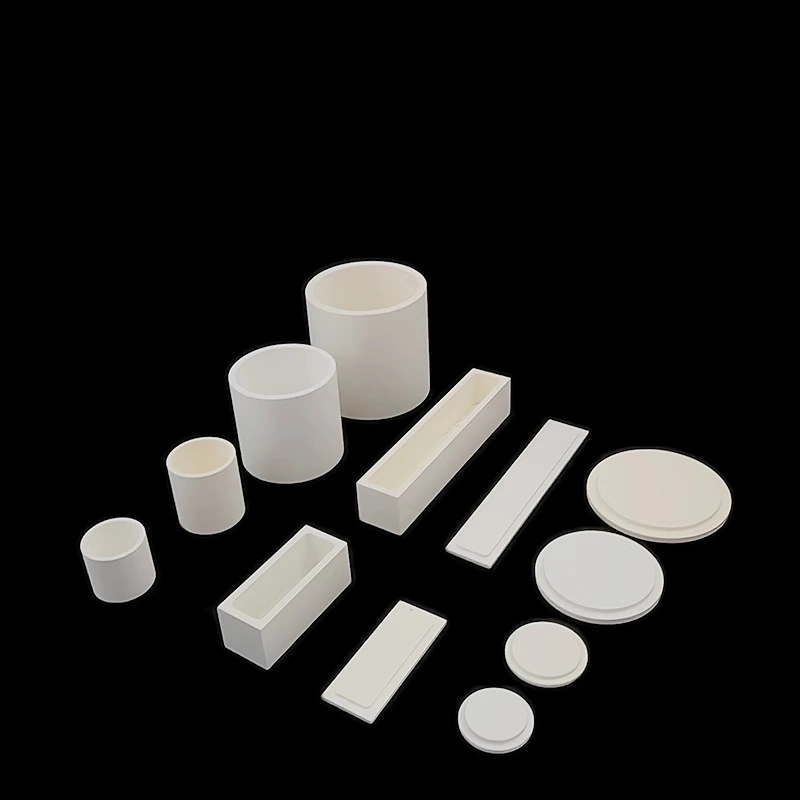
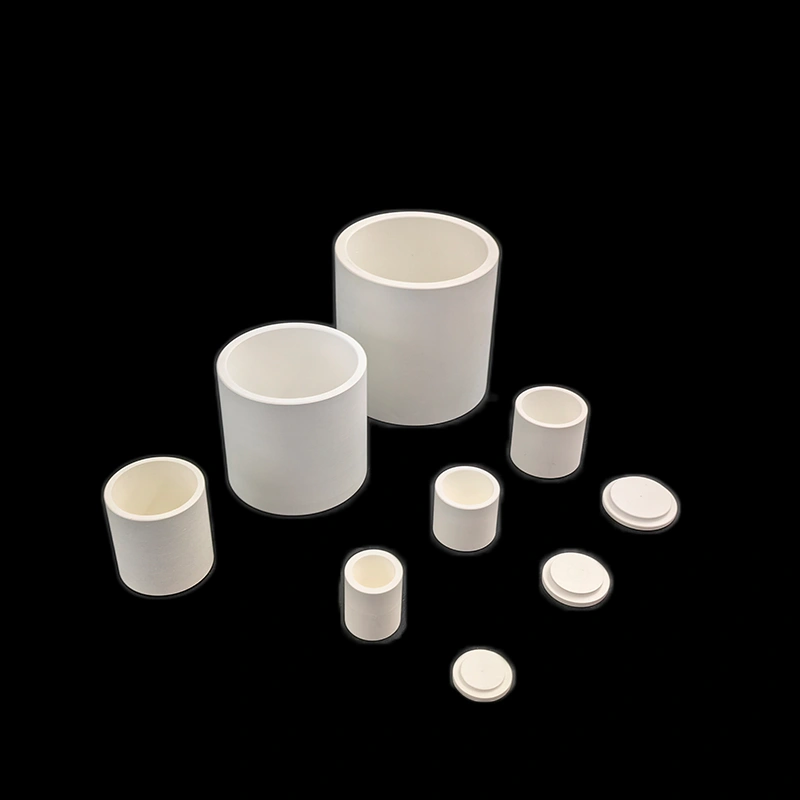
