ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer enables high-temperature, high-voltage, and high-frequency device architectures by providing a wide-bandgap semiconductor foundation with stable crystal quality, strong electrical uniformity, and high thermal conductivity. Its ability to support thinner drift layers, lower switching losses, and consistent epitaxial behavior makes it suitable for power conversion systems used in EV inverters, photovoltaic inverters, energy-storage converters, industrial drives, RF amplifiers, and optoelectronic devices. These performance characteristics create a continuous engineering pathway toward higher efficiency, reduced system size, and improved long-term reliability across advanced power-electronics platforms.
Advanced Material and Device-Level Features of Silicon Carbide Wafer
- High Breakdown Strength
The material sustains a critical electric field of ~2.8 MV/cm, enabling thinner drift layers without compromising voltage capability.
- High Saturation Velocity
The electron saturation drift velocity reaches 2×10⁷ cm/s, reducing charge-carrier transit limitations during high-frequency commutation.
- Intrinsic High-Temperature Limit
An intrinsic thermal limit exceeding 600 °C permits processing and device operation well beyond the thermal margins of silicon materials.
- Reduced Micropipe Density
Commercial 4H-SiC substrates achieve micropipe densities commonly below 0.1 cm⁻², lowering catastrophic defect formation in high-voltage designs.
- Basal-Plane Dislocation Control
Basal-plane dislocation counts can be maintained within a few ×10³ cm⁻², limiting stacking-fault propagation in bipolar devices.
- Epitaxial Thickness Uniformity
Wafer-level thickness variation and doping uniformity mapping typically achieve <2% deviation across the active area.
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity values near 4.9 W/cm·K enable rapid heat extraction from the active region during high-frequency switching.
- High Hardness and Mechanical Strength
Mechanical hardness exceeding Mohs 9 minimizes surface scratching during wafer handling and lithography preparation.
- Controlled Wafer Bow and Warp
Advanced surface preparation keeps bow/warp values within stringent device-processing tolerances, often under tens of microns depending on wafer format.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Wafer
Silicon Carbide Wafer exhibits a wide-bandgap semiconductor structure with strong electrical uniformity, high thermal conductivity, and stable crystal integrity, enabling reliable operation under elevated voltage, temperature, and switching frequency in advanced power-electronics and RF applications.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material System |
4H-SiC / 6H-SiC |
| Bandgap Energy |
3.23 eV |
| Critical Breakdown Field |
~2.8 MV/cm |
| Thermal Conductivity |
~4.9 W/cm·K |
| Electron Saturation Velocity |
2×10⁷ cm/s |
| Intrinsic Temperature Limit |
>600 °C |
| Micropipe Density |
<0.1 cm⁻² |
| Basal-Plane Dislocation Density |
few ×10³ cm⁻² |
| Epitaxial Thickness Uniformity |
<2% deviation |
| Doping Uniformity |
high in-plane stability |
| Surface Roughness (SSP/DSP) |
low-RMS polished finish |
| Crystal Orientation Stability |
high-precision (0001) structure |
| Electrical Type |
N-type / Semi-insulating |
| Thermal Expansion Behavior |
SiC-consistent CTE stability |
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Wafer
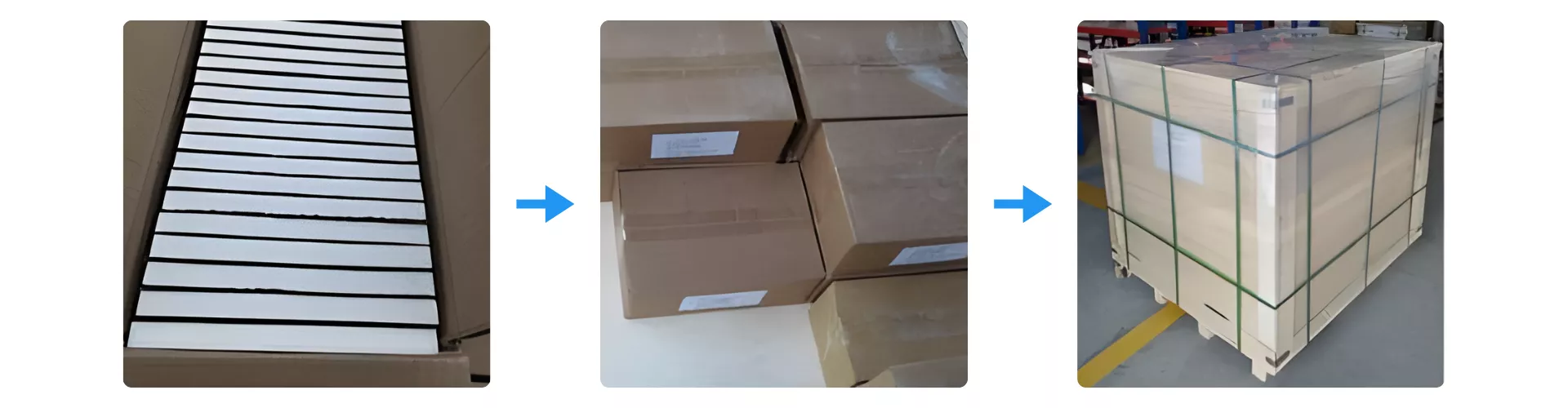
Packaging of Silicon Carbide Wafer
Silicon Carbide Wafer is packed through a controlled multi-layer process designed to protect surface integrity and prevent mechanical stress during long-distance transport. Each wafer stack is first arranged in lined trays, then placed into reinforced cartons with clear labeling for traceability. The cartons are finally consolidated onto palletized loads with full-edge protection and strapping to ensure stability from factory dispatch to customer receipt.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer for Overcoming High-Demand Power-Electronics Challenges
The Silicon Carbide Wafer supplied by ADCERAX® enables power-electronics designers to address system-level challenges in environments where high voltage, elevated switching frequency, and thermal stress combine to limit the performance of conventional semiconductor materials. Its wide-bandgap behavior, strong thermal conduction, and stable epitaxial uniformity provide tangible engineering advantages in conversion systems used across energy, mobility, and industrial-grade infrastructure.
