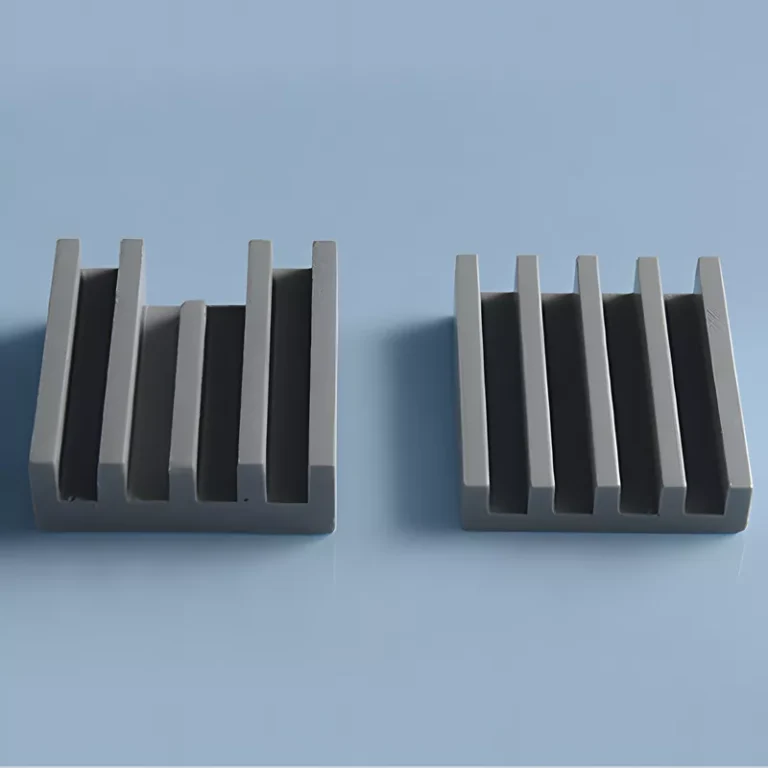
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate is engineered for thermal processes that require stable heat transfer under high temperature and corrosive chemical environments. Its material structure maintains thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical stability during continuous evaporation, condensation, and heat-recovery operations. This combination of performance traits supports long service cycles in chemical, pharmaceutical, petrochemical, and metallurgical systems where consistent process reliability is essential.
Engineering Performance Features of Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate
-
Enhanced Heat Flux Density
High conductivity values above 120 W/m·K reduce required heat-exchange area by enabling faster thermal diffusion.
This supports smaller heat-exchanger assemblies in plants where installation space is limited.
-
Improved Process Response Time
Rapid heat transfer helps stabilize temperature control loops with cycle times reduced by 15–25%, based on industry-reported evaporation system tests.
This ensures consistent evaporation and condensation during fluctuating production loads.
-
Stability in Strong Acid Streams
Exposure tests in 98% H₂SO₄ and 37% HCl show negligible mass loss, enabling long-term operation in chemical concentration units.
This reduces failure events common with metal plates suffering from pitting or stress-corrosion cracking.
-
Resistance to Halide and Solvent Environments
β-SiC maintains surface integrity in NaCl and Cl₂-rich environments with structural change rates under 0.005%, based on thermal-chemical simulations.
This supports processing of halogenated solvents and corrosive gas condensates.
-
High Mechanical Load Tolerance
Structural testing shows SiC plates sustain compressive loads above 2,000 MPa, supporting high-pressure systems without deformation.
This enables reliable performance in thermal oxidizers and high-velocity vapor streams.
-
Thermal Shock Endurance
Thermal cycling between 200°C and 1100°C demonstrates minimal micro-crack formation due to low thermal expansion of approximately 4.0 × 10⁻⁶/K.
