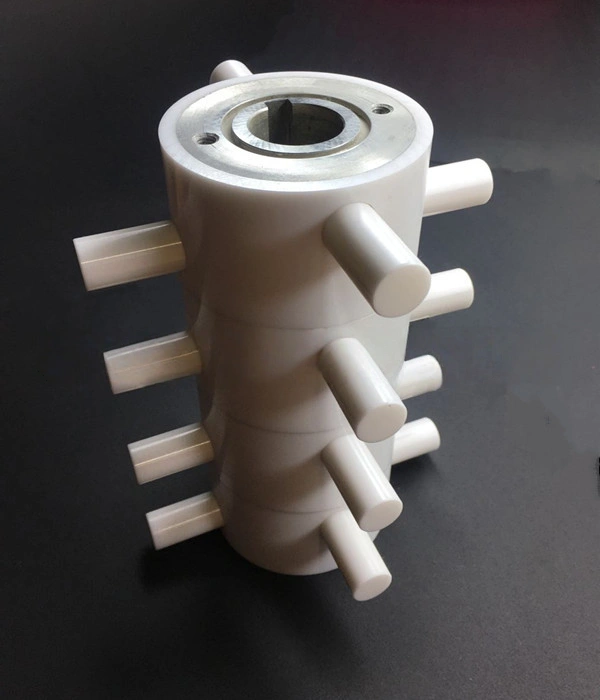
Alumina ceramic dispersion rotor is a high-purity Al₂O₃ (alumina) rotating element used as the core wear part in horizontal sand mills and bead mills. Driven by the motor, it spins at high speed to generate centrifugal force and shear, accelerating grinding beads (such as zirconia beads) so they continuously impact and disperse the slurry, achieving fine and uniform particle size.
Alumina Ceramic Dispersion Rotor Advantages
-
High wear resistance under high bead load
The alumina ceramic dispersion rotor uses high-purity Al₂O₃ with very high hardness and flexural strength, supporting long service life in high-energy grinding zones where beads and slurry continuously impact the rotor surface. -
Low metal contamination in sensitive formulations
The rotor’s fully ceramic construction prevents direct exposure of steel surfaces to the slurry, helping to reduce iron and chromium pickup in battery materials, electronic inks and functional fillers where metal contamination is critical. -
Stable performance at process temperature
High-temperature stability and low water absorption of alumina ceramics help maintain rotor dimensions and mechanical strength during continuous operation, supporting consistent gap control and dispersion efficiency in long production runs. -
Ceramic surface with good cleanability
The fine, dense alumina surface offers low porosity, which reduces material adhesion and makes cleaning between color changes or product campaigns easier, limiting cross-contamination. -
Compatible with zirconia beads and ceramic liners
The alumina ceramic dispersion rotor works with zirconia grinding media and ceramic liners used in many sand mills for heat-sensitive or chemically aggressive products, supporting a fully non-metal contact zone.
Alumina Dispersion Rotor Properties
| Property | Unit | 99.5% Al₂O₃ | 99.6% Al₂O₃ | 99.7% Al₂O₃ | 99.8% Al₂O₃ | 99.9% Al₂O₃ | 99.99% Al₂O₃ |
| Alumina content | % | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.99 |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.89 | 3.91 | 3.92 | 3.93 | 3.94 | 3.98 |
| Open porosity | % | 0 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Color | – | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory |
| Water absorption | % | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Young’s modulus (Elastic modulus) | GPa | 375 | 356 | 357 | 358 | 359 | 362 |
| Shear modulus | GPa | 152 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bulk modulus | GPa | 228 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Poisson’s ratio | – | 0.22 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Compressive strength | MPa | 2600 | 2552 | 2554 | 2556 | 2558 | 2570 |
| Flexural strength | MPa | 379 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 320 |
| Fracture toughness | MPa·m¹ᐟ² | 4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hardness | GPa | 14.1 (≈1440 kg/mm²) | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 35 | 32–37 | 33–38 | 34–39 | 35–40 | 36–42 |
| Thermal shock resistance ΔT | °C | – | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 228 |
| Maximum use temperature (no load) | °C | ≤1750 | 1755 | 1760 | 1765 | 1770 | 1800 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 10⁻⁶/°C | 8.4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Specific heat | J/kg·K | 880 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Volume resistivity | Ω·cm | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ |
| Dielectric constant (relative permittivity) | – | 9.8 | 9.83 | 9.84 | 9.85 | 9.86 | 9.92 |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 16.9 | 23.2 | 23.4 | 23.6 | 23.8 | 24 |
| Dissipation factor (loss factor @ 1 kHz) | – | 0.0002 | – | – | – | – | – |
Alumina Ceramic Dispersion Rotor Specifications
| Alumina Ceramic Dispersion Rotor | ||||
| Item No. | Outer Diameter(mm) | Inner Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) | Purity |
| AT-SM-Z001 | 45 | 28 | 400 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z002 | 60 | 40 | 400 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z003 | 84 | 64 | 400 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z004 | 95 | 75 | 500 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z005 | 125 | 100 | 630 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z006 | 155 | 130 | 700 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z007 | 160 | 140 | 750 | 95%-99% |
| AT-SM-Z008 | 180 | 150 | 800 | 95%-99% |
Alumina Dispersion Rotor Packaging
- Each alumina ceramic dispersion rotor is first wrapped in a soft protective film to protect the working surfaces from abrasion.