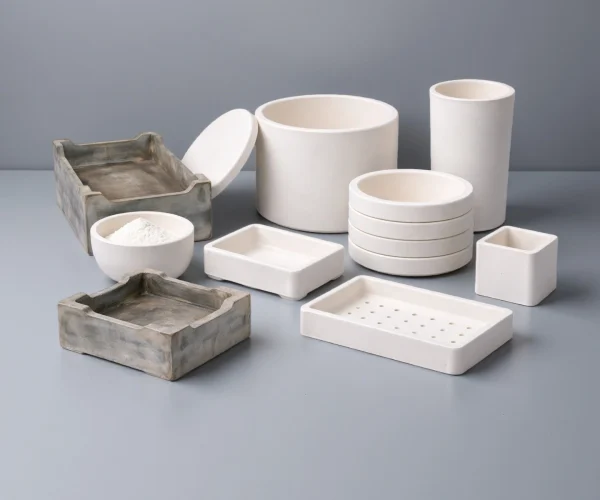
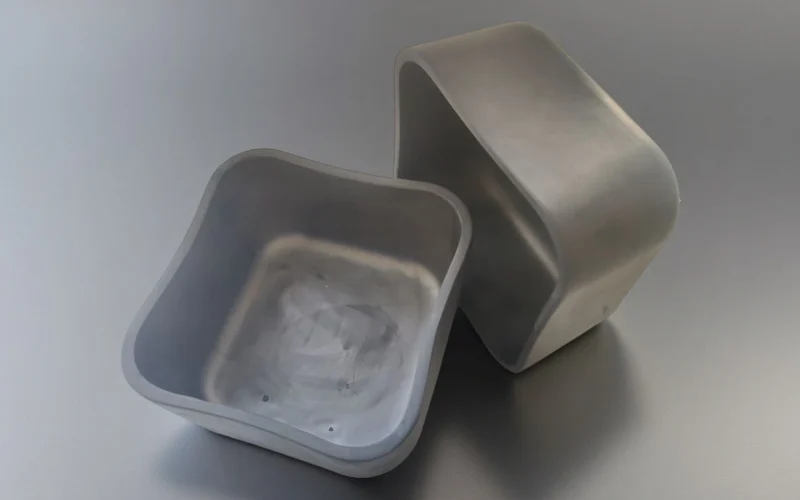
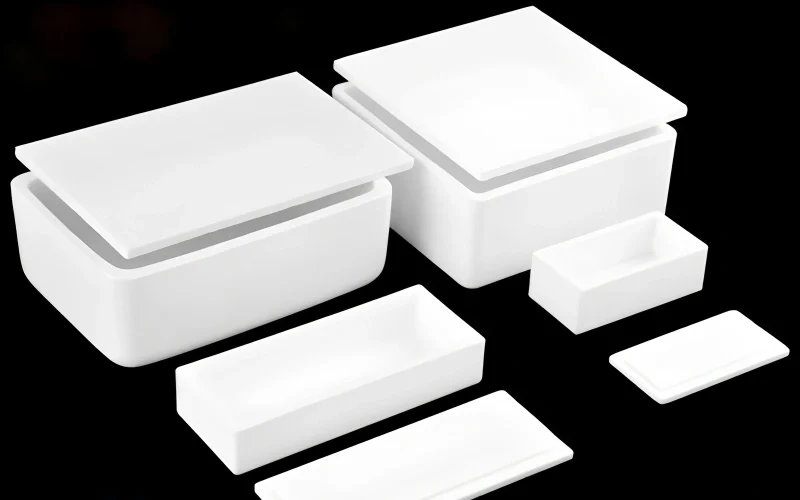
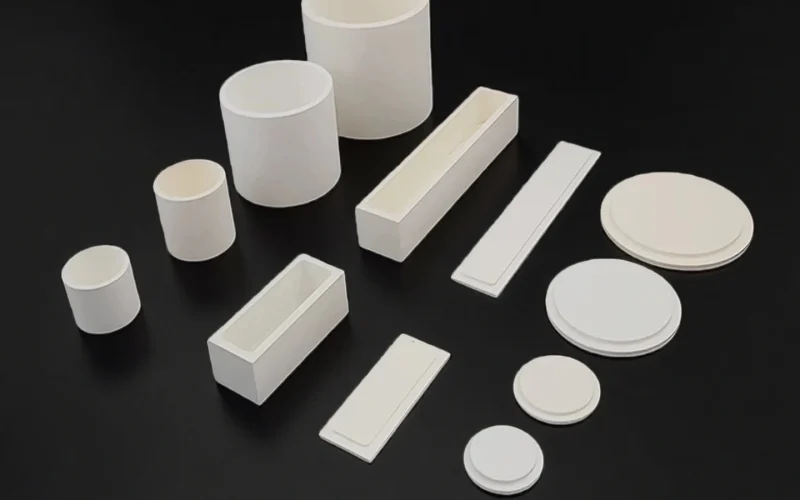
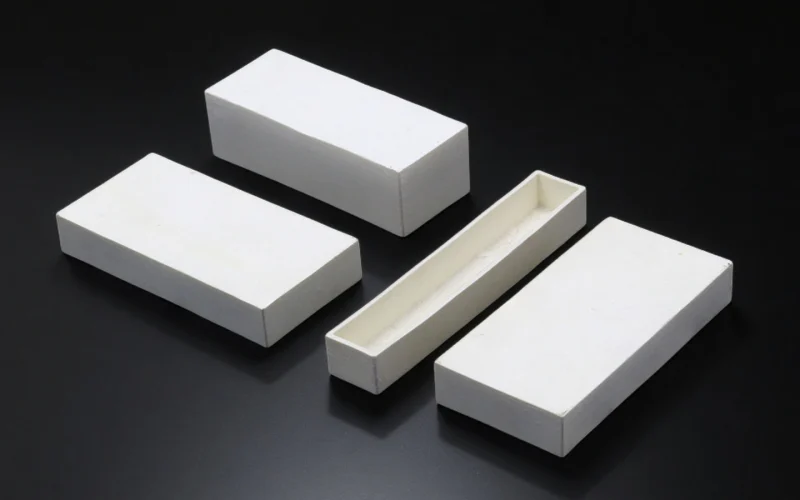
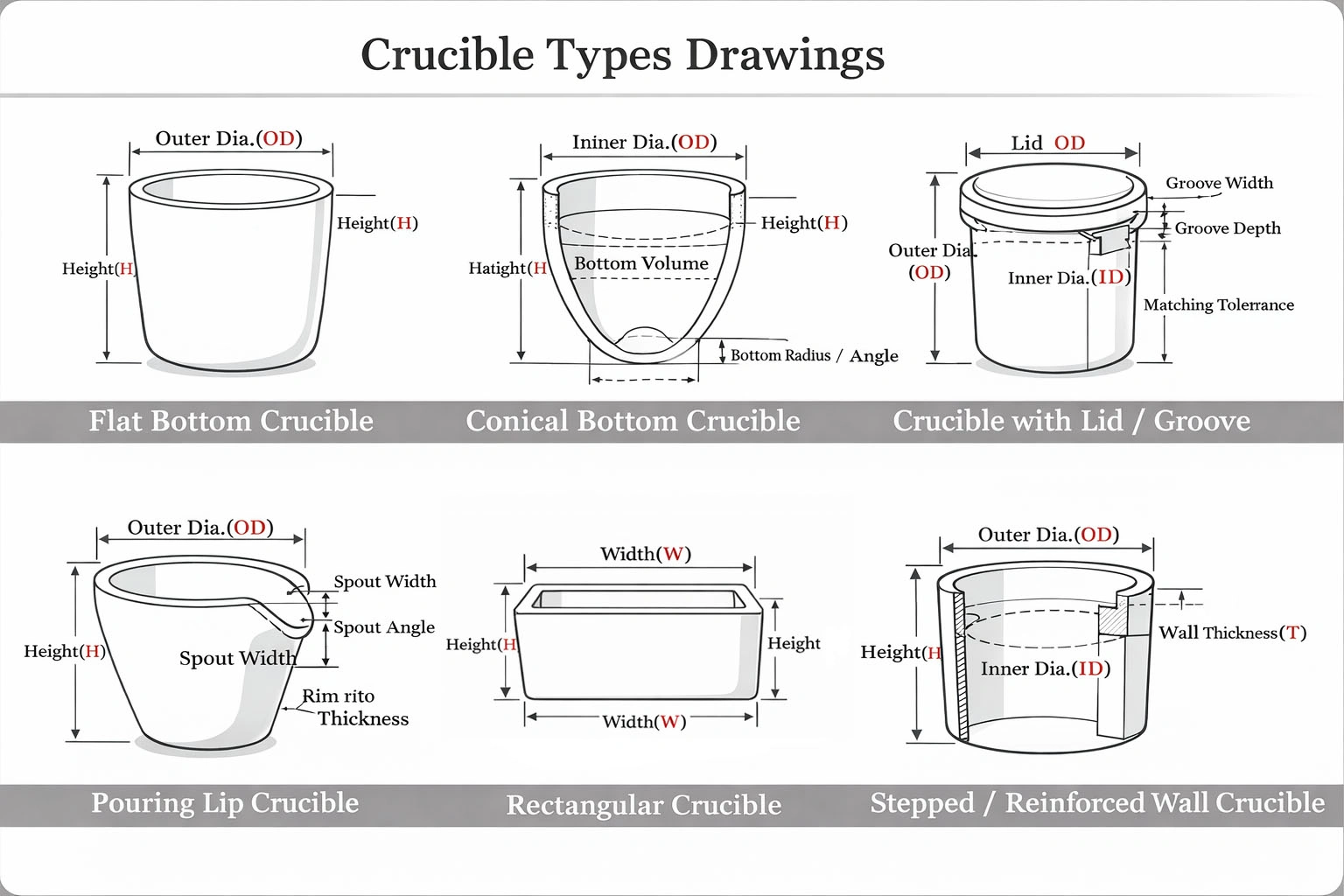
Ceramic Sintering Crucible for Powder and Material Sintering
——Engineered for contamination control, thermal shock resistance, and production-scale durability.
Ceramic sintering crucibles provide contamination-controlled containment for powder consolidation in metal injection molding, additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and technical ceramics production.
