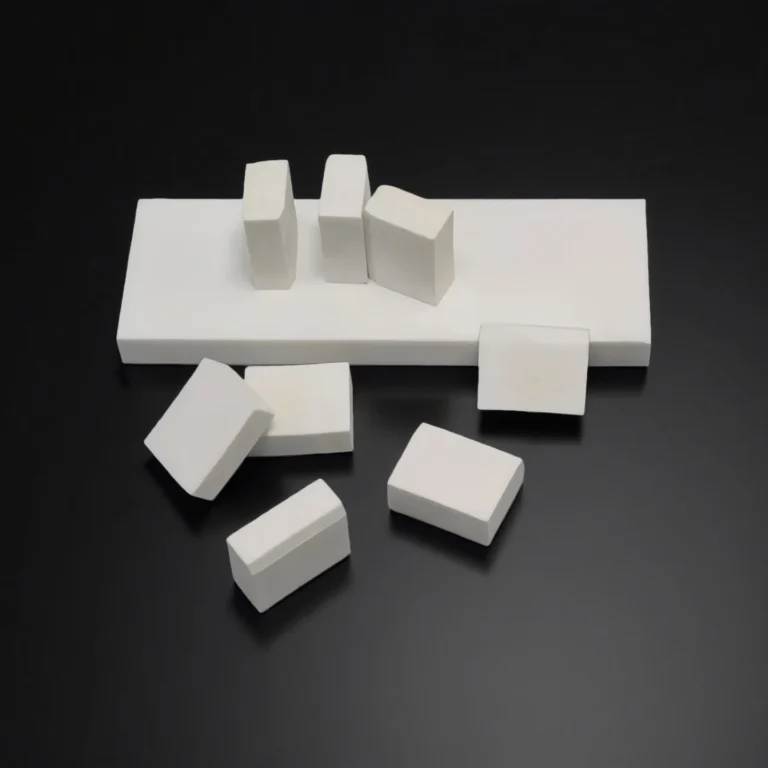
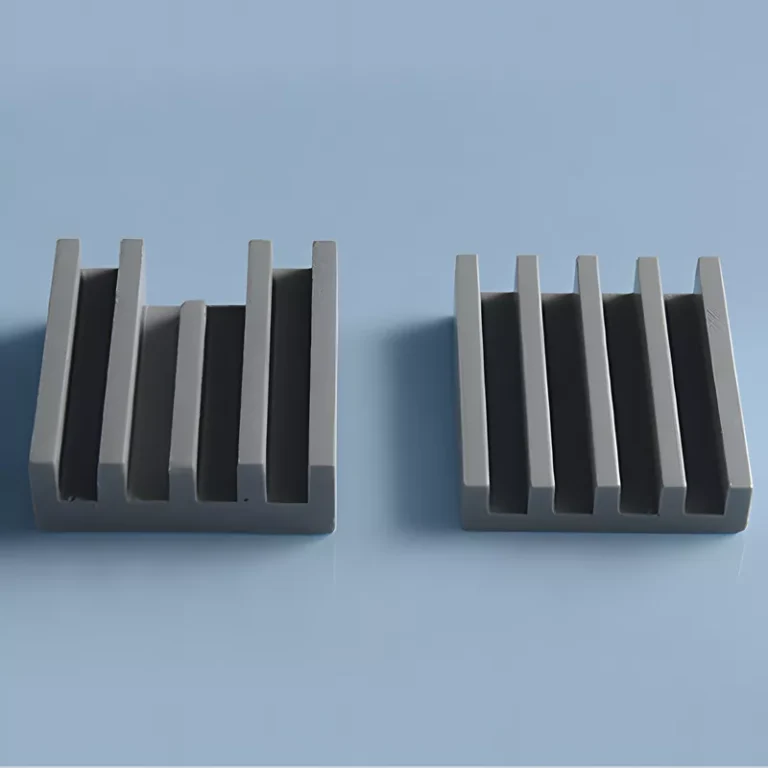
ADCERAX® Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor is engineered for semiconductor and LED epitaxy environments where thermal uniformity, surface stability, and long-cycle durability are critical. Its multi-cavity structure supports consistent heat transfer and controlled gas-flow behavior, enabling reliable performance across deposition, annealing, and plasma-based processes. This design allows the component to maintain structural integrity through repeated high-temperature cycles, providing stable support for advanced thin-film and compound-semiconductor production.
