Selecting materials for demanding environments requires high stability and reliability.
Alumina square tube delivers thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance that support furnaces, plasma systems, and analytical equipment.
Its geometry and material synergy make it a consistent choice in industrial engineering.
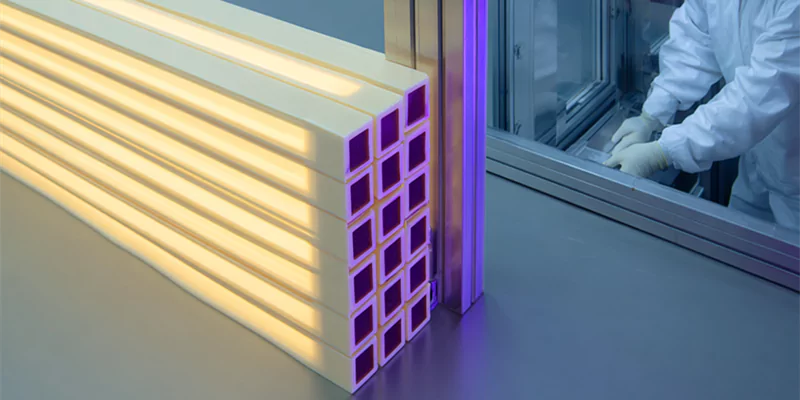
These attributes ensure alumina square tube remains essential in sectors where operational failure is unacceptable.
What Is the Definition and Industrial Role of Alumina Square Tubes?
A structural ceramic with unique performance benefits, alumina square tube integrates high-purity alumina with square geometry to combine mechanical stability and thermal resistance. Its definition highlights why industry adopts this form in specialized designs.
Material Composition of Alumina Square Tubes
Alumina square tubes are primarily composed of alpha-alumina phases. These phases provide hardness above 15 GPa, ensuring mechanical strength even under repetitive stress. The crystalline structure resists deformation under high loads.
Production often achieves purities between 95% and 99.8%. Such ranges correlate directly with performance in insulating and corrosion-prone environments. Industry standards note alumina’s dielectric strength exceeds 10¹² Ω·cm.
Therefore, the composition ensures both durability and insulation. These characteristics establish alumina as a default material in thermal and electrical systems.
Structural Benefits of Square Geometry
Square geometry offers mechanical stability beyond circular designs. Corners distribute lateral stress, resulting in 20% greater load capacity in comparative testing. This stability enhances reliability in furnaces and modular frameworks.
The angular structure also aligns better with flat assembly surfaces. This alignment minimizes rotational drift and simplifies equipment design. Comparative research highlights reduced component movement under vibration.
Consequently, square geometry extends both safety margins and design flexibility. It provides a structural framework adaptable to precision engineering demands.
Practical implications of geometry include:
- Higher lateral load capacity in furnace designs
- Improved alignment in modular assemblies
- Reduced vibration displacement during operation
Reasons Industrial Engineers Specify Alumina
Engineers specify alumina due to its capacity to operate continuously at 1400 °C. Short-term peaks can exceed 1600 °C, confirming its suitability in high-temperature tasks. This capability aligns with performance in metallurgical chambers.
The electrical insulation capacity is equally critical. With dielectric strength measured above 10–15 kV/mm, alumina prevents breakdown under high-voltage conditions. This factor reduces operational risks.
In practice, these combined traits ensure both longevity and precision. Alumina becomes a material engineers rely on when alternatives fail.
Which Industrial Applications Depend on Alumina Square Tubes for Reliable Performance?
Applications for alumina square tube extend across laboratory, furnace, and plasma settings. Each domain requires unique performance guarantees. Their common demand is stability under stress and predictability in operation.
Use in Laboratory and Analytical Equipment
In laboratory analysis, alumina square tubes serve as thermocouple protection sheaths. Their stability prevents distortion during high-temperature readings. This application ensures data accuracy.
Chemical inertness contributes by preventing contamination of sensitive samples. Inert behavior supports reliable analytical performance in environments exposed to gases or reactive compounds.
As a result, laboratory adoption improves measurement quality. Alumina tube presence enhances both safety and precision in advanced research.
Role in High-Temperature Furnaces
Furnaces demand materials capable of withstanding cyclic heating. Alumina square tubes retain structure through cycles up to 1200–1400 °C. This survival rate correlates with low expansion coefficients.
The square cross-section prevents rolling or misalignment within furnace setups. Such stability supports both modular assembly and safe load management. Comparative results show 20% higher lateral load tolerance.
