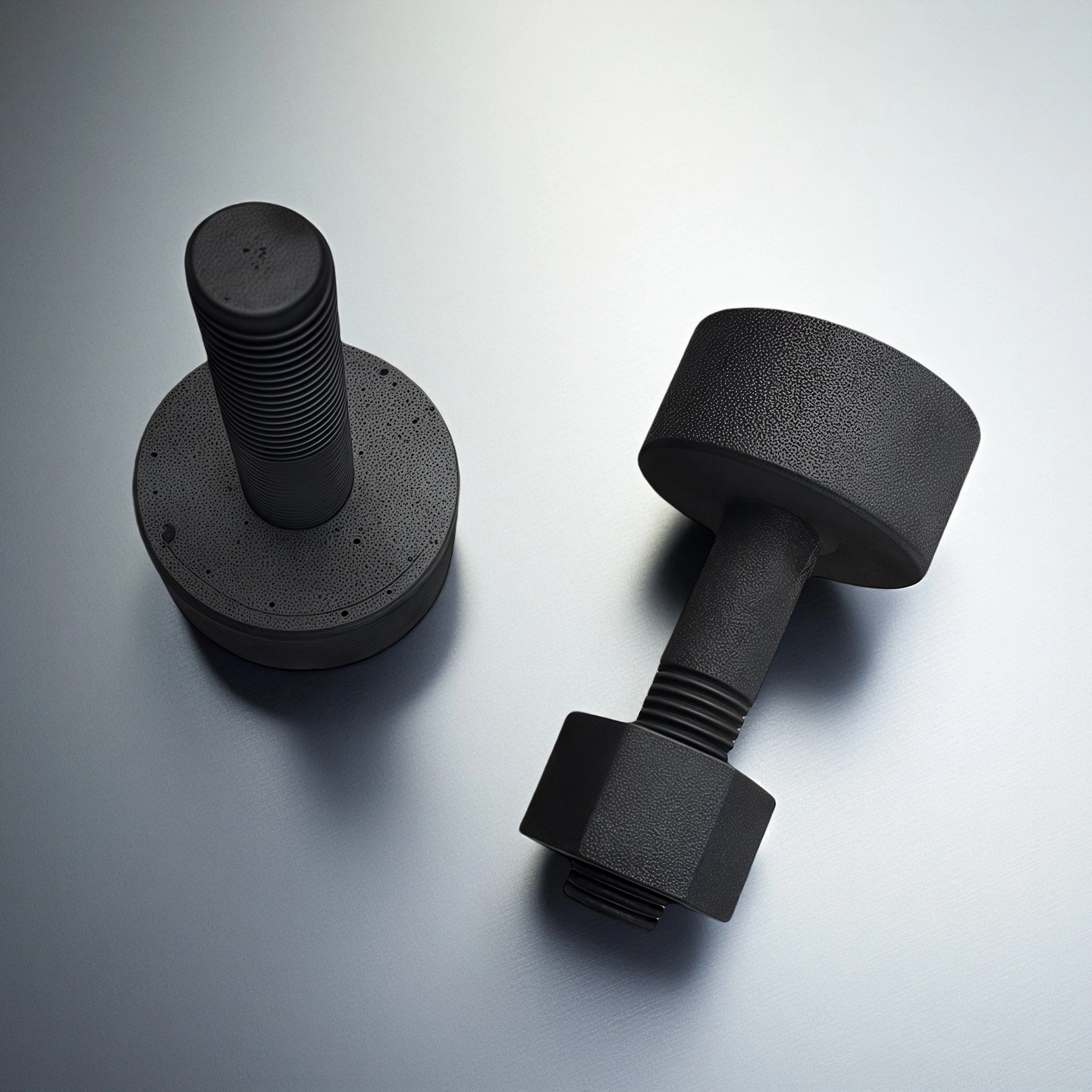
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw are engineered for environments where elevated temperature, corrosive media, and mechanical cycling demand fastening materials with stable structural behavior. Their α-SiC composition supports long-term performance in petrochemical systems, metallurgical furnaces, marine installations, and aerospace thermal units, creating reliability where metallic fasteners lose strength or degrade. This combination of thermal endurance, chemical inertness, and wear resistance allows Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw to maintain consistent preload and thread integrity across continuous industrial operation.
Advanced Performance Characteristics of Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw
-
Thermal Load Stability
The material retains more than 80% of its room-temperature flexural strength at 1200°C, allowing secure fastening across continuous thermal cycles.
-
Creep-Free Performance
Creep strain remains below 0.2% during 100-hour exposure at 1100°C, preventing bolt elongation during prolonged high-temperature service.
