Magnesia ceramic plate—is a solid ceramic sheet made primarily from magnesium oxide (MgO). It is engineered for use in high-temperature, electrically insulating, and thermally stable environments. The mgo plate is used in furnaces, heaters, and sintering processes for insulation, support, and thermal protection.
Magnesia Ceramia Plate Benefits
- Flatness control: ground faces and Ra-tuned surfaces reduce part imprint during sintering.
- Edge integrity: controlled chamfer/R-edge minimizes chipping at handling and thermal cycling.
- Hole/location accuracy: stable dimensional accuracy for fixtures and heater bolt patterns.
- High-temp dielectric stability: maintains insulation in hot zones where polymers and micas fail.
- Surface optioning: raw, fine-ground, or polished face to match contact and cleanliness needs.
Properties of Mgo Ceramia Plates
|
Properties |
Unit |
Value |
|
Material |
% |
99 MgO |
|
Density |
g/m³ |
3.5 |
|
Bulk Density |
g/m³ |
2.8 |
|
ApparentPorosity |
% |
20 |
|
Compressive Strength |
MPa |
50 |
|
FlexuralStrength |
MPa |
16 |
|
Refractoriness |
SK |
42< |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
W/(m.K) |
5 |
|
Coefficient of thermal expansion (20~1000℃) |
10-6/K |
13 |
|
Operating temperature |
Max (℃) |
2200 |
|
Room temperature |
Room temperature (℃) |
1800 |
Mgo Ceramia Plate Specifications
Type 1: Mgo Round Plates

|
Mgo Round Plates |
|
Item No. |
Diameter(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
|
AT-MO-P1001 |
25 |
5 |
|
AT-MO-P1002 |
25 |
3 |
|
AT-MO-P1003 |
30 |
3 |
|
AT-MO-P1004 |
30 |
5 |
|
AT-MO-P1005 |
36.5 |
4.5 |
|
AT-MO-P1006 |
41 |
4.5 |
|
AT-MO-P1007 |
41 |
10 |
|
AT-MO-P1008 |
51 |
3 |
|
AT-MO-P1009 |
59 |
4.5 |
Type 2: Mgo Square Plates

|
Mgo Square Plates |
|
Item No. |
Length(mm) |
Width(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
|
AT-MO-P2001 |
68.5 |
55 |
2.2 |
|
AT-MO-P2002 |
96 |
30 |
5 |
|
AT-MO-P2003 |
78 |
65 |
2 |
|
AT-MO-P2004 |
120 |
60 |
3 |
|
AT-MO-P2005 |
120 |
60 |
10 |
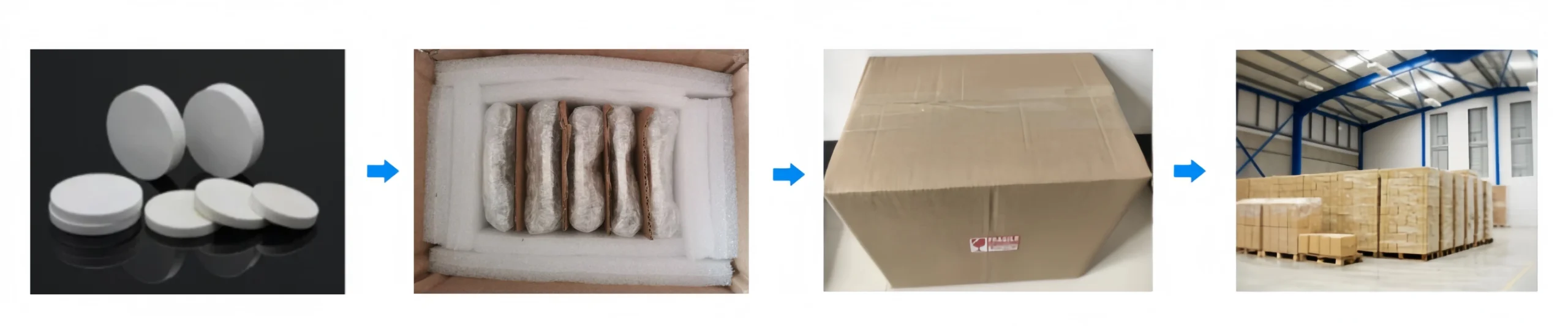
Magnesium Oxide Plate Packaging
- Each plate is individually wrapped in foam
- Sealed in moisture-proof bags

Mgo Ceramic Plate Usage Instructions
Proper handling and operation of mgo plates ensure consistent performance, longer service life, and safety in high-temperature equipment. Follow these key guidelines during installation, operation, and maintenance.
-
Install
1. Inspect before use: Check for any cracks, edge chips, or surface scratches. Reject or mark plates with visible damage before assembly.
2. Mounting surface: Always mount on a flat, level support base to distribute load evenly; avoid point contacts that may induce stress fractures.
3. Alignment: Use ceramic spacers or shims for height adjustment when building multi-plate beds.
4. Fastening: For heaters or fixtures, confirm bolt torque and isolate metal contact using ceramic washers or sleeves to prevent current leakage.
5. Thermal compatibility: Match expansion with adjacent materials to prevent warping during temperature cycling.
-
Use
1. Heating & cooling: Follow controlled ramp-up and ramp-down rates; avoid direct cold-air exposure to hot plates to minimize thermal shock.
2. Surface protection: Keep contact faces clean; use interleaf sheets or alumina papers when powders or parts could sinter onto the plate.
3. Load management: Centre components on the plate to balance thermal stress.
4. Process tracking: Record the number of heating cycles per plate to plan maintenance or replacement intervals.
5. Atmosphere caution: In reducing or vacuum environments, verify compatibility of MgO grade to avoid surface reduction or micro-pitting.
-
Store
1. Environment: Store in a dry, dust-free area, away from corrosive vapours and vibration.
2. Stacking: Avoid stacking heavy objects directly on thin plates; use cardboard or foam separators.
3. Protection: Keep polished or ground faces covered with protective film or soft paper interleaves.
4. Identification: Label orientation and batch number for traceability; store vertically for thicker plates to prevent bowing.
-
Clean
1. Routine cleaning: Remove dust or loose debris with clean compressed air or a soft, dry brush.
2. Residue removal: For stuck material, use a non-metallic scraper or fine abrasive pad; avoid steel tools that can leave conductive residues.
3. Moisture control: If the plate has absorbed humidity, pre-bake at 150–200 °C for 1–2 hours before reuse.
4. No chemical wash: Do not use acid or alkaline cleaners that could alter the ceramic surface.
-
Cautions & Common Misoperations
1. Avoid thermal shock: Never quench or expose hot plates to cold airflow or liquids.
2. Prevent contamination: Do not mark working surfaces with graphite, ink, or metal tools.
3. Handle carefully: Use two hands or vacuum lifters when moving large plates; sudden edge impact may cause micro-cracks.
4. Check fit after multiple cycles: Plates may show minor warp or wear — replace if flatness deviation exceeds tolerance.
5. Regular inspection: A Visual check after each 100 h of operation is recommended for continuous furnaces.