ADCERAX supports custom ceramic sintering crucible designs with:
- Material selection (alumina, SiC, ZTA, boron nitride) matched to temperature, atmosphere, and powder chemistry
- Geometry optimization for multi-layer stacking, furnace loading systems, and thermal stress distribution
- Batch consistency control to prevent contamination and extend service life
The Problem with Conventional Sintering Crucible Materials
Engineers consolidating metal powders, technical ceramics, or sintered composites often start with metal trays, graphite boats, or low-grade refractory containers.
These materials perform adequately in moderate-temperature debinding or preheating stages but fail during high-temperature sintering cycles where dimensional stability, chemical inertness, and thermal shock resistance become critical.
Common failure:
🔹Metal containers → oxidize, warp, or react with sintering atmospheres above 1000 °C
🔹Graphite boats → contaminate oxygen-sensitive alloys; incompatible with oxidizing atmospheres
🔹Low-grade refractories → introduce impurities, deform under load, or crack during rapid heating and cooling cycles required for production throughput
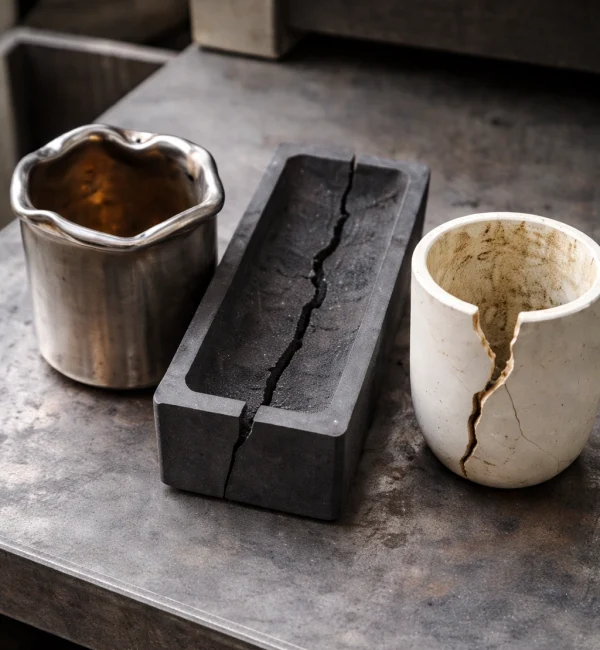

Causes of Conventional Sintering Crciucible Failure
These failures stem from inherent material limitations, not process design flaws.