Advanced Performance Features of the Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
-
Plasma Attack Resistance
Exposure to Cl₂, H₂, NH₃, and O₂ plasmas shows erosion rates under 0.3 mg/cm²/hr, ensuring long cycle life.
-
Low CTE Thermal Shock Endurance
A CTE value of 4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K minimizes thermal shock damage during aggressive heating ramps.
-
Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
The susceptor maintains heat flow efficiency supported by SiC conductivity values of 120–180 W/m·K, enabling rapid thermal stabilization.
-
Dense Microstructure Reliability
SSiC density exceeding 3.10 g/cm³ limits plasma-induced erosion in halogen-rich environments.
-
High Hardness Stability
Material hardness above HV 2500 prevents progressive pocket deformation under repeated wafer loading.
-
Concentricity Control
Rotational balance is maintained through pocket concentricity within ±0.05 mm, reducing thermal skew across wafers.
- Flatness Stability
Surface flatness better than 0.03 mm across the full plate prevents local hotspots and thermal bowing.
- Pocket Depth Consistency
Cavity depth variation stays within ±0.02 mm, supporting uniform gas flow and thermal boundary behavior.
Technical Specifications of Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
The Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor demonstrates stable thermal behavior, controlled structural integrity, and quantified material performance suitable for high-temperature epitaxy, plasma environments, and repeated thermal cycling.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Type |
RBSiC / SSiC |
| Density |
3.05–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Hardness |
HV > 2500 |
| Thermal Conductivity |
120–180 W/m·K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) |
4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶ /K |
| Maximum Service Temperature |
Up to 1200°C |
| Flexural Strength |
250–320 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
2200–2400 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus |
380–420 GPa |
| Plasma Erosion Rate |
< 0.3 mg/cm²/hr |
| Chemical Resistance |
Stable in halogens, ammonia, acids, alkalis |
| Porosity |
< 0.1% |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) |
0.4–0.8 μm |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
≥ 300 rapid heat cycles |
| Electrical Resistivity |
10⁵–10⁶ Ω·cm |
Dimensions of Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
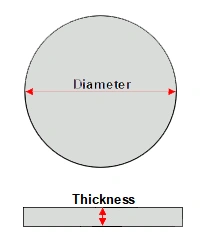
|
Silicon Carbide Susceptor for PVD |
|
Item No. |
Outer Diameter(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
Purity(%) |
|
AT-THG-CZ1001 |
230 |
3 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ1002 |
300 |
1.4 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ1003 |
300 |
3 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ1004 |
330 |
1.4 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ1005 |
330 |
3 |
99 |
|
Silicon Carbide Susceptor for ICP |
|
Item No. |
Outer Diameter(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
Purity(%) |
|
AT-THG-CZ2001 |
300 |
3 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ2002 |
300 |
4.4 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ2003 |
330 |
4.4 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ2004 |
330 |
3 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ2005 |
380 |
4.4 |
99 |
|
AT-THG-CZ2006 |
380 |
3 |
99 |
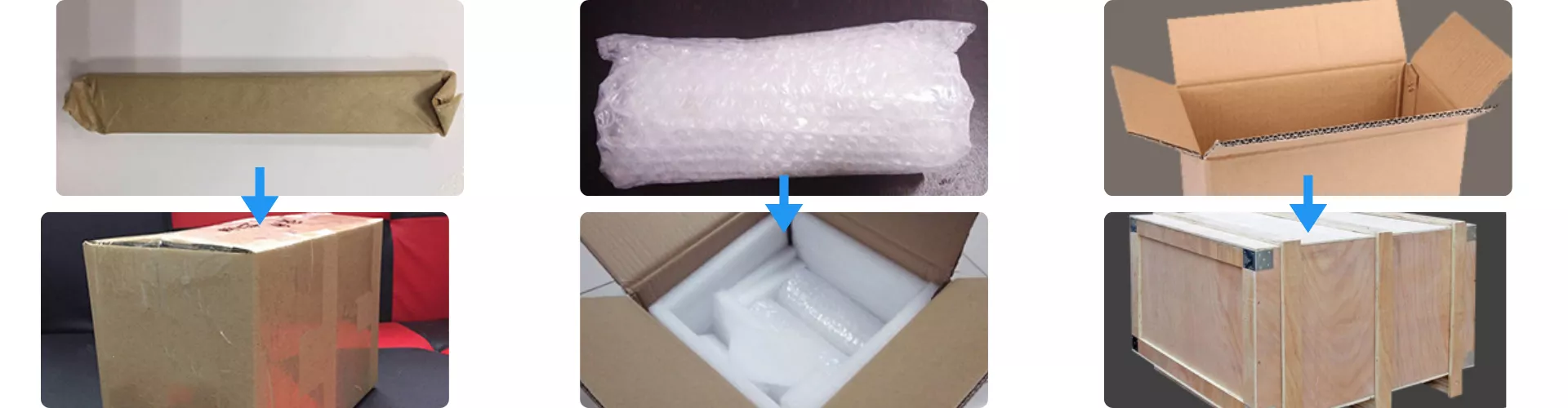
Packaging for Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor is packaged using a multilayer protection system that prevents vibration, impact, and moisture intrusion during international transport. Each unit is first wrapped in anti-scratch paper and bubble film, then secured within a foam-lined carton to stabilize all cavity areas. For long-distance shipments, the carton is reinforced inside a wooden crate to ensure structural safety throughout handling and loading processes.