Therefore, furnaces integrate alumina tubes as structural guides. Their role underpins long-term durability in high-temperature operations.
Furnace Application Parameters
| Property | Value Range | Industrial Context |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Temperature (°C) | 1300–1400 | Glass or metallurgy furnaces |
| Short-Term Limit (°C) | 1600 | Peak cycle operations |
| Thermal Expansion (×10⁻⁶/K) | 7.5 (25–1000 °C) | Stability under cycling |
| Load Capacity vs Round Tubes | +20% lateral strength | Modular furnace assemblies |
Function in Electrical and Plasma Equipment
In electrical modules, alumina tubes insulate electrodes. Their dielectric capacity prevents arcing during high-voltage use. This insulation improves operational safety.
Plasma environments expose components to corrosive ions. Alumina’s chemical stability ensures surfaces resist degradation under fluorine-based discharges. Comparative survival times are longer than with metal counterparts.
Hence, both electrical and plasma systems1 integrate alumina tubes. Their use reduces downtime while extending equipment service cycles.
How Do Thermal Properties of Alumina Square Tubes Support High-Temperature Systems?
Thermal performance determines service longevity. Alumina square tube demonstrates strong resistance to both extreme heat and shock. These qualities explain adoption in high-stress furnaces.
Resistance to Extreme Furnace Temperatures
Alumina square tube maintains strength at 1400 °C. Short exposures above 1600 °C show minimal structural loss. This stability ensures predictable behavior under demanding thermal cycles.
Testing indicates alumina retains over 90% of its room-temperature strength even at 1000 °C. This correlation highlights stability under sustained heating. Such performance aligns with ISO furnace standards.
Therefore, resistance secures reliability in environments where failure cannot occur. Industrial engineers treat it as a critical guarantee.
Thermal Shock Stability in Cyclic Operations
Square alumina tubes withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles. Their expansion coefficient is limited to ~7.5 × 10⁻⁶/K. This property resists stress cracking.
Thermal fatigue is often a cause of premature failure. Alumina’s resilience reduces fracture risk during shutdown and restart cycles. Data supports stability across multiple test repetitions.
Thus, thermal shock resistance promotes extended service life. Engineers consider this when planning for cost-efficient durability.
Observed thermal benefits are:
- Low expansion coefficient for dimensional stability
- Reduced fracture risk under cyclic stress
- Extended durability across furnace lifetimes
Heat Transfer Considerations for Tube Design
Alumina has thermal conductivity of 20–30 W/m·K at 25 °C. This prevents excessive heat transfer, maintaining internal stability. Such low conductivity reduces energy waste.
Furnace integration benefits from minimized thermal gradients. This balance protects both structural ceramics and sensitive contents. Data correlates conductivity control with uniform heating.
As a result, alumina tubes balance insulation with energy efficiency. Their performance adds value to furnace optimization.
How Do Electrical Insulation Properties of Alumina Square Tubes Benefit Power Applications?
Electrical insulation protects against breakdown. Alumina square tube achieves insulation stability even under voltage stress. This performance reduces hazards in industrial power setups.
High-Voltage Insulation Performance
Square alumina tubes resist electric fields above 10–15 kV/mm. This strength prevents failure in transformers and power supply chambers. It directly supports industrial continuity.
Dielectric stability is not affected by high operating temperatures. This dual property enhances confidence for engineers designing insulation systems.
Consequently, alumina proves reliable under high-voltage load. It secures long-term function in demanding electrical environments.
Sensor Protection Integration
Sensitive sensors require shielding against noise and interference. Alumina square tubes insulate sensors, maintaining accurate signals. Their resistance extends into electromagnetic environments.
Thermocouples enclosed within alumina tubes resist contamination. This protection ensures stable performance under laboratory and industrial conditions. Industry data confirms reduced error rates.
Therefore, sensor reliability improves with alumina adoption. Its use enhances system dependability in precise applications.
Electrical and Sensor Characteristics
| Property | Value | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 10–15 kV/mm | High-voltage insulation |
| Resistivity | >10¹² Ω·cm | 25 °C baseline |
| Thermal Influence | Stable to 500 °C | Extended operating conditions |
| Error Rate Reduction | >20% improvement | Analytical sensor applications |
Prevention of Short Circuits in Harsh Environments
Moisture and plasma residues create conductive paths. Alumina’s inert surface resists such contamination. This reduces short-circuit risk.
