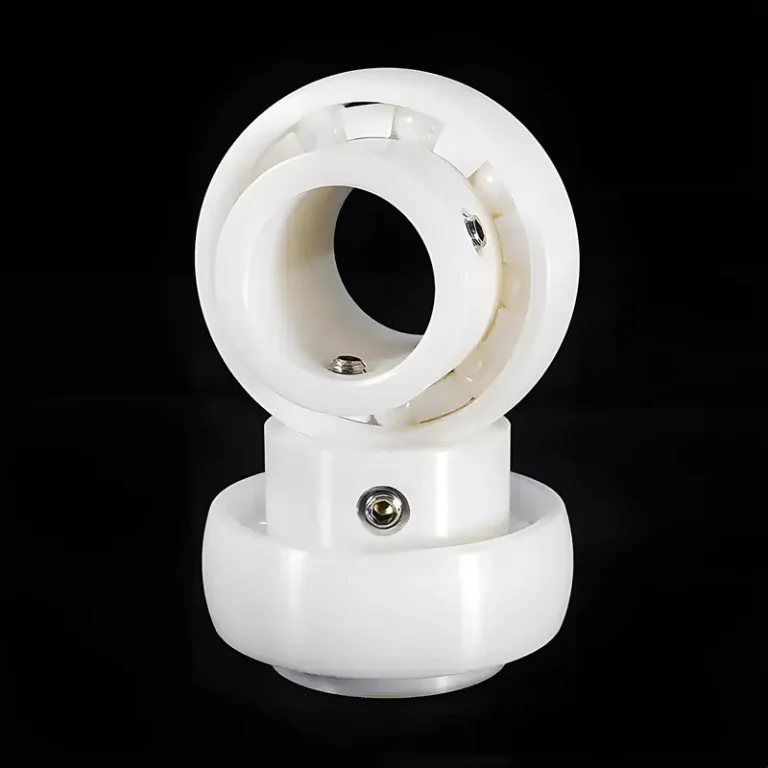
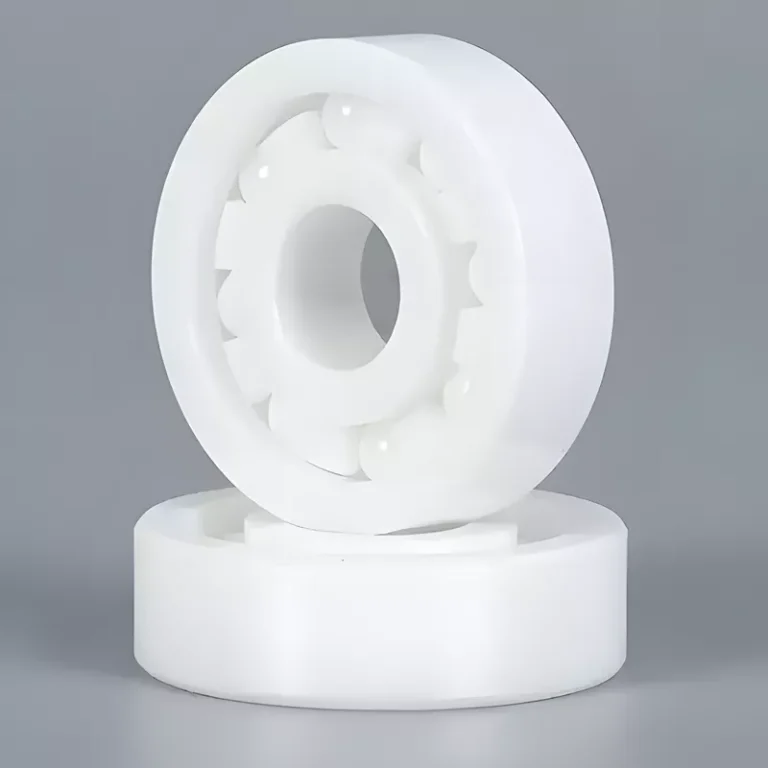
ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing is engineered to support simultaneous axial and radial loads at high rotational speeds in precision spindle systems. Its single-direction load orientation and fixed contact angle design provide enhanced rigidity and running accuracy in dynamic applications like machine tools, turbine motors, and high-frequency drives. This structure differs fundamentally from self-aligning, deep groove, outer spherical, and thrust variants by enabling sustained angular performance under continuous unidirectional thrust.
Angular Performance Advantages of Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing
- Engineered with a fixed contact angle of 15° to 40°, this bearing type enables directional load control not possible with spherical or self-aligning bearings. It withstands continuous axial thrust in one direction while maintaining radial precision.
- Unlike deep groove types, which favor radial loads, this design supports axial loads up to 60% of the total applied force. This allows greater stiffness in motor spindles and turbine applications requiring high thrust.
- Its angular design reduces deflection under axial force by up to 35% compared to thrust-only bearings, improving repeatability in high-speed machining centers.