ADCERAX® Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor for Solving Complex Process Challenges
The ADCERAX® Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor addresses operational challenges across high-temperature material processing environments where thermal uniformity, plasma resistance, and cycle stability directly affect production output and coating consistency.
-
Precision Multi-Wafer Growth for GaN / III–V LED Epitaxy Using Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Multi-Pocket Thermal Uniformity
The multi-cavity SiC structure maintains a highly consistent thermal field, supported by thermal conductivity of 120–180 W/m·K, preventing localized overheating during GaN/III–V nucleation. This uniformity stabilizes wavelength formation mechanisms, reducing cross-wafer variation in early epitaxy stages.
2. High Geometry Retention Under Halogen Exposure
The dense SSiC matrix exhibits a plasma erosion rate below 0.3 mg/cm²/hr in halogen environments, preserving pocket shape and cavity depth over long runs. This stability prevents chamber-to-chamber adjustments caused by drift in wafer support geometry.
3. Concentricity-Controlled Cavity Structure
Precise cavity alignment with concentricity held within ±0.05 mm ensures identical heat coupling across all wafer positions. This supports synchronous crystalline growth and minimizes brightness inconsistency across multi-wafer batches.
✅ ️Problem Solved
LED epitaxy producers frequently encounter divergent thermal profiles across pockets, causing noticeable wavelength drift between wafers during GaN and III–V growth. Variations in pocket geometry or surface erosion force repeated recalibration of growth recipes, interrupting production flow and increasing scrap ratios in high-throughput lines. ADCERAX® enhances batch stability by providing SSiC carriers that retain cavity shape and thermal balance through hundreds of high-temperature cycles, significantly reducing thermal divergence across loading positions. This results in more predictable film nucleation behavior and measurably improved uniformity in optical output distributions.
-
High-Density PVD Thin-Film Manufacturing for Hard Coatings and Optical Layers with Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
✅Key Advantages
1. Ion-Bombardment Surface Stability
The dense SiC microstructure resists plasma roughening with erosion rates 3–4 times lower than typical alumina or coated graphite carriers. This stability prevents edge disturbance under repeated ion exposure and maintains film uniformity across all load positions.
2. High-Temperature Shape Integrity
A service tolerance up to 1200°C enables the susceptor to retain geometric stability during extended high-power PVD cycles. This mitigates misalignment or tilt that would otherwise disrupt deposition rate consistency and film microstructure.
3. Wear-Resistant Pocket Architecture
With hardness above HV 2500, pocket edges resist rounding during repeated loading and unloading. This retention of form prevents positional drift that often causes coating thickness deviation across substrates.
✅ ️Problem Solved
PVD coating facilities commonly report thickness drift or microstructural inconsistency when carriers deform under thermal and plasma stress. Conventional carriers gradually roughen or warp, causing progressive misalignment that affects optical, mechanical, or wear-resistant layers. ADCERAX® addresses these issues by supplying high-density SiC susceptors that sustain dimensional integrity and maintain stable heat transfer during high-density plasma cycles. This stability significantly reduces corrective maintenance and maintains deposition uniformity across multiple loading positions, improving overall coating repeatability in continuous production environments.
-
Controlled High-Temperature Material Processing for Vacuum Thermal Systems Using Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor
✅Key Advantages
1. Low-Drift Thermal Expansion Behavior
A controlled CTE of 4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K minimizes thermal-induced distortion during material phase transition treatments. This allows consistent heat propagation that supports stable densification of advanced ceramics or optical materials.