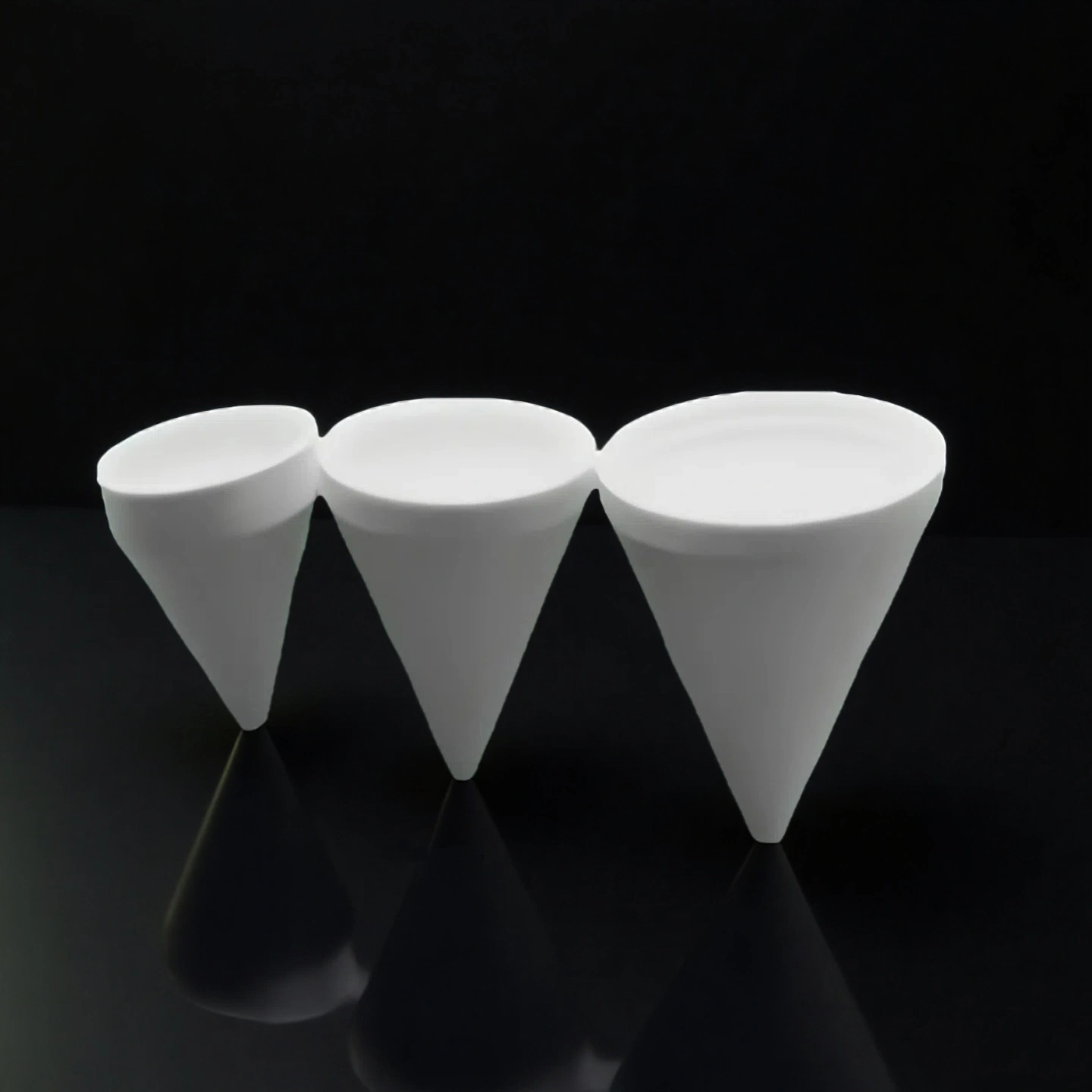