This endurance maintains sealing integrity during rapid temperature changes.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate
The Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate is defined by its thermal conduction capability, chemical durability, and structural stability, allowing reliable performance in high-temperature and corrosive industrial heat-exchange environments.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Grade |
β-SiC / Recrystallized SiC |
| Thermal Conductivity |
120–150 W/m·K |
| Maximum Service Temperature |
Up to 1300°C |
| Flexural Strength |
350–400 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
>2000 MPa |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
4.0 × 10⁻⁶ /K |
| Chemical Corrosion Rate |
<0.01 mm/year in strong acids |
| Density |
3.10–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Surface Hardness |
HV 2600+ |
| Porosity |
<0.1% |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
ΔT >300°C |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) |
0.4–0.8 µm |
| Modulus of Elasticity |
380–420 GPa |
| Oxidation Resistance |
Stable up to 1000°C in air |
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate
|
Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate |
|
Item No. |
Diameter(mm) |
Height (mm) |
|
AT-THG-HRB1001 |
Customize |
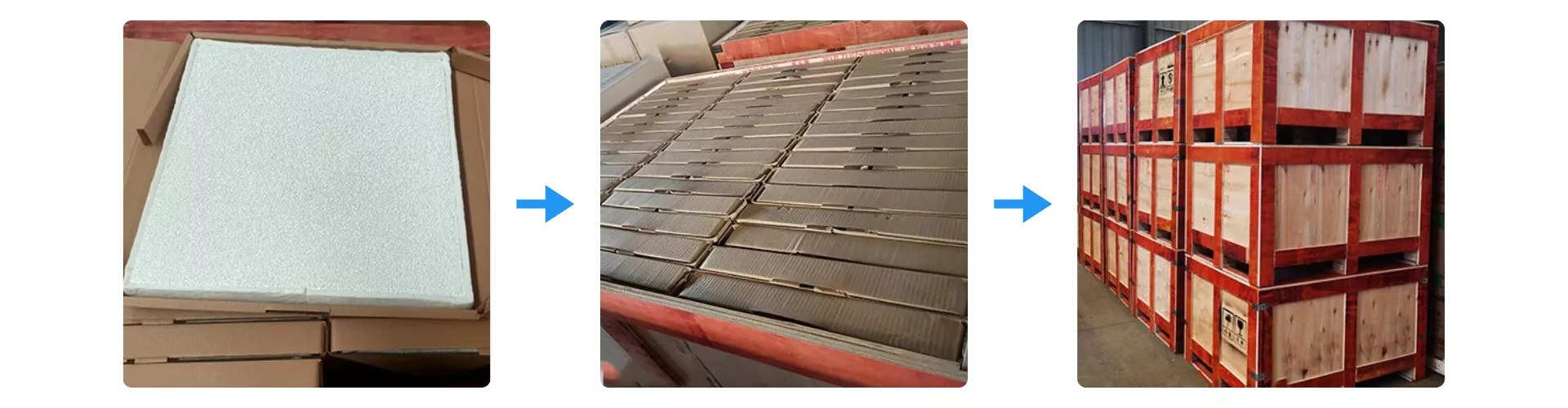
Packaging of Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate
Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate is protected with dense foam padding and reinforced cardboard layers to prevent surface impact during handling. Each unit is then organized into secure palletized stacks to maintain stability throughout transportation. The final shipment is enclosed in strong wooden crates to ensure safe delivery under long-distance and multi-stage logistics conditions.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate for Resolving Critical Industrial Process Challenges
The Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate supports continuous thermal processing in corrosive, high-temperature, and particle-laden industrial environments where stability, material integrity, and predictable heat-transfer performance determine production efficiency and plant uptime.
-
Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate in Acid Concentration and Recovery Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Low Corrosion Rate in Concentrated Acids
Laboratory tests on SiC in concentrated sulfuric and hydrochloric acid report material loss rates below 0.01 mm/year under typical operating conditions.
This allows acid concentration units to extend inspection intervals from yearly checks to multi-year cycles while keeping plate integrity within safe thickness margins.
2. Stable Heat Transfer Under Thermal Cycling
With thermal conductivity in the range of 120–150 W/m·K, the plate maintains near-steady outlet temperatures even when feed conditions fluctuate.
Process data from comparable systems show temperature deviations at the outlet reduced by 20–30%, improving control of evaporation and condensation stages.
