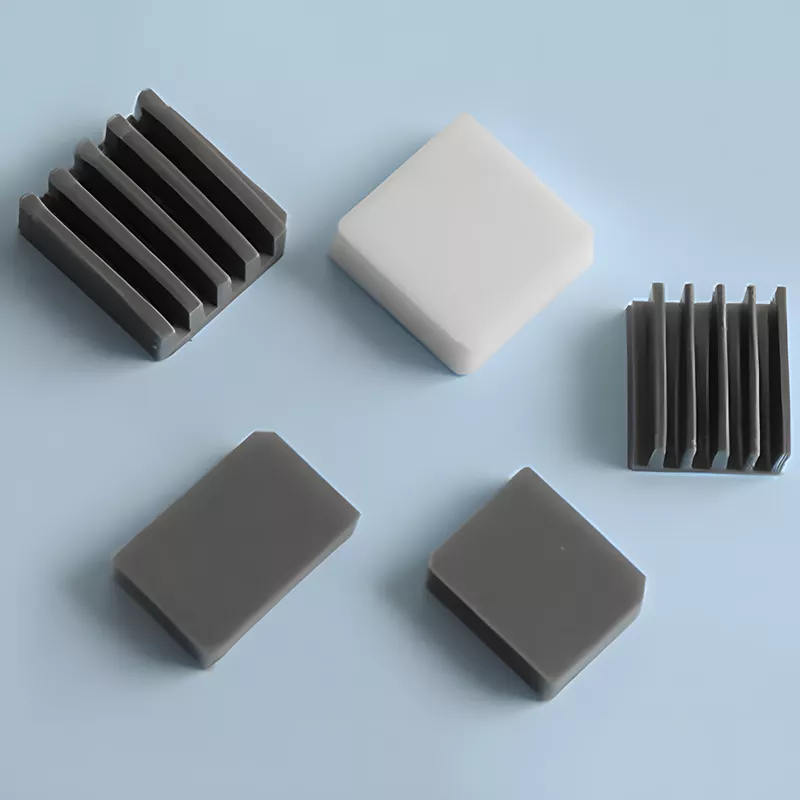
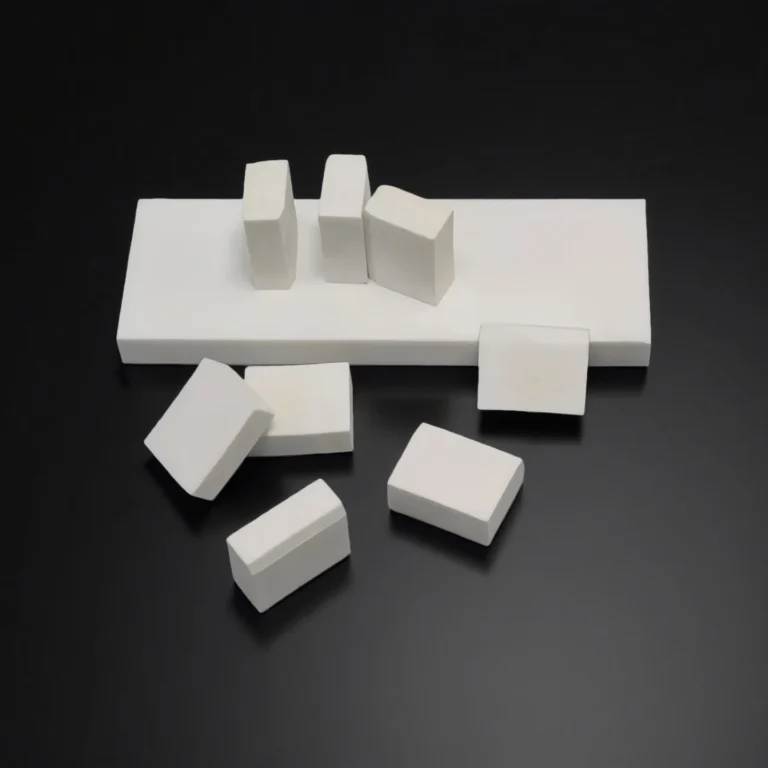
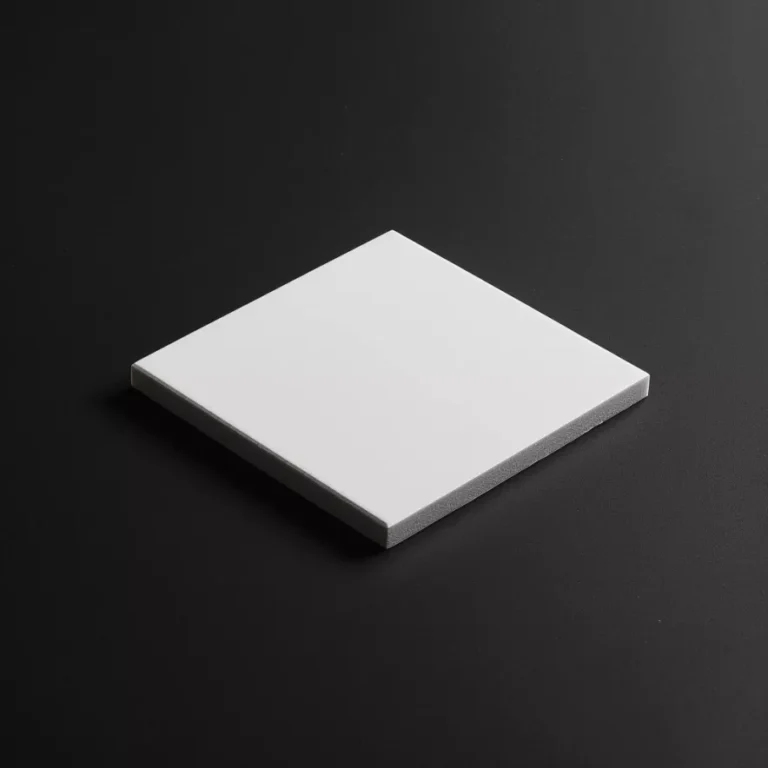
ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sink is engineered for thermal management systems where high heat flux, corrosive media, and elevated operating temperatures converge. Its silicon-carbide structure maintains stable thermal conductivity across demanding industrial environments, allowing temperature distribution to remain consistent during continuous operation. This performance supports industries that require reliable heat dissipation and long-term structural stability in power-electronics assemblies, high-temperature equipment, and chemical processing lines.
Advanced Functional Features of SiC Heat Sink
-
High Thermal Conductivity and Stable Heat-Flux Control
The SiC Heat Sink maintains uniform heat spreading by utilizing a thermal conductivity that reaches 120–150 W/m·K, enabling rapid dissipation of localized heat during continuous industrial operation.
This stable conductivity level remains consistent even at temperatures up to 1400–1500°C, ensuring that system thermal profiles stay uniform during prolonged thermal cycling.
Its low thermal expansion coefficient of 4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶ /K reduces thermally induced stress accumulation during rapid heating and cooling transitions.
-
Mechanical Strength for Long-Term Structural Reliability
It offers flexural strength values in the range of 320–420 MPa, supporting structural stability in assemblies exposed to mechanical load and vibrational forces.
Its compressive strength often exceeds 2000 MPa, allowing the component to maintain shape and contact pressure in high-load thermal interfaces.
Dimensional rigidity is retained through repeated process cycles due to high elastic modulus values of 390–420 GPa, preventing substrate warping under thermal or mechanical gradients.
-
Chemical and Environmental Stability in Reactive Atmospheres
They withstand oxidizing atmospheres up to 1100–1200°C, allowing long-term exposure without surface degradation in air-firing or furnace environments.
It remains chemically stable in acidic and alkaline media, including environments containing HCl, NaOH, or oxidizing gases, ensuring consistent performance during chemical thermal-control operations.
Porosity levels as low as 12–15% reduce reactive species penetration, extending operational service life in plasma, vapor, or corrosive gas systems.
Technical Specifications for Industrial Evaluation
The SiC Heat Sink exhibits stable thermal behavior, mechanical robustness, and chemical resistance suitable for long-duration operation in high-temperature and corrosive industrial environments. These characteristics support its use in power-electronics assemblies, furnace structures, plasma systems, and chemical processing equipment where consistent thermal conduction and structural reliability are essential.