2. Ultra-Low Porosity for Reactive Gas Stability
With porosity below 0.1%, gas infiltration into the carrier body is minimized, reducing reaction-driven degradation during repeated exposure to reactive atmospheres. This sustains long-term platform stability across many thermal cycles.
3. Geometry Preservation Through Cyclic Heating
The structural durability of SiC enables the platform to survive 300+ rapid heating transitions without cavity drift. This consistency ensures predictable temperature mapping within vacuum chambers during successive heating sequences.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Vacuum thermal processors frequently struggle with platform drift caused by thermal gradients, reactive atmospheres, and repeated cycling. These changes can result in microcracking of ceramic or optical components, uneven material density, and unpredictable outcomes across treatment batches. ADCERAX® enhances chamber stability by utilizing low-porosity, low-CTE SiC susceptors that maintain consistent geometry and uniform heat distribution across extended thermal sequences. This reduces batch-to-batch variation, supports consistent densification outcomes, and improves process reliability in demanding high-temperature environments.
ADCERAX® Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor User Guide for Safe and Stable Operation
The Multi-Pocket Silicon Carbide Susceptor operates within thermal, mechanical, and chemical environments that require controlled handling practices to maintain long-term stability and predictable process performance.
-
Handling and Pre-Operation Preparation
1. Proper Surface Protection
Always handle the susceptor with clean gloves to avoid transferring contaminants that may interfere with heat distribution or gas-flow behavior. Light contact with metallic tools should be avoided to prevent micro-scratches near cavity edges. Maintaining a clean surface before installation helps ensure consistent wafer interaction during early thermal cycles.
2. Initial Cleanliness Verification
Inspect the surface under adequate lighting to confirm the absence of particles, residues, or liquid marks. Any contamination should be removed using approved non-abrasive wipes to avoid altering surface roughness. A clean starting condition supports stable film nucleation and consistent thermal response.
3. Controlled Environment Staging
Store the component in a low-dust area before loading it into process equipment. Exposure to airborne contaminants may lead to particle adhesion that becomes difficult to remove after heating. Maintaining pre-operation cleanliness helps prevent surface drift across extended usage cycles.
-
Installation and Alignment Procedures
1. Cavity Position Verification
Check that each pocket is properly oriented relative to the system’s heating plane before tightening fixtures or clamps. Misaligned cavities can cause thermal imbalance during ramp-up events. Ensuring consistent cavity alignment supports uniform wafer heating across all load positions.
2. Load Path Stability
Make sure the susceptor sits evenly on its support points without rocking or tilt. Any uneven stress concentration may induce geometry shift during repeated hot–cold cycles. A stable base position minimizes mechanical distortion throughout long-duration processing.
3. Non-Impact Mounting
Avoid dropping, knocking, or forcing the carrier into its slot, especially around pocket edges. Even small impacts may initiate micro-cracks that propagate under high temperatures. Gentle placement helps preserve structural integrity throughout high-temperature exposure.
-
Operational Use During Thermal and Plasma Processes
1. Heat Ramp Awareness
Ensure that heating and cooling rates follow equipment recommendations to avoid introducing thermal shock. Abrupt transitions can increase stress concentrations at cavity boundaries. Moderate ramp control improves long-cycle consistency in high-temperature applications.
2. Plasma Exposure Monitoring
For plasma-based operations, verify system parameters that may intensify erosion, such as high-energy ion settings or extended exposure time. Over-aggressive conditions accelerate surface degradation. Monitoring these parameters helps maintain low erosion rates during continuous cycles.
3. Stable Gas-Flow Management
Confirm that gas-flow paths and chamber distribution settings are correctly balanced before each run. Irregular flow can cause uneven heating behavior across multiple pockets. Balanced gas delivery promotes predictable thermal patterns and deposition uniformity.
-
Post-Operation Care, Cooling, and Storage
1. Controlled Cooling Practices
Allow the susceptor to cool naturally inside the system chamber before removal. Sudden exposure to room-temperature airflow may introduce thermal gradients harmful to geometry stability. A gradual cooldown supports structural longevity and minimizes internal stress.
2. Surface Cleaning After Use
Remove residues with compatible cleaning agents that do not alter SiC surface chemistry. Avoid abrasive pads or high-force scrubbing to protect pocket geometries. Routine cleaning maintains consistent surface interaction in repeated production cycles.
3. Protective Packaging and Storage
Store the cooled component in a protective foam-lined container to avoid accidental impact or dust accumulation. Environmental humidity should be kept low to limit unwanted surface reactions. Protective storage reduces the risk of damage between operating cycles.

![]()