-
Oxidation and Salt Exposure Stability
In SO₂ and NOₓ atmospheres, oxidation depth remains below 5 μm after 200 hours, while salt-fog exposure causes 0% rust formation.
-
Low Thermal Expansion
The coefficient of thermal expansion remains at 4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶ /K, reducing dimensional drift during furnace cycling.
-
High Wear Resistance
The wear index shows 200× longer thread durability than manganese steel under identical load and torque conditions.
-
Vibration Fatigue Resistance
Mechanical endurance tests show less than 3% stiffness reduction after 10⁶ vibration cycles at industrial frequencies.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw
Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw exhibit stable mechanical strength, reliable thermal endurance, and strong chemical inertness, supporting consistent fastening performance in high-temperature and corrosive industrial environments. Their α-SiC composition provides dependable structural behavior under thermal cycling, mechanical loading, and exposure to aggressive media.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Type |
α-Silicon Carbide (α-SiC) |
| Density |
3.10–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Open Porosity |
< 0.2% |
| Flexural Strength (RT) |
360–420 MPa |
| Flexural Strength (1200°C) |
≥ 80% retention |
| Compressive Strength |
> 2200 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus |
380–420 GPa |
| Hardness (Vickers) |
2300–2600 HV |
| Thermal Conductivity |
85–120 W/m·K |
| Thermal Expansion (CTE) |
4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶ /K |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
ΔT > 250°C/min |
| Maximum Service Temperature |
1300–1400°C (oxidizing) |
| Acid Resistance |
Mass loss <0.03 mg/cm²·day |
| Alkali Resistance |
Mass loss <0.05 mg/cm²·day |
| Oxidation Resistance |
Oxidation depth <5 μm / 200 h |
| Salt-Corrosion Stability |
0% rust formation |
| Electrical Resistivity |
> 10⁴ Ω·cm |
| Microstructure |
Fine-grain α-SiC, low defect content |
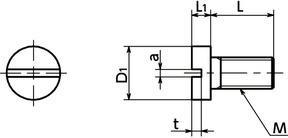
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw
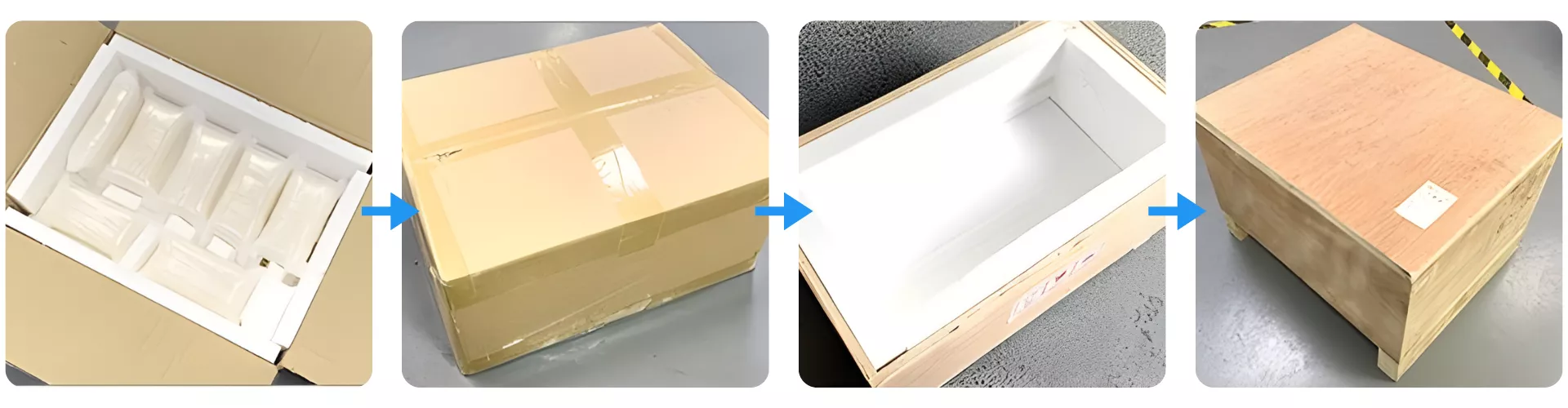
Protective Packaging for Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw
Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw are packed in shock-absorbing foam compartments that prevent contact and eliminate vibration damage during transport. Each inner carton is fully sealed before being placed into a reinforced plywood crate lined with impact-resistant material. This multilayer packaging structure ensures safe international delivery and preserves the mechanical integrity of every component.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw Resolve Critical Industrial Challenges in High-Temperature, Corrosive, and Long-Cycle Environments
The operational environments of petrochemical reactors, metallurgical furnaces, and marine desalination units place extreme stress on fastening components. ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw support stable, long-term fastening performance where metal bolts deform, corrode, seize, or fail under cyclic thermal loads, aggressive chemical exposure, and vibration-intensive conditions. The following scenarios illustrate how these properties address industry-specific challenges.