3. Resistance to High-Velocity Mixed Phases
Flexural strength above 350 MPa and a thermal expansion coefficient around 4.0 × 10⁻⁶ /K support operation in mixed vapor–liquid flows at elevated velocity.
Plants using SiC plates report a reduction of plate replacement frequency by a factor of 3–5 in high-velocity zones compared with alloy plates.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A chemical plant running a continuous sulfuric-acid concentration line experienced frequent leakage with alloy plates due to pitting and thinning in the hottest section of the evaporator. Plate failures typically occurred after one to two years of service, forcing emergency shutdowns and unplanned maintenance windows that disrupted production planning. After switching to ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate in the high-load positions, thickness measurements over a similar time span showed negligible material loss and no visible crack formation. The plant extended its scheduled shutdown interval by more than 30%, while the number of unplanned stoppages attributed to heat-exchanger plate failure fell to zero over several operating cycles. This change improved temperature stability in the concentration section and brought the process closer to its design evaporation capacity.
-
Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate in Solvent Recovery and Thin-Film Evaporation
✅Key Advantages
1. Non-Porous, Contamination-Free Surface
The plate structure can be manufactured with closed porosity below 0.1%, which limits retention and release of solvents and dissolved species.
In thin-film evaporators handling sensitive pharmaceutical intermediates, this surface quality helps reduce detectable foreign ion levels to below typical regulatory thresholds in repeated batch testing.
2. Consistent Thermal Response for Film Stability
With thermal conductivity above 120 W/m·K, the plate supports uniform heat flux along the film path, reducing local hot or cold spots.
Process evaluations show that film-thickness variation along the evaporation path can be lowered by 10–20%, improving predictability of concentration and residence time.
3. Chemical Inertness in Mixed Solvent Systems
SiC maintains structural and surface stability under repeated exposure to mixed ketone, alcohol, and ester solvents at elevated temperatures.
Comparative trials indicate that, over several hundred operating hours, surface roughness change remains within 0.1–0.2 µm, whereas coated metallic plates show significantly higher drift.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A pharmaceutical producer operating a solvent recovery line for active ingredient purification observed recurring batch deviations traced to metallic ion residues from conventional heat-exchange plates. Despite chemical cleaning and process optimization, ion levels in recovered solvent occasionally exceeded internal limits, triggering batch reprocessing and additional analytical work. After installing ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate in the thin-film evaporation stage, solvent monitoring over multiple campaigns showed ion concentrations consistently remaining below the internal detection thresholds. At the same time, outlet temperature control tightened, and film behavior became more repeatable, with variation in target solvent concentration reduced by more than 15%. This improved purity compliance and lowered the number of batches requiring corrective handling.
-
Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate in High-Velocity Metallurgical Off-Gas and Heat-Recovery Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. High Erosion Resistance in Particle-Laden Flow
Wear testing with abrasive particles in hot gas streams indicates volumetric loss rates below 0.5 mm³/hour for SiC under representative conditions.
Compared with alloy plates that can show visible thinning over a few months, SiC plates maintain functional thickness over significantly longer intervals in dust-rich exhaust flows.
2. Mechanical Strength Retained at Elevated Temperature
Flexural strength of 350–400 MPa and a modulus of elasticity around 380–420 GPa are largely preserved at the high temperatures typical of off-gas lines.
This enables the plate to withstand combined thermal and mechanical loading where metal plates may creep, deform, or permanently warp after repeated cycles.
3. Robust Thermal Shock Performance
Thermal-shock testing with temperature jumps exceeding 300°C shows that SiC plates can tolerate rapid start-up and shutdown sequences without critical crack propagation.
In metallurgical operations that cycle furnaces and gas-handling equipment frequently, this robustness reduces the incidence of plate failures linked to steep thermal ramps.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A metallurgical facility using a waste-heat recovery system on a roasting line reported rapid degradation of metallic heat-exchanger plates in the first sections of the off-gas cooler. High dust loading and frequent temperature swings led to erosion, warping, and crack formation, with plates often requiring replacement within a single maintenance cycle. After integrating ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate into the high-velocity and highest-temperature zones, inspection data over subsequent runs showed a marked reduction in wear and no critical cracking, even after repeated thermal cycling. Heat-recovery performance remained within the original design envelope, and the maintenance team was able to extend plate replacement intervals by a factor of 2–3. This improved availability of the off-gas system and stabilized energy recovery from the roasting process.