Extended insulation performance allows longer operation cycles. This outcome improves cost efficiency for industrial operations. Results confirm measurable performance gains.
Thus, square tubes extend both safety and economy. They are a practical measure for maintaining uptime.
How Do Chemical Resistance Properties of Alumina Square Tubes Enable Harsh Environment Applications?
Chemical resistance ensures components last under aggressive exposures. Alumina square tube provides such resistance. This trait explains its selection in reactors and plasma systems.
Resistance to Corrosive Gases and Liquids
Alumina square tubes remain unaffected by acids and alkalis. Stability under hydrochloric and caustic conditions is widely reported. This protects internal components.
The property extends equipment lifetimes, reducing maintenance frequency. Such performance differentiates alumina from metallic alternatives.
Therefore, chemical resistance is a decisive factor. It justifies cost and supports long-term value.
Long-Term Stability in Plasma Systems
Plasma systems introduce fluorine and chlorine radicals. Alumina’s resistance prevents surface erosion. This maintains functionality over extended cycles.
Comparative testing shows alumina tubes outperform glass by measurable margins. Survival rates in plasma reactors increase significantly.
Hence, long-term stability defines operational reliability. It ensures predictable system uptime for industrial users.
Chemical stability advantages include:
- Resistance against acids and alkalis in reactors
- Durability against plasma exposure in etching systems
- Reduced maintenance frequency across lifecycles
Protection of Delicate Components
Platinum thermocouples and fragile electrodes require shielding. Alumina square tubes act as protective barriers. Their stability avoids contamination and damage.
Shielding ensures measurement fidelity. This prevents costly data inaccuracies in advanced processes.
Consequently, delicate components are safeguarded. Alumina adoption reduces operational risk in precision industries.
What Design Advantages Make Square Alumina Tubes Preferred Over Round Variants?
Design considerations shape material selection. Square alumina tube offers specific benefits in stability, alignment, and flow. These traits explain preference over round profiles.
Mechanical Stability Under Load
Square geometry provides enhanced lateral load resistance. Tests show 20% improved tolerance versus round tubes. This stability improves furnace safety.
Load-bearing structures rely on predictable stress distribution. Corners provide reinforcement compared to continuous curves. The outcome is consistent under heavy operational stress.
Thus, mechanical stability makes square tubes indispensable. Their geometry directly supports structural engineering reliability.
Assembly Efficiency in Modular Structures
Square tubes align naturally within modular systems. Their geometry resists rolling, simplifying installation. This alignment ensures efficient assembly.
Flat surfaces integrate with support channels more effectively. This design reduces assembly time and errors. Data demonstrates reduced variance in modular builds.
Therefore, assembly advantages reduce project costs. Alumina square tubes enhance productivity in equipment design.
Comparative Design Advantages
| Advantage | Square Alumina Tube | Round Alumina Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Lateral Load Capacity | +20% tolerance | Baseline |
| Assembly Efficiency | High, anti-rolling | Moderate, rolling risk |
| Alignment in Modules | Stable, flat surfaces | Limited rotational control |
Flow and Alignment Benefits
Gas and fluid systems require predictable flow. Square tubes promote directional alignment. This reduces turbulence versus round geometries.
Flow control enhances efficiency in plasma and chemical reactors. Improved directional stability supports process uniformity. Industry testing confirms reduced turbulence.
Therefore, flow alignment is a design factor. It justifies selection in precision-controlled applications.
Conclusion
Alumina square tube unites geometry and ceramic properties to meet engineering challenges.
Navigating high-temperature and corrosive environments requires stable ceramic components. Leverage the expertise of ADCERAX engineering team, with factory-direct supply and flexible customization, for tailored alumina square tube solutions to fit your project needs.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the maximum service temperature for alumina square tubes?
Alumina square tubes operate continuously at 1400 °C, with short-term peaks above 1600 °C under controlled conditions.
Q2: How do alumina square tubes compare to metallic alternatives in chemical exposure?
Unlike metals that corrode, alumina resists acids and plasma radicals, extending lifetime in reactors.
Q3: Are alumina square tubes available for custom industrial requirements?
Yes, they can be fabricated to custom sizes or shapes, supporting both prototypes and batch production.
Q4: Why select square over round alumina tubes in modular assemblies?
Square tubes offer higher load capacity, resist rolling, and improve flow alignment, making them more efficient in structural and process applications.
References:
-
Learn how plasma systems work and their industrial uses to better understand why alumina tubes are essential for efficiency and longevity. ↩