| Property |
Specification |
| Density |
3.05–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Conductivity |
120–150 W/m·K |
| Maximum Operating Temperature |
1400–1500°C |
| Thermal Expansion |
4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶ /K |
| Flexural Strength |
320–420 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
>2000 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus |
390–420 GPa |
| Porosity |
12–15% |
| Hardness |
Mohs 9–9.5 |
| Acid Resistance |
Stable in HCl / H₂SO₄ |
| Alkali Resistance |
Stable in NaOH media |
| Oxidation Resistance |
1100–1200°C in air |
Dimensions of SiC Heat Sink
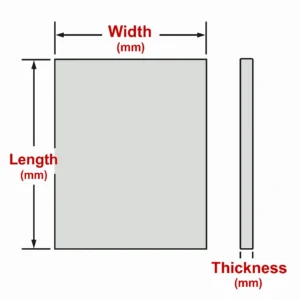
|
Silicon Carbide SiC Heat Sink |
|
Model No. |
Length (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Thickness (mm) |
Surface Profile |
|
AT-SIC-P1047 |
10 |
10 |
1.5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1048 |
10 |
10 |
2 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1049 |
10 |
10 |
3 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1050 |
10 |
10 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1051 |
10 |
12 |
2.5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1052 |
10 |
15 |
2 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1053 |
11 |
13 |
5 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1054 |
15 |
15 |
2 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1055 |
15 |
15 |
3 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1056 |
15 |
15 |
4 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1057 |
15 |
15 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1058 |
20 |
20 |
10 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1059 |
20 |
20 |
10 |
Grooved |
|
AT-SIC-P1060 |
20 |
20 |
2.5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1061 |
20 |
20 |
2 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1062 |
20 |
20 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1063 |
20 |
20 |
5 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1064 |
25 |
25 |
10 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1065 |
25 |
25 |
2.5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1066 |
25 |
25 |
3 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1067 |
25 |
25 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1068 |
25 |
25 |
5 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1069 |
25 |
25 |
8 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1070 |
30 |
30 |
10 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1071 |
30 |
30 |
2.5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1072 |
30 |
30 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1073 |
30 |
30 |
5 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1074 |
30 |
30 |
8 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1075 |
35 |
35 |
10 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1076 |
40 |
40 |
3 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1077 |
40 |
40 |
4 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1078 |
40 |
40 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1079 |
40 |
40 |
5 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1080 |
40 |
40 |
7 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1081 |
40 |
40 |
8 |
Corrugated |
|
AT-SIC-P1082 |
50 |
50 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1083 |
50 |
50 |
5 |
Perforated |
|
AT-SIC-P1084 |
60 |
60 |
5 |
Flat Plate |
|
AT-SIC-P1085 |
60 |
60 |
8 |
Flat Plate |
|
Remarks: Adhesive / Non-Adhesive |
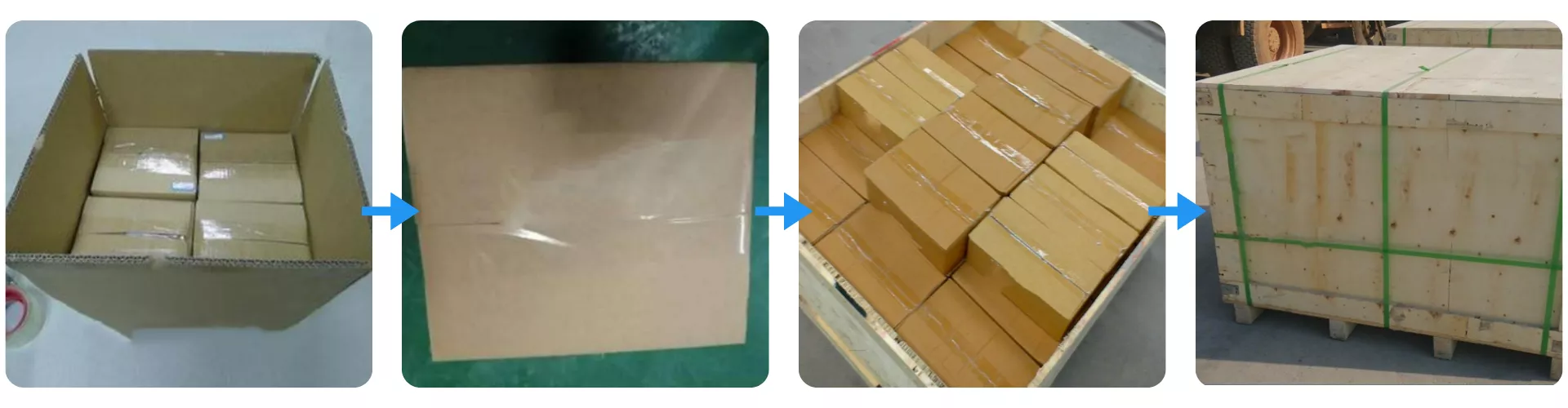
Packaging of SiC Heat Sink
The SiC Heat Sink is packed through a multi-layer process that protects each component during international transportation. Individual units are first secured in reinforced inner cartons, which are then sealed and consolidated into a heavier outer box to prevent movement. The boxed goods are finally fixed inside a strapped wooden crate to ensure stability against vibration, stacking load, and long-distance freight conditions.

ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sink Resolves Critical Thermal Challenges in Industrial Systems
The ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sink is used in industrial systems where sustained heat flux, corrosive gas exposure, and rapid thermal transitions create operational instability. Its material characteristics support prolonged reliability in sectors such as power-electronics cooling, metallurgical furnace modules, chemical-reactor thermal plates, plasma-cleaning auxiliaries, and high-output laser assemblies.
-
High-Load IGBT Inverter Cabinets in Industrial Drives
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Heat Conduction at Elevated Cabinet Temperatures
The SiC Ceramic Heat Sink maintains 120–150 W/m·K conductivity even when cabinet temperatures rise substantially during continuous switching cycles. This enables predictable thermal spreading when metal blocks lose efficiency due to thermal saturation.
2. Minimal Thermal Drift Under High Switching Frequencies
With a thermal expansion rate of 4.0–4.5×10⁻⁶/K, the SiC Heat Sink remains dimensionally stable while the inverter endures frequent power cycling. This stability reduces stress around semiconductor mounts where thermal gradients typically increase junction drift.
3. Effective Cooling in Airflow-Restricted Enclosures
The SiC matrix retains conduction performance independent of airflow turbulence or limited ventilation pathways. This provides consistent heat removal in compact inverter cabinets where fan-generated convection is insufficient.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Industrial drive manufacturers frequently report progressive temperature creep in IGBT modules when switching frequencies rise, causing non-uniform heat propagation through metallic blocks. Junction temperatures can fluctuate with each duty cycle, leading to unstable conduction and accelerated degradation. In compact cabinet designs, restricted airflow further limits the effectiveness of conventional cooling blocks. ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sinks reduce these fluctuations by maintaining high thermal conductivity even under increased cabinet temperatures and repeated switching cycles. Field data from automation lines shows that conduction uniformity improves measurably when using SiC, supporting stable inverter behavior during long-duration operation.
-
Furnace-Mounted Heat Equalizing Blocks in Powder Metallurgy Processing
✅Key Advantages
1. High-Temperature Structural Integrity in Sintering Zones
The Silicon Carbide Heat Sink remains structurally stable at 1400–1500°C, preventing the geometric distortion that metal heat-distribution blocks experience during cyclical furnace loading. This ensures uniform thermal contact surfaces throughout extended sintering runs.
2. Consistent Thermal Equalization Across Furnace Profiles
With thermal conductivity maintained between 120–150 W/m·K, the SiC Heat Sink reduces thermal gradients that alter powder densification. This produces a more uniform heat field across the critical working zone.
3. Oxidation Resistance Under Repeated Furnace Cycling
Oxidation stability up to 1100–1200°C prevents surface scaling that alters heat-transfer pathways in metallic blocks. The stable SiC surface maintains predictable thermal flow after numerous furnace cycles.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Powder metallurgy plants often encounter inconsistent sintering results due to thermal imbalance caused by deformation of metallic equalizing blocks. After multiple furnace cycles, thermal drift increases and leads to variable density distribution within the processed parts. Oxidation scales on metal blocks further disrupt heat transfer, amplifying these inconsistencies. ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sinks maintain consistent conductivity and geometry throughout repeated high-temperature cycling, enabling predictable furnace conditions. Operational observations show that temperature variations across the sintering zone are reduced when SiC equalizing blocks replace metal, improving process repeatability and material uniformity.
-
Corrosion-Exposed Thermal Plates in Acidic and Alkaline Chemical Reactors
✅Key Advantages
1. Chemical Stability Under Acidic and Alkaline Vapor Exposure
The SiC Heat Sinks maintain its structural and thermal properties in environments containing acidic vapors such as HCl and alkaline condensates like NaOH. This stability prevents the thickness loss and surface degradation typical of metallic cooling plates.
2. Predictable Thermal Transfer in Mixed-Gas Reactors
Thermal conductivity remains between 120–150 W/m·K even when the reactor atmosphere contains humidity and oxidizing gases. This ensures a stable thermal profile during both continuous and batch operations.