-
Silicon Carbide Wafer in 800-V EV Traction Inverters for Thermal Load Reduction
✅Key Advantages
1. High Thermal Conductivity Heat Path
The substrate’s thermal conductivity around 4.9 W/cm·K creates an efficient heat-spreading path from the active device region into the module baseplate. This allows junction temperature rise during rapid traction inverter switching to be reduced by 10–20 °C compared with silicon-based solutions under comparable drive cycles.
2. Wide-Bandgap High-Temperature Stability
With a bandgap of 3.23 eV, the material maintains stable on-state and blocking behavior at junction temperatures exceeding 175 °C. This extended thermal margin lets EV inverters sustain higher continuous current operation without derating during long-distance or high-load driving.
3. High Breakdown Field for Compact Drift Layers
A critical breakdown field near 2.8 MV/cm supports thinner drift regions for 650–1700 V class devices while keeping blocking capability intact. This directly contributes to lower conduction loss and can support 2–3× higher power density at the inverter level when combined with SiC-optimized layouts.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In one 800-V traction inverter platform, silicon switches operating at elevated frequency produced rising junction temperatures and forced designers to oversize the cooling system to maintain safe limits. Efficiency targets were difficult to reach because switching losses and thermal cycling constrained both current capability and power density. After adopting ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer as the device substrate, the inverter stage demonstrated a reduction in switching-related loss of approximately 60–80% compared with a silicon IGBT baseline. Junction temperature peaks were lowered by more than 10 °C, and the required cooling mass was reduced in the range of 30–50%, allowing the traction inverter to meet long-distance efficiency targets while keeping the enclosure compact.
-
Silicon Carbide Wafer in Utility-Scale PV Inverters Facing Efficiency Loss at High Power Density
✅Key Advantages
1. High-Frequency Switching Capability
The electron saturation velocity of approximately 2×10⁷ cm/s supports efficient charge transport under high dv/dt and di/dt conditions in large PV inverters. This enables higher switching frequencies that can contribute to system efficiency gains of 1–3% while maintaining stable device behavior over long operating hours.
2. Uniform Epitaxial Layer for Parallel Devices
Epitaxial thickness variation kept below 2% across the wafer reduces parameter spread in on-resistance and leakage among parallel-connected devices. This uniformity helps large PV inverters maintain balanced current sharing across phases and modules, which is critical when processing hundreds of kilowatts of DC power.
3. Thermal Robustness in Outdoor Conditions
With an intrinsic temperature limit above 600 °C, Silicon Carbide Wafer retains material integrity and electrical stability under elevated ambient temperatures typical of outdoor PV fields. This high-temperature robustness allows inverter designs to operate reliably with smaller heatsinks, supporting 30–60% reductions in overall power-stage volume in high-density cabinets.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A utility-scale PV project experienced efficiency drop and thermal drift in inverters as switching frequency was increased to reduce magnetic component size. Silicon-based devices showed rising switching loss and unstable characteristics during hot summer operation, narrowing the safe design margin in compact enclosures. By transitioning the power stage to devices built on ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer, the inverter achieved a measured system efficiency improvement of about 1–3 percentage points at high load. Thermal imaging confirmed lower hotspot temperatures and more uniform temperature distribution, which allowed engineers to reduce heatsink volume by roughly 30–40% while maintaining stable grid-compliant performance across long operating hours.
-
Silicon Carbide Wafer for High-Load Industrial Drive Systems Requiring Stable High-Frequency Switching
✅Key Advantages
1. Low Defect Density Under Dynamic Load
Micropipe densities controlled below 0.1 cm⁻² and basal-plane dislocation levels in the range of few ×10³ cm⁻² limit defect-driven premature breakdown during current surges. This low defect landscape provides a robust foundation for high-frequency PWM control in variable-speed drives subject to frequent torque changes.
2. Stable Electrical Behavior During Thermal Cycling
The combination of 3.23 eV bandgap and high breakdown field near 2.8 MV/cm maintains consistent blocking and conduction behavior over repeated thermal cycles. This stability supports reliable operation in industrial environments where drive cabinets experience continuous load and temperature fluctuations.
