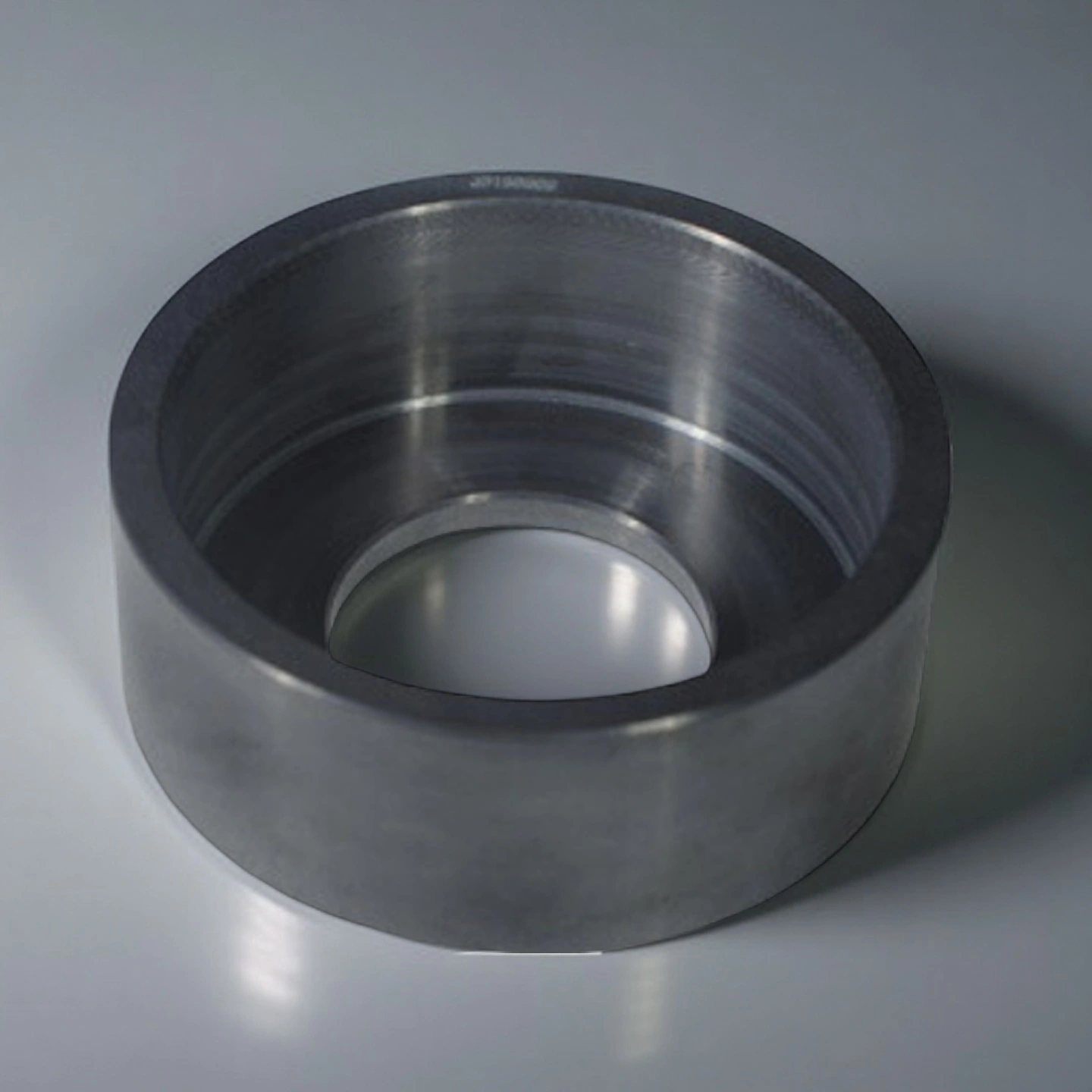
The silicon nitride exhaust hood is a custom-machined Si₃N₄ ceramic exhaust cover for polysilicon reduction furnaces, hydrogenation furnaces, and high-temperature reduction reactors. Standard and custom geometries are available for different furnace tops and exhaust ducts, with wall thickness and flange details tailored to match the existing steel structure.
Silicon Nitride Exhaust Hood Benefits
-
Geometry matched to furnace exhaust and electrode layout
The silicon nitride exhaust hood can be produced with integrated exhaust channels, baffles, and cut-outs so that it fits directly around electrode assemblies and gas outlets without separate adapters. -
High strength in thin-wall design
Gas-pressure sintered Si₃N₄ allows thin walls in the exhaust hood while maintaining flexural strength above 700 MPa, which reduces weight on metal frames and simplifies handling. -
Stable performance under rapid thermal cycling
The low thermal expansion of the Si₃N₄ exhaust hood limits thermal stress during hot–cold cycles in polysilicon reactors, which lowers crack initiation risk during start-ups and shutdowns. -
Resistance to process gas and condensates
Silicon nitride shows low wettability to molten silicon and good resistance to hydrogen and halogen-containing exhaust, so the exhaust hood surface stays cleaner and less prone to build-up over multiple campaigns. -
Electrical insulation in high-voltage electrode zones
The Si₃N₄ exhaust hood acts as an insulating barrier near electrodes and bus bars, which helps to maintain creepage distance and reduce unintended flashover risk at the furnace top.
Si3N4 Ceramic Exhaust Hood Properties
| Si3N4 Type | Gas pressure sintering Si3N4 | Hot pressing sintering Si3N4 | High thermal conductivity Si3N4 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.25 |
| Flexture strength (MPa) | 700 | 900 | 600~800 |
| Young Modulus (GPa) | 300 | 300 | 300~320 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 2500 | 3000 | 2500 |
| Hardness (GPa) | 15 | 16 | 15 |
| Fracture toughness (MPa*m1/2) | 5~7 | 6~8 | 6~7 |
| Maximum working temperature (℃) | 1100 | 1300 | 1100 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m*K) | 20 | 25 | 80~100 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (/℃) | 3*10-6 | 3.1*10-6 | 3*10-6 |
| Thermal shock resistance (ΔT ℃) | 550 | 800 | / |
Si3N4 Ceramic Exhaust Hood Specifications
| Silicon Nitride Exhaust Hood | ||
| Item No. | Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
| AT-SIN-WZ1001 | Customize | |
| Silicon Nitride Protective Cover | ||
| Item No. | Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
| AT-SIN-QZ1001 | Customize | |
| Silicon Nitride Heat Shield | ||
| Item No. | Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
| AT-SIN-GZ1001 | Customize | |
Si3N4 Exhaust Hood Packaging
- Each Si₃N₄ exhaust hood is wrapped in soft foam or bubble material to protect machined surfaces.