Temperature-dependent oxidation and phase instability
- Metals form oxide scales; graphite combusts in air; low-cost refractories undergo phase transformations that cause cracking or dimensional drift.
Chemical reactivity with sintering atmospheres and powder compositions
- Container materials react with reducing gases, vacuum environments, or reactive metal powders, introducing contamination that degrades sintered part properties.
Thermal expansion mismatch and creep deformation
- High heating rates and extended hold times cause warping, sagging, or permanent deformation in metal and low-density ceramic containers.
Poor thermal shock resistance
- Rapid temperature changes during heating, cooling, or emergency shutdowns induce thermal stress fractures in brittle refractories or fatigue cracking in ductile metals.
Porosity-driven contamination pathways
- Open porosity in low-fired refractories absorbs processing gases, residual binder, or lubricants, which later outgas and contaminate the sintered product.
Why Ceramic Sintering Crucible Solve This Failure?
Ceramic sintering crucibles eliminate oxidation, contamination, and deformation failures inherent to metal trays and graphite boats. Material selection directly affects sintered part purity, dimensional accuracy, and thermal cycling durability—particularly critical in high-temperature atmospheres where conventional containers fail.
Ceramic Sintering Crucible Advantages
Thermal stability
Maintain dimensional integrity from 1200–1800 °C depending on ceramic high purity grade
No phase transformation or creep deformation during extended sintering hold times
Flat bottom geometry remains stable under loaded powder beds
Chemical Inertness
Compatible with oxidizing, inert, reducing, and vacuum atmospheres
No reaction with metal powders, ceramic oxides, or sintering additives
Eliminate contamination pathways that degrade sintered part properties
Contamination control
High-density, low-porosity structures prevent impurity absorption and outgassing
High-purity grades (≥99% alumina) for contamination-sensitive applications
Pre-fired surfaces reduce binder residue pickup and batch-to-batch cross-contamination
Thermal shock resistance
Mullite and ZTA grades survive rapid thermal cycles for production throughput
Controlled thermal expansion minimizes stress concentration during temperature transients
Engineered wall thickness distributions balance thermal mass and shock survival
Different Ceramic Sintering Crucible Material Options
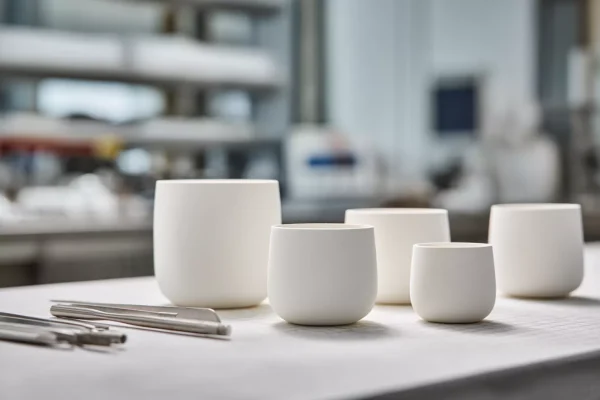

High purity options, stable at high temperature, low contamination risk in many sintering systems
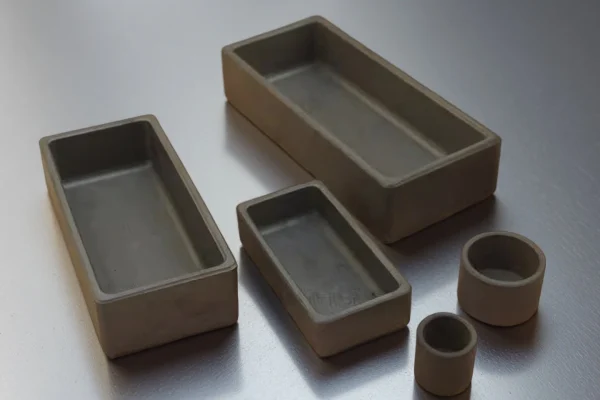

High thermal conductivity enabling more uniform temperature across the crucible body, strong at temperature.
Higher fracture toughness and better tolerance to thermal gradients and handling impacts.
Ceramic Sintering Crucible Selection Guide for Powder and Material Sintering
Material and geometry selection depend on sintering temperature, atmosphere, powder chemistry, loading configuration, and thermal cycling frequency. The framework below helps engineers specify a ceramic sintering crucible that maintains dimensional stability, contamination control, and thermal shock resistance.
