Alumina ceramic pin is a high-temperature locating and insulating pin made from alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic, used in welding fixtures, jigs, and automation equipment to position parts accurately under heat and electrical load. Compared with steel pins, an alumina ceramic pin offers electrical insulation, high wear resistance, and stable dimensions in repeated welding cycles, so fixtures keep consistent reference points and require less maintenance and cleaning.
Alumina Ceramic Pin Key Advantages
-
Dimensional Stability Under Repeated Thermal Cycles
Each alumina ceramic pin maintains stable geometry during repeated heating and cooling in welding operations, which helps fixtures preserve consistent positioning accuracy over long production runs and reduces the risk of positional drift caused by thermal deformation. -
Strong Resistance to Weld Spatter Adhesion
The dense ceramic locating surface resists weld spatter bonding more effectively than untreated steel pins, so the locating diameter remains more consistent over time, reducing manual cleaning frequency and minimizing unplanned fixture downtime. -
Reliable Electrical Insulation for Welding Processes
The alumina ceramic pin electrically isolates the workpiece from the fixture body during resistance and projection welding, which stabilizes current paths, lowers the risk of short circuits through the fixture, and improves overall welding process control. -
Precision Ground Fit for Standard Bushings and Sleeves
The pin diameter and key locating features are precision-ground to controlled tolerances, allowing direct fitment into standard bushings and locator blocks without secondary modification, which simplifies fixture assembly and replacement procedures. -
Upgrade Compatibility with Existing Metal Fixtures
Non-standard tip shapes, stepped sections, shoulders, and transition radii can be produced to match existing metal pin geometries, so customers can replace steel pins with alumina ceramic pins while keeping the original jig structure unchanged. -
Consistent Wear Behaviour at High Contact Areas
In high-contact locating points, the alumina ceramic pin shows stable wear behaviour compared with softer metal pins, which helps maintain repeatable contact conditions between the pin and the workpiece over extended operating cycles. -
Stable Performance in High-Temperature Welding Environments
The alumina ceramic pin remains mechanically stable at typical resistance and projection welding temperatures, so it does not soften, creep, or plastically deform as metal locating pins may do under continuous heat exposure.
Al2O3 Ceramic Pin Properties
| Property | Unit | 99.5% Al₂O₃ | 99.6% Al₂O₃ | 99.7% Al₂O₃ | 99.8% Al₂O₃ | 99.9% Al₂O₃ | 99.99% Al₂O₃ |
| Alumina content | % | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.99 |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.89 | 3.91 | 3.92 | 3.93 | 3.94 | 3.98 |
| Open porosity | % | 0 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Color | – | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory |
| Water absorption | % | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Young’s modulus (Elastic modulus) | GPa | 375 | 356 | 357 | 358 | 359 | 362 |
| Shear modulus | GPa | 152 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bulk modulus | GPa | 228 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Poisson’s ratio | – | 0.22 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Compressive strength | MPa | 2600 | 2552 | 2554 | 2556 | 2558 | 2570 |
| Flexural strength | MPa | 379 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 320 |