-
Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw for High-Temperature and Corrosive Petrochemical Reactors
✅Key Advantages
1. Preload Retention Under Reactor Cycling
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw retain more than 80% of their room-temperature flexural strength at reactor wall temperatures around 1200°C, so they keep clamp force stable across reformer and cracking furnace cycles. This strength retention limits preload loss that typically appears in metal fasteners after a few hundred high-temperature cycles.
2. Low Corrosion Rate in Acid and Oxidant Service
In mixed acid and oxidizing gas exposure (H₂SO₄, HCl, SO₂), measured mass loss for the SiC surface remains below 0.03 mg/cm²·day, while alloy steel fasteners in similar tests show material loss an order of magnitude higher. This low corrosion rate reduces section thinning and helps maintain thread engagement depth over multiple planned shutdowns.
3. Seizure-Free Turnaround Disassembly
After more than 3 full turnaround cycles in pilot testing, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw show torque-increase on removal of less than 10% compared with initial installation values, whereas conventional steel bolts often exceed 30% due to surface oxidation and galling. This behavior simplifies disassembly work scopes, shortens bolt-handling time per flange, and reduces the risk of damaged studs during maintenance windows.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A large petrochemical complex operating parallel steam reformer trains reported recurring issues with metal fasteners on hot manifolds, including bolt seizure, flange misalignment, and corrosion damage during each scheduled turnaround. Over a two-year period, engineering records showed several unplanned interventions directly linked to degraded reactor bolts and repeated stud replacement during every shutdown. After selectively replacing critical positions with ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw, the site recorded zero bolt-seizure events over the next three turnaround cycles and no loss of clamp integrity in interim inspections. Maintenance teams reported a clear reduction in time spent cutting or drilling out damaged fasteners, and process engineers confirmed that flange alignment remained stable through full thermal operating envelopes. This case demonstrated that the SiC fastening set could meet reactor service demands that had previously exceeded the capability of metallic bolts.
-
Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw for High-Cycle Metallurgical Furnaces and Powder Sintering Lines
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Stiffness Over Extended Furnace Cycles
Mechanical testing shows that ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw experience stiffness reduction of less than 3% after more than 1000 simulated furnace heat–cool cycles, whereas alloy fasteners exhibit much higher loss in modulus. This stability helps maintain fixture geometry in sintering and annealing equipment where small angular shifts accumulate over many batches.
2. Low Creep Deformation at High Temperature
Under sustained load at temperatures above 1000°C, creep strain in the SiC fasteners remains below 0.1% over a test duration of 100 hours, while common high-temperature steels show several times that value. This low creep response allows support frames, jigs, and rails to retain alignment, avoiding gradual sagging that would otherwise affect product flatness and throughput.
3. Thread Durability in Abrasive Powder Atmospheres
In wear tests with entrained oxide and metal powders, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw achieve thread life more than 200× that of manganese steel when subjected to equivalent torque and cycle counts. This high level of thread durability reduces the rate of thread rounding and backlash, keeping clamping forces consistent even in furnaces where airborne particulate is unavoidable.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A metallurgical producer running continuous sintering and annealing lines experienced recurring fixture misalignment and increased scrap rates attributed to deformation of high-temperature steel bolts. Internal tracking showed that fixture adjustments and bolt replacements were needed after fewer than 400 furnace cycles, and dimensional audits indicated progressive tilting of support elements in hot zones. After adopting ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw for the most critical fastening points, the maintenance interval for fixture correction extended beyond 1200 cycles, and the number of bolt-related alignment interventions dropped sharply. Production data over the following year showed a measurable reduction in geometry-related rework on sintered components and more stable line capability indices. The switch demonstrated that SiC fasteners could sustain furnace cycling and abrasive conditions that had previously driven frequent corrective actions on the line.
-
Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw for Marine Desalination, Offshore Structures, and High-Salinity Circulation Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Zero Rust in Prolonged Salt-Fog Exposure
Salt-fog chamber tests show 0% rust formation on ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw surfaces after multi-week exposure, while carbon steel bolts in the same environment show visible corrosion within a few days. This resistance to chloride-driven attack protects thread form and bearing surfaces in desalination frames and seawater piping supports.
2. Low Torque Increase After Marine Service
After extended operation in high-humidity, high-salinity environments, removal torque for the SiC fasteners rises by less than 15% relative to installation torque, compared with significantly higher increases observed for stainless steel fasteners. The limited torque growth indicates that threads remain free from heavy deposits and corrosion products, enabling predictable disassembly during maintenance outages.