3. Low-Porosity Barrier Against Reactive Media
A porosity level of 12–15% restricts penetration of aggressive chemical species. The dense SiC matrix avoids internal weakening or reaction pathways that lead to structural instability in alternative materials.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Chemical processing lines frequently experience performance degradation in metal thermal plates when exposed to cycles of acidic vapor, alkaline residues, or oxidizing atmospheres. Corrosion gradually reduces metal thickness and lowers heat-transfer efficiency, causing reactor temperature inconsistencies that disrupt controlled reaction pathways. High humidity and mixed gas concentrations accelerate this deterioration, shortening the operational lifespan of metal-based cooling components. ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sinks maintain thermal performance and surface integrity in these conditions because their material chemistry resists reaction with corrosive media. Process engineers report more stable temperature uniformity and longer service intervals after replacing corroded metal plates with SiC components.
Operational Guidance for Reliable Use of the ADCERAX® SiC Heat Sink
The SiC Heat Sink used in industrial thermal-management systems requires a clear understanding of handling, installation, and operational practices to ensure consistent performance across high-heat-flux and corrosive environments. This section provides practical guidance to help users maintain structural stability, preserve thermal efficiency, and avoid premature wear during long-term operation.
-
Installation Requirements for Stable Thermal Contact
1. Ensure Proper Mounting Pressure
The mounting force applied to the SiC Heat Sink must remain within a controlled range to avoid introducing uneven stress during operation. Excessive pressure can reduce contact uniformity and affect heat-spreading performance. It is essential to verify that fasteners, clamps, or frames distribute loading in a balanced way.
2. Confirm Surface Cleanliness Before Assembly
Surfaces must be free from debris, oil films, or oxidation layers to maintain stable thermal conduction paths. Contaminants may increase thermal resistance, causing localized temperature variations under high load. Cleaning with non-abrasive agents is recommended to preserve the machined surface of the component.
3. Use Compatible Interface Materials
If thermal interface materials are required, select products rated for temperatures compatible with >1400°C industrial use. Incompatible compounds may degrade, leaving residues that interfere with long-term thermal transfer. Testing small areas before full installation helps verify compatibility.
-
Operating Conditions for Consistent Thermal Performance
1. Avoid Rapid Temperature Escalation Beyond System Ratings
Sudden temperature rises may introduce thermal shock into surrounding structures, especially in mixed-material assemblies. Maintaining controlled temperature ramps preserves the stable thermal conductivity of the SiC body. This is particularly important in systems where heat flux can fluctuate sharply.
2. Monitor Airflow or Fluid-Cooling Pathways
Even though SiC retains thermal performance under restricted airflow, blocked ducts or contaminated cooling media can lower system efficiency. Regular inspection of fans, ducts, or coolant flow ensures consistent heat dissipation across the operating cycle.
3. Prevent Exposure to Abrasive Particulates
Abrasive particles circulating in air or fluid streams may wear adjacent materials and alter surface contact conditions. Ensuring clean, filtered media minimizes the risk of micro-scratches or buildup that can influence thermal transfer stability during extended operation.
-
Handling and Storage Practices for Long-Term Integrity
1. Store in Low-Humidity, Covered Areas
Although SiC is chemically stable, excessive ambient humidity may affect the metal assemblies stored nearby. Keeping components in a dry, sheltered environment protects surrounding packaging and mounting hardware. Proper storage helps maintain operational consistency over time.
2. Use Protective Padding During Transport
Rigid ceramics require buffering to prevent impact damage during loading and unloading. Shock-absorbing padding reduces the risk of chipping edges or creating micro-fractures that could influence heat-spreading behavior. All crates or cartons should be handled according to industrial-grade safety standards.
3. Avoid Stacking Without Structural Support
Placing heavy items directly on top of the heat sink can cause uneven stress distribution. If stacking is necessary, structural frames or spacers should be used to maintain proper load paths. This prevents deformation of packaging layers during warehouse storage.
-
Maintenance Recommendations for Extended Service Life
1. Perform Scheduled Visual Inspections
Regular checks allow early discovery of surface deposits, corrosion residues from nearby equipment, or mechanical wear. Identifying these conditions helps maintain stable thermal contact through the service cycle. Inspections should follow fixed maintenance intervals aligned with equipment duty cycles.
2. Remove Deposits Using Approved Cleaning Agents
Cleaning materials must be non-abrasive and chemically compatible with SiC to avoid surface modification. Deposits from furnace environments, chemical vapors, or airborne particulates should be removed promptly. Preserving a clean surface supports uniform thermal transfer across the entire heat-sink topography.
3. Verify Fastener Stability During Overhauls
Mechanical clamps or frames may loosen over long-term operation, especially in equipment with cyclical heating. Periodic re-torquing ensures stable mechanical coupling between the heat sink and adjoining components. Maintaining reliable mechanical contact improves thermal performance retention over extended service periods.