Key Selection Parameters
Operating temperature range and hold time: Maximum sintering temperature, dwell duration, and heating/cooling rates determine thermal stress and refractory stability needs.
Atmosphere composition: Oxidizing (air), inert (argon, nitrogen), reducing (hydrogen), or vacuum conditions dictate chemical compatibility requirements.
Powder reactivity and contamination sensitivity: Reactive metals or high-purity ceramics require low-porosity, high-purity crucible materials.
Geometry and loading configuration: Crucible depth, wall thickness, and bottom flatness affect heat distribution and stacking stability.
Thermal cycling frequency: Frequent cycling demands thermal shock resistance; continuous operations prioritize creep resistance.
Ceramic Sintering Crucible Material Comparison
The following materials are commonly specified, each with distinct performance profiles:
| Material | Strengths in This Application | Limitations | Best-fit Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | High purity, stable at high temperature, low contamination risk. | Moderate thermal shock; cracks under fast ramps or uneven load. | Oxidizing/inert sintering, often >1200 °C (grade/cycle dependent). | Baseline choice; raise purity/density for sensitive powders. |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Tougher; handles gradients and handling impacts better. | Higher cost and density. | Fast cycling, stress-prone shapes, frequent handling. | Use when cracking/chipping drives scrap. |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High thermal conductivity; reduces gradients and warpage. | Atmosphere-dependent oxidation; check powder compatibility. | Inert/controlled atmospheres; uniform heat transfer needed. | Good when gradients are the main failure cause. |
Which Ceramic Crucible Fits for Powder Sintering?
Crucible form in the lab is typically driven by what the method needs the crucible to do—containment depth, residue recovery, pouring control, or small-sample measurement. The configurations below map these practical needs to common laboratory setups, so results stay consistent between runs.
Cylindrical Ceramic Sintering Crucibles
Deep charge holding; less spill risk. For furnace heat treatment and long soaks.
Ceramic Saggar for Sintering with Lid
Faster heating; easier loading/cleaning. For shallow samples and quick cycles.
Semicircular Ceramic Crucible for Lab
Stable support for long/narrow samples. For tube-furnace zones and directional heating.
Rectangular Ceramic Sintering Crucible
Maximizes usable volume and stacking. Use for batch heating powders and solids.
Typical Powder Sintering Applications Using Ceramic Crucibles
Ceramic sintering crucibles are used across metal injection molding, additive manufacturing, technical ceramic production, powder metallurgy, and hard metal sintering. Material and geometry selection depend on operating temperature, atmosphere, and contamination sensitivity.
Metal injection molding (MIM) sintering
Stainless steel, titanium, and tungsten powder consolidation in hydrogen or vacuum atmospheres, requiring contamination-free containment from 1200–1600 °C.
Powder metallurgy pressing and sintering
Iron, copper, and specialty alloy powder densification in reducing or inert atmospheres, where crucible chemical stability prevents oxidation or carburization.
Hard metal and cermet production
Tungsten carbide-cobalt (WC-Co) sintering in vacuum or hydrogen atmospheres, requiring crucibles that resist cobalt wetting and maintain dimensional stability above 1400 °C.
Technical ceramic powder sintering
Alumina, zirconia, and silicon nitride consolidation in air or controlled atmospheres, demanding high-purity crucibles to prevent impurity-driven grain growth or phase contamination.
Magnetic material sintering
Ferrite, rare earth magnet, and soft magnetic alloy consolidation, where low contamination and consistent heating profiles are critical to magnetic property development.
Additive manufacturing powder bed sintering
Binder jet and metal 3D printing post-processing, where part dimensional accuracy depends on crucible flatness and thermal uniformity.
Ceramic Sintering Crucible Failure Modes & Mitigation
Even ceramics can fail if thermal gradients, mechanical loading, or chemical compatibility are not aligned with the design. The following outlines common failure modes observed in sintering service, along with typical mitigation measures used to reduce risk.