3. Enhanced Uptime Through Power-Stage Robustness
High thermal conductivity around 4.9 W/cm·K and controlled epitaxial uniformity help reduce localized overheating and electrical drift in the power devices. In practice, this robustness can lower drive-related unplanned downtime by 20–30% when systems are exposed to frequent start–stop and high-torque load profiles.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In a high-load conveyor and compressor installation, variable-speed drives built on silicon switches showed instability in high-frequency control loops after extended operation under fluctuating load. Thermal cycling and current spikes led to intermittent faults and forced maintenance stops, shortening the effective service interval of the drive cabinets. After migrating the power stage to devices fabricated on ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer, fault statistics over a comparable operating period showed a reduction in drive-related trip events on the order of 20–30%. Temperature monitoring also indicated tighter junction-temperature control during rapid load changes, supporting more stable motor control and extending the practical service window between maintenance interventions.
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Wafer User Guide for Reliable Power-Electronics Integration
Silicon Carbide Wafer requires controlled handling, installation, and environmental preparation to fully realize its wide-bandgap advantages in high-voltage and high-frequency systems. This guide outlines the key technical considerations engineers should follow to ensure stability, performance consistency, and long-term reliability across diverse power-electronics platforms.
-
Handling and Surface Protection Guidelines
1. Avoid Direct Contact
The wafer surface should be treated as a precision interface, and direct finger contact must be avoided to reduce contamination risk. Stable device performance depends on maintaining an uncontaminated surface prior to epitaxy or metallization. Any handling process should prioritize low-particle and low-moisture exposure to protect surface integrity.
2. Use Cleanroom-Compatible Tools
All tools used for wafer movement should meet cleanroom compliance and feature non-abrasive materials to prevent micro-scratches. Even minor surface abrasions can influence leakage stability and breakdown consistency in high-voltage systems. Operators should rely solely on non-metallic, certified wafer carriers to maintain safe handling.
3. Control Airborne Particulates
Wafer unpacking and preparation should be performed in controlled air environments to minimize dust accumulation. Small particles lodged on the surface can interfere with lithography or epitaxial uniformity during fabrication. Maintaining stable ISO-classified environments ensures consistent downstream processing.
-
Environmental and Thermal Management Practices
1. Maintain Stable Thermal Cycles
Power-electronics integration requires the wafer to experience predictable thermal profiles to protect crystal structure. Sudden temperature gradients can cause stress accumulation that affects electrical uniformity. A controlled approach to heating and cooling, along with strict ramp-rate management, is essential for long-term reliability.
2. Ensure Adequate Heat Dissipation
High switching frequencies generate local hotspots that require engineered cooling paths to manage thermal load. System designers should validate that heat sinks, substrates, and interface materials support stable extraction of thermal energy. Proper thermal transfer pathways allow consistent junction-temperature control across dynamic load cycles.
3. Avoid Contaminant-Driven Oxidation
Even though the material withstands elevated temperatures, contaminants in air or process gases can influence high-temperature stability. Exposure to reactive atmospheres must be minimized when the wafer operates near its thermal limits. Maintaining clean thermal environments strengthens long-term device behavior during high-energy operation.
-
Electrical Integration and Device-Level Considerations
1. Validate High-Voltage Margins
Device blocks designed around the wafer should maintain sufficient safety headroom when operating near elevated voltage limits. Proper margining ensures the breakdown field is not inadvertently exceeded in fast-transient or surge conditions. Engineers should integrate predictive surge-tolerance modeling when designing traction or conversion systems.
2. Control Switching Speed and dv/dt
The wafer supports high-frequency switching, yet excessive dv/dt can induce unintended stress in gate-drive circuits. Controlled gate-drive shaping helps maintain switching integrity across full load ranges. Incorporating dv/dt-optimized driver configurations improves long-term reliability and system stability.
3. Ensure Uniform Current Distribution
Parallel device configurations must confirm consistent electrical loading across all substrate channels. Uneven current flow leads to localized heating and long-term drift that affects system behavior. Designers should apply current-balancing topology checks during early system layout stages.
-
Storage, Transportation, and Long-Term Preservation Requirements
1. Maintain Controlled Humidity During Storage
Wafer boxes must be stored in humidity-regulated environments to avoid moisture absorption that can affect surface properties. Prolonged exposure to ambient humidity may introduce thin contamination layers on polished surfaces. A dry-cabinet or desiccant-supported system is recommended for long-term warehousing.
2. Use Shock-Protected Packaging
Transportation must rely on anti-vibration trays, reinforced cartons, and palletized loads to prevent fracture risk. Mechanical shock can propagate micro-cracks that remain invisible until later processing stages. Ensuring multi-layer impact protection reduces handling-related defects during international shipment.
3. Label and Track Storage Conditions
Each batch should carry traceability records and physical condition logs to ensure consistent quality control. Tracking environmental exposure helps engineers identify variables affecting device performance. A complete traceability dataset supports predictable integration into power-electronics production flows.
![]()