- Constructed from ZrO₂ with a thermal expansion rate of 10.3×10⁻⁶/K, the bearing maintains its preload integrity under rapid temperature shifts. This ensures dimensional stability even during prolonged high-RPM operation.
- Operating reliably at temperatures up to 600 °C, depending on cage material, it outperforms metal hybrids that degrade above 350 °C. This supports long-cycle use in turbine and vacuum systems.
- The material’s thermal behavior and mechanical stability allow >90% preload consistency after 500 hours of accelerated life testing, based on SMB and CSCeramic test data.
- Designed for axial-preloaded assembly, it enables rotational accuracy within 0.0015 mm, critical for CNC spindles and high-resolution positioning arms. Other ceramic bearing types lack this unidirectional rigidity.
- Optimized contact geometry allows >25% larger contact ellipse than deep groove bearings under the same load, minimizing localized stress and extending service life in axial load paths.
- Bearings are configured with fixed angular orientation, enabling precise preload tuning across paired sets, a requirement not achievable with spherical or thrust-only designs.
Technical Properties of Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing
Designed for unidirectional axial loading and high-speed environments, the Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing offers exceptional thermal resistance, mechanical integrity, and rotational control. Its material composition and angular geometry enable stable operation in chemically aggressive and thermally unstable systems, such as CNC spindle heads, vacuum drives, and high-frequency rotating assemblies.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Grade |
Y-TZP / 99.8% ZrO₂ |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
10.3 × 10⁻⁶/K |
| Max Operating Temperature |
600 °C (with PEEK or PTFE cage) |
| Friction Coefficient (Dry Air) |
0.0012 (source: SMB Bearings) |
| Density |
6.05 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength |
950 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness |
>1200 HV |
| Elastic Modulus |
205 GPa |
| Electrical Resistivity |
>10¹² Ω·cm |
| pH Resistance Range |
pH 1–14 (acid, base, salt) |
| Axial Load Orientation |
Unidirectional (fixed contact angle) |
| Rotational Accuracy Deviation |
< 0.0015 mm (at full speed) |
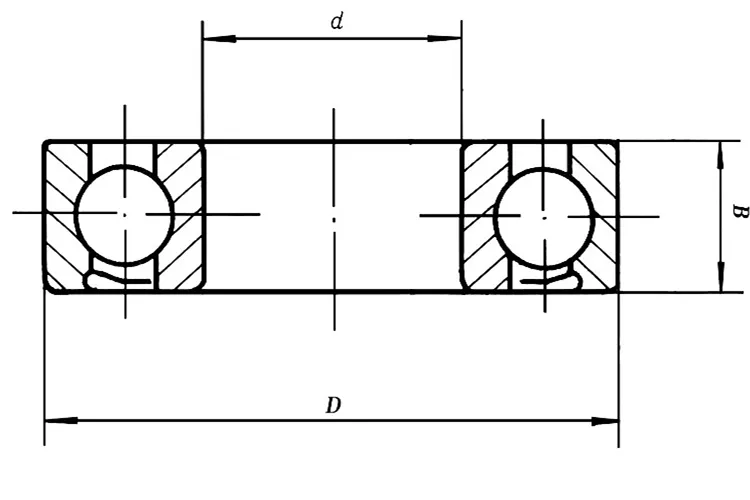
Specifications of Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing
Packaging of Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing
Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing units are individually cushioned using anti-friction sleeves and foam-lined compartments to prevent impact damage. All items are batch-labeled and stored in humidity-controlled inventory zones before shipment. Final export cartons are stack-loaded with reinforced edges to ensure structural stability during international freight.

How ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing Resolves Load Precision and Thermal Drift Challenges Across Axial-Driven Industrial Systems
Engineered for directional axial loading under continuous high-speed rotation, the Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing from ADCERAX® directly addresses structural deformation, heat distortion, and precision instability across advanced mechanical systems.
-
Spindle Head Assemblies in CNC Multi‑Axis Machining Centers
✅Key Advantages
1. Angular Rigidity Under Axial Cutting Load
Maintains a fixed 25°–40° contact angle to support sustained thrust in one direction during high‑torque milling.
This prevents axial displacement that typically appears in deep‑groove or spherical bearings when cutter load increases.
2. Micro‑Vibration Suppression at High Speed
Achieves runout stability < 0.0015 mm under full RPM ramp‑up conditions in multi‑axis spindle heads.
This directly reduces chatter marks and improves surface uniformity during 5‑axis dynamic contouring.
3. Heat‑Stable Preload Retention
Retains >90% preload after 500+ hours of thermal cycling between 30°C and 320°C.
This eliminates progressive spindle drift caused by heat‑induced expansion in conventional steel‑race bearings.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A German precision CNC manufacturer reported surface waviness and micro‑step deviation (< ±5 µm tolerance) when using hybrid deep‑groove bearings in a 24,000 RPM spindle. During intensive contour milling, preload loss caused cutter runout and rework rates increased by 11%. After switching to ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearings with controlled contact angle pairing, spindle axial rigidity remained stable across thermal cycles, reducing geometric compensation steps by 38% and eliminating surface chatter defects in production-grade machining.