3. Vibration and Shock Endurance on Offshore Equipment
In vibration endurance tests representing offshore pump skid duty, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw maintain clamping integrity with less than 2% change in preload after 10⁶ vibration cycles. This performance helps prevent joint loosening and structural instability in circulation systems subjected to continuous mechanical excitation.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A coastal desalination facility using conventional stainless steel bolts on high-pressure seawater skids reported frequent cases of seized and heavily corroded fasteners during scheduled maintenance. Inspection logs showed that many bolts could not be removed without cutting, and replacement counts per service interval were rising as the plant aged in a marine environment. After replacing critical joint locations with ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw, the facility observed that fasteners remained free of visible rust through full service intervals and could be removed using standard tools without destructive methods. Over several maintenance cycles, the number of bolt replacements per skid declined markedly, and technicians noted a reduction in time allocated to freeing or replacing corroded fasteners. The improved stability and serviceability of the joints confirmed that SiC fasteners could handle the combined effects of salinity, humidity, and vibration that had previously pushed metallic bolts beyond their limits.
How to Use ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw for Stable, Safe, and Consistent Operation
Using Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw correctly is essential for ensuring long-term fastening stability in demanding thermal and chemical environments. The following guidelines summarize the key considerations engineers should understand when installing, handling, and maintaining these components in industrial systems.
-
Installation Preparation for Silicon Carbide Bolt and Screw
1. Clean Contact Interfaces Thoroughly
Before installation, ensure that all mating surfaces are free of dust, scale, and residual chemicals. Contaminants can create uneven seating and introduce local stress points during tightening. Proper surface preparation improves load distribution and reduces the likelihood of micro-fracture initiation.
2. Inspect Fastener Geometry Before Use
Review each bolt and nut for visible chipping or abnormal surface marks prior to assembly. Although SiC exhibits high hardness, impacts during handling can introduce defects that propagate under load. Early inspection helps maintain system stability by ensuring every fastener begins service in optimal condition.
3. Match Turning Tools to Ceramic Fasteners
Use properly sized, smooth-jaw tools to prevent point-loading on ceramic heads. Excessively sharp or worn tools can create concentrated stress, especially during final torque application. Controlled mechanical contact preserves the integrity of the fastening surfaces.
-
Proper Tightening and Assembly Practices
1. Apply Gradual, Uniform Torque
Tightening should be performed in gradual steps to avoid sudden torsional spikes that exceed the elastic region of the ceramic shank. Incremental torque application supports predictable preload development across the joint. This method also reduces mechanical shock to thread surfaces.
2. Use Compatible Nuts and Washers
Pairing SiC bolts with chemically and thermally matched washers and nuts improves dimensional stability during heating cycles. Material mismatch can introduce differential expansion stresses that affect clamping reliability. Using matched components ensures consistent performance at elevated temperatures.
3. Avoid Over-Torque Conditions
Excessive torque can result in localized compressive stress at the thread root. Following recommended torque guidelines prevents micro-cracking and supports long-term joint stability. Under controlled tightening, SiC fasteners deliver consistent preload even under thermal cycling.
-
Handling and Storage Recommendations
1. Store Fasteners in Protective Compartments
Keep all components in their protective foam or segmented trays to prevent impact-induced edge damage. Hard ceramic surfaces can chip if struck against other hardware. Proper storage preserves thread accuracy and geometry.
2. Maintain a Controlled Environment
Store fasteners in a dry, clean environment to avoid introduction of contaminants prior to assembly. Although SiC is chemically inert, surface cleanliness plays a key role in maintaining consistent joint contact. Controlled storage conditions support reliability during installation.
3. Separate by Thread Type and Size
Prevent mixing of metric and imperial threads by clearly segregating fasteners before use. Ensuring the correct pairing avoids cross-threading and mechanical binding that could compromise structural performance. Clear sorting improves workflow efficiency for engineering teams.
-
Maintenance and Periodic Inspection Practices
1. Schedule Regular Visual Inspections
Inspect fastening points for surface wear, discoloration, or thread degradation during planned maintenance intervals. SiC fasteners resist corrosion, but mechanical damage can still accumulate over long service durations. Routine inspections help identify replacement needs early.
2. Monitor Preload Consistency Over Cycles
Track joint performance across thermal cycles to ensure preload remains within expected ranges. SiC’s low creep characteristics support stability, but system loads and reactor dynamics can affect clamp force over time. Monitoring preload trends supports predictive maintenance workflows.
3. Check Mating Components for Deformation
Even when SiC fasteners remain stable, metallic mating parts may distort under high thermal loads. Identifying deformation early prevents indirect stress transfer to the ceramic fastener. This practice ensures system-level reliability.

![]()