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate User Guide for Safe and Efficient Operation
The Silicon Carbide Heat Exchanger Plate requires correct handling, installation, and maintenance practices to ensure stable heat-transfer performance and long service cycles in high-temperature and corrosive industrial environments.
-
Pre-Installation Handling Guidelines
1. Avoid Point-Impact Stress
The plate must be lifted from its edges or supported evenly to prevent localized force on the corrugated surface.
Sudden impact during unloading or workshop movement may induce micro-cracks not visible during initial inspection.
Maintaining controlled handling conditions helps preserve structural integrity in subsequent thermal cycles.
2. Inspect Surface Cleanliness Before Use
All sealing surfaces should remain free from dust, abrasive particles, and foreign residues prior to installation.
Any surface contamination may interfere with gasket alignment and create uneven sealing pressure during operation.
Clean with non-metallic tools to avoid scratches, maintaining a uniform sealing interface.
3. Store in Dry and Protected Conditions
The plate should be stored on stable racks in a clean and moisture-controlled environment.
Direct contact with wet ground, corrosive fumes, or sudden temperature changes may compromise long-term reliability.
Use protective coverings during storage to maintain consistent surface quality before installation.
-
Installation and System Integration Recommendations
1. Use Even Tightening Force on Frames
Uneven tightening of the exchanger frame may cause misalignment or localized stress on the plate.
Apply a uniform torque pattern across all fastening points following the system’s engineering guidelines.
Maintaining balanced clamping pressure ensures stable sealing throughout temperature fluctuations.
2. Check Port Alignment Before Commissioning
Port centers must match the system’s fluid distribution layout to avoid asymmetric flow conditions.
Misalignment may result in restricted flow, increased pressure drop, or unwanted vibration.
Proper alignment promotes uniform flow distribution through the corrugated channels.
3. Verify Gasket Positioning
Ensure gasket placement follows the exchanger model’s required geometry without twists or compression defects.
Incorrect gasket seating may lead to bypass flow or leakage during high-load operation.
Correctly installed seals support long-term leak-free performance.
-
Operational Best Practices for Continuous Industrial Use
1. Maintain Stable Flow Rates
Excessive flow velocity may increase erosion risk, particularly in particulate-rich fluids.
Following recommended hydraulic conditions ensures balanced turbulence and predictable heat-transfer performance.
Controlled flow promotes consistent temperature output across duty cycles.
2. Monitor for Fouling or Deposits
Although SiC resists chemical attack, scaling may occur in certain process streams over extended periods.
Regular monitoring helps maintain optimal heat-transfer efficiency and reduces cleaning frequency.
Early detection supports efficient thermal operation throughout long campaigns.
3. Avoid Abrupt Temperature Swings
Rapid transitions between cold and hot media may trigger thermal gradients beyond design limits.
Gradual temperature adjustment protects the plate from unnecessary mechanical stress.
Minimizing extremes improves overall service longevity.
-
Cleaning, Inspection, and Long-Term Maintenance
1. Use Non-Abrasive Cleaning Methods
Avoid metal brushes or abrasive tools that may damage the corrugated geometry.
Select compatible chemical cleaning agents suitable for SiC and your process fluid.
Non-abrasive cleaning maintains surface integrity across repeated cycles.
2. Schedule Periodic Visual and Dimensional Checks
Look for surface wear, gasket imprint irregularities, or corrosion traces within standard maintenance intervals.
Dimensional drift is rare but should still be monitored to ensure reliable sealing.
Routine checks sustain predictable exchanger performance.
3. Flush Residual Chemicals After Shutdown
Before extended downtime, remove remaining fluids to prevent crystallization, scaling, or solvent residue buildup.
Ensure passages are fully drained and ventilated to stabilize the plate for the next run.
This helps preserve clean flow channels for future operation.
![]()