-
Ceramic Bearing Integration in Vacuum Dry Pumps for Chemical Gas Handling
✅Key Advantages
1. Chemical Inertness Across Reactive Gas Streams
Zirconia maintains structural stability in pH 1–14 environments where metal bearings corrode or seize.
This supports pumping of halogen-rich and acidic exhausts without surface degradation.
2. Dry‑Run Stability Without Lubricants
Operates at a friction coefficient ~0.0012 (dry air), preventing shaft scoring when lubricants cannot be used.
Deep‑groove or thrust designs depend on film lubrication and fail rapidly under dry vacuum cycling.
3. Axial Load Control in High‑Temperature Vacuum
Withstands sustained operation up to 600°C (cage‑dependent) without losing angular preload.
This prevents rotor wobble, a known failure mode in chemically aggressive pump systems.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A Korean chemical process equipment supplier experienced repeated dry‑pump shutdowns due to bearing seizure when handling chlorinated exhaust gases. Steel bearings corroded within 3–6 weeks, and ceramic thrust bearings could not maintain axial positioning under vacuum load. After integrating ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearings, dry pumps achieved continuous operation exceeding 4,000 hours with no shaft vibration increase, stabilizing vacuum pressure curves and reducing maintenance intervals from monthly to semi‑annual service cycles.
-
Robotic Elbow Joints in High‑Speed Material Handling Arms
✅Key Advantages
1. Axial Thrust Retention in Oscillatory Motion
Supports up to 60% axial load fraction in repetitive pivoting cycles where deep‑groove bearings lose angular constraint.
This preserves precise joint trajectory in high‑velocity pick‑and‑place systems.
2. Structural Deflection Resistance Under Cyclic Stress
An elastic modulus of 205 GPa minimizes angular displacement during oscillating torque transitions.
This is critical in robotic arms where servo position feedback tolerates deviations of only a few microns.
3. Long‑Cycle Positional Stability
Maintains >90% stiffness retention after millions of joint reversal cycles, verified in accelerated fatigue testing.
Prevents joint “softening,” a failure mode common in spherical and self‑aligning bearings.
✅ ️Problem Solved
An automotive automation integrator reported increasing positional drift in robotic weld arms after 1.2 million pick‑and‑rotation cycles. Deep‑groove bearings developed backlash, causing ±0.12 mm end‑effector misalignment and weld gap inconsistencies. After adopting ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearings, joint drift remained below ±0.01 mm over equivalent cycle counts, reducing recalibration frequency by over 70% and improving production uptime in high‑throughput assembly lines.
ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing User Guide for Precision Axial-Load Applications
To ensure optimal performance and extended lifespan, proper handling and system integration of ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Angular Contact Ball Bearing must follow its axial-load-specific design logic.
-
Axial Preload Direction and Contact Angle Orientation
1. Correct Mounting Direction
Always install the bearing in the designed load-carrying direction based on its fixed contact angle. Incorrect axial alignment may lead to thrust instability.
2. Avoid Bidirectional Load Configurations
These bearings are not designed for reversing axial forces or oscillating axial dynamics. Unidirectional preload must be maintained throughout rotation.
3. Spindle System Integration
Align spindle shaft geometry with the bearing’s angular plane to ensure continuous line-contact. Radial misalignment can degrade angular stiffness.
-
Thermal Management During High-Speed Operation
1. Temperature Gradient Control
Differential thermal expansion across the shaft and housing must be minimized. Symmetric cooling paths are essential to reduce angular drift.
2. Avoid Thermal Shocks
Sudden ambient temperature changes during machine start or stop cycles can induce micro-fractures. Allow for gradual thermal equilibrium.
3. Compatible Lubricant Selection
Use only high-temperature-compatible lubricants rated for ceramic contact pairs. Low-viscosity or incompatible fluids can disrupt preload.
-
Assembly and Torque Application Guidelines
1. Controlled Axial Torque
Over-tightening leads to loss of internal contact geometry. Use torque-limiting tools to maintain preload tolerances.
2. Cleanroom Assembly Standards
Particulate ingress at assembly stage may create uneven axial resistance. Cleanroom or filtered environments are strongly recommended.
3. Isolate from Shock Loads
Avoid hammering, press-fitting, or impact during installation. Ceramic angular systems lack impact absorption tolerance.
-
Maintenance Strategy for Predictable Performance
1. Scheduled Inspection Intervals
Even under non-lubricated service, contact angle stability must be audited periodically. Use vibration monitoring to detect preload decay.
2. Rotation Direction Consistency
Reverse operation undermines bearing orientation and reduces service life. Maintain directional consistency throughout lifecycle.
3. Component Pairing Validation
Mating components (shaft/housing) must meet flatness and roundness tolerances. Precision interface ensures angular integrity.