| Fracture toughness | MPa·m¹ᐟ² | 4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hardness | GPa | 14.1 (≈1440 kg/mm²) | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 35 | 32–37 | 33–38 | 34–39 | 35–40 | 36–42 |
| Thermal shock resistance ΔT | °C | – | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 228 |
| Maximum use temperature (no load) | °C | ≤1750 | 1755 | 1760 | 1765 | 1770 | 1800 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 10⁻⁶/°C | 8.4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Specific heat | J/kg·K | 880 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Volume resistivity | Ω·cm | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ | >1×10¹⁴ |
| Dielectric constant (relative permittivity) | – | 9.8 | 9.83 | 9.84 | 9.85 | 9.86 | 9.92 |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 16.9 | 23.2 | 23.4 | 23.6 | 23.8 | 24 |
| Dissipation factor (loss factor @ 1 kHz) | – | 0.0002 | – | – | – | – | – |
Alumina Ceramic Pin Specifications
Type 1: Alumina Ceramic Pin with Thread
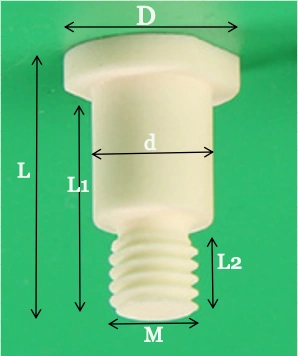
| Alumina Ceramic Pin with Thread | |||||||
| Item No. | D (mm) | d (mm) | L1(mm) | L2 (mm) | L(mm) | M | Purity(%) |
| AT-CP-L001 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 9 | M2 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L002 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 25 | 16 | 29 | M2.5 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L003 | 8.6 | 6 | 65 | 40 | 70 | M3 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L004 | 9 | 7.5 | 50 | 35 | 55 | M3 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L005 | 10.5 | 9 | 43 | 27 | 47 | M5 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L006 | 11.8 | 8 | 67 | 42 | 72 | M4 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L007 | 12.5 | 8 | 52 | 33 | 56 | M8 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L008 | 15 | 10 | 46 | 24 | 50 | M8 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L009 | 16.4 | 11.5 | 80 | 40 | 84 | M10 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L010 | 18 | 14 | 53 | 35 | 57 | M12 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L011 | 21 | 15.5 | 45 | 35 | 48.5 | M14 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-L012 | 23 | 16 | 32 | 22 | 36 | M14 | 96-99 |
Type 2: Alumina Ceramic Pin without Thread
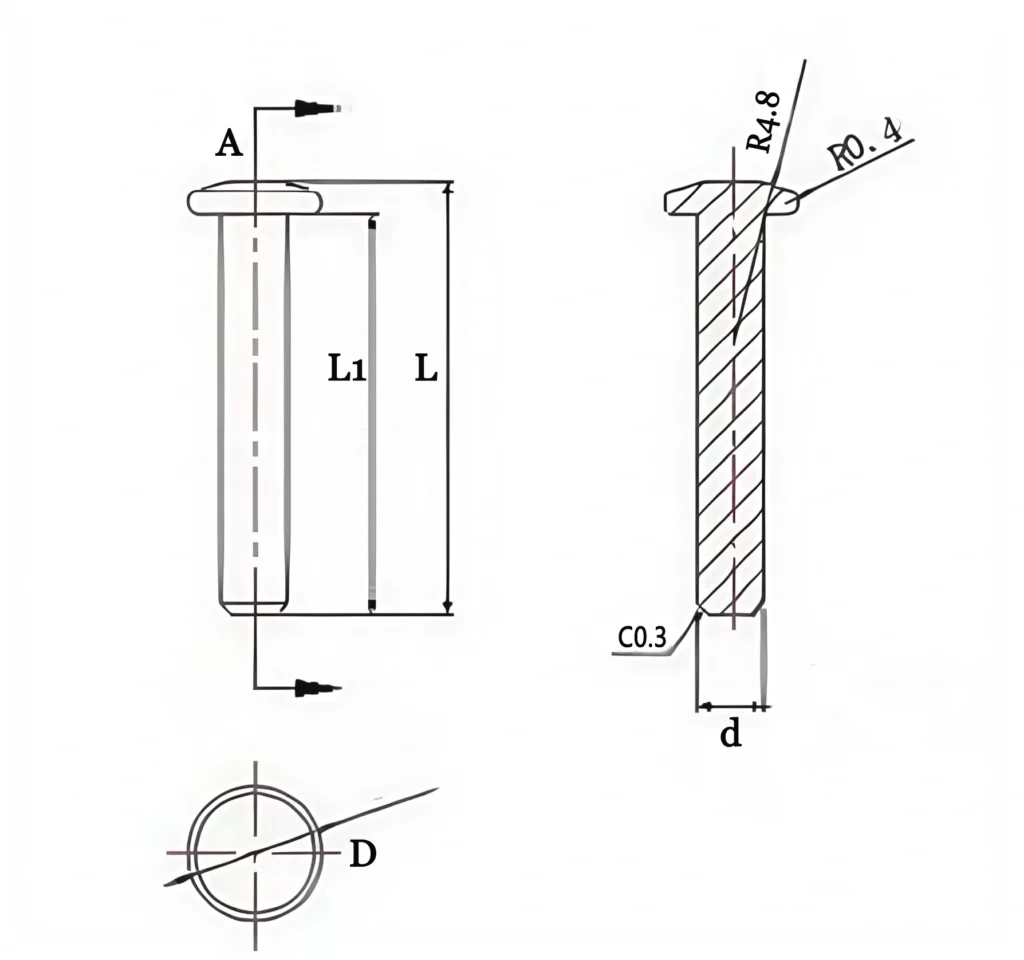
| Alumina Ceramic Pin without Thread | |||||
| Item No. | D(mm) | d (mm) | L1 (mm) | L (mm) | Purity(%) |
| AT-CP-D001 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D002 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D003 | 11 | 5 | 13 | 16 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D004 | 11.8 | 6.3 | 15 | 18 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D005 | 12.6 | 8 | 16.5 | 20 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D006 | 13.5 | 10 | 20 | 24 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D007 | 15 | 10 | 14.5 | 17 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D008 | 16.4 | 11 | 21 | 23 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D009 | 18.5 | 14 | 40 | 45 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D010 | 20 | 15 | 43 | 47 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D011 | 24.2 | 16.2 | 52 | 56 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D012 | 25 | 20 | 16 | 20 | 96-99 |
| AT-CP-D013 | 30 | 18 | 40 | 46 | 96-99 |
Alumina Ceramic Pin Packaging
- Each alumina ceramic pin is first wrapped or separated in protective blister cells or foam slots to prevent ceramic-to-ceramic contact during transport.