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Design / Material Adjustment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial or corner cracking | Fast ramps, large thermal gradients, sharp corners, uneven loading | Add corner radii, balance wall/base thickness, slow ramp near critical ranges, consider tougher ceramic (e.g., zirconia) | Cracks often start at edges and corners under cycling |
| Powder contamination / discoloration | Chemical interaction, impurity pickup, residue from prior runs, porous surface | Increase purity/density, dedicate crucibles by powder system, tighten cleaning protocol | Contamination risk rises with reactive powders and long soaks |
| Warpage / dimensional drift | Creep at peak temperature, excessive stacking load, poor support points | Reinforce base, reduce span, lower stacking pressure, improve support layout, select higher creep-resistance ceramic | Large trays and thin bases are most sensitive |
| Surface spalling / edge chipping | Thermal shock, impact during handling, local overheating at contact points | Add protective edge features, improve handling tools, reduce thermal shock, choose shock-tolerant material direction | Edge damage becomes the next cycle’s crack origin |
| Sticking / adhesion to parts | Liquid-phase formation, reactive chemistry, rough/porous surface | Specify smoother/denser surface, use separators/setter plates, verify material compatibility | Validate with the actual powder and atmosphere window |
Customize Ceramic Sintering Crucible
Standard crucibles do not always match sintering process requirements. ADCERAX supports custom Ceramic Sintering Crucible designs to improve contamination control, thermal cycling durability, and dimensional stability under loaded powder beds.
Why Custom Sintering Crucibles Are Specified?
Peak temperature, dwell time, or ramp rates exceed standard crucible limits
Crucible geometry must fit furnace loading systems, multi-layer stacking, or setter configurations
Contamination control requires a specific material grade or surface finish
Powder bed depth or part arrangement needs custom dimensions, partitions, or drainage features
Repeat warping occurs at edges, corners, or support points during thermal cycling
What Can be Customized in Ceramic Sintering Crucibles?
Geometry & Structure
- Inner diameter / outer diameter / depth
- Wall & base thickness
- Rectangular / cylindrical / boat-shaped / custom profiles
- Flat bottom / raised bottom / drainage channels (powder bed stability)
- Stacking features (rim steps, positioning tabs, support posts for multi-layer loading)
- Partition walls or compartments for powder separation
Material & Grade
- Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- Zirconia and ZTA
- Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
- Boron Nitride (BN)
- Quartz (SiO₂)
Surface & Performance Tuning
- Inner surface finish to reduce powder adhesion and improve part release
- Edge rounding to limit chipping and stress concentration during thermal cycling
- Density / porosity tuning for contamination-sensitive sintering processes
- Tightened dimensional control for multi-layer stacking, furnace fixtures, and automated loading systems
Custom Ceramic Sintering Crucible: What to Provide?
To evaluate a custom crucible, engineers typically provide:
Powder type and chemistry
Operating temperature and thermal cycling
Furnace type and loading configuration
Required powder bed depth and crucible geometry
Drawing, sketch, or reference sample
Engineering Checklist for Ceramic Sintering Crucibles
Confirming these items before quotation reduces trial-and-error and helps match the crucible design to the sintering reality.
Operating Environment (Sintering)
| Operating Environment (Sintering) |
|---|
| ☐ Peak sintering temperature (setpoint): ____ °C |
| ☐ Furnace atmosphere defined (air / inert / reducing / vacuum): ____ |
| ☐ Heating & cooling rate range (typical): ____ °C/min |
Process & Material Compatibility
| Process & Material Compatibility |
|---|
| ☐ Powder or green body chemistry defined and contamination sensitivity assessed |
| ☐ Risk of chemical interaction or sticking with crucible material evaluated |
| ☐ Cross-contamination control approach identified |
Design Parameters
| Design Parameters |
|---|
| ☐ Crucible or tray geometry confirmed (ID/OD, height, wall or base thickness, corner radii) |
| ☐ Load per crucible and stacking configuration clarified |
| ☐ Dimensional tolerance requirements defined (flatness, fit, stability) |
Operational
| Operation & Handling |
|---|
| ☐ Handling method reviewed (tongs, fixtures, impact risk) |
| ☐ Cleaning and reuse method defined |
| ☐ Any recurring failure history shared (crack location, cycle step) |
Get in touch with us
Share your powder type, temperature profile, atmosphere conditions, and loading configuration with our engineering team.
Visit the Ceramic Crucible page for standard specifications, or submit drawings for custom geometry and manufacturability review.
info@adcerax.com
+(86) 0731-74427743 | WhatsApp: +(86) 19311583352
Within 24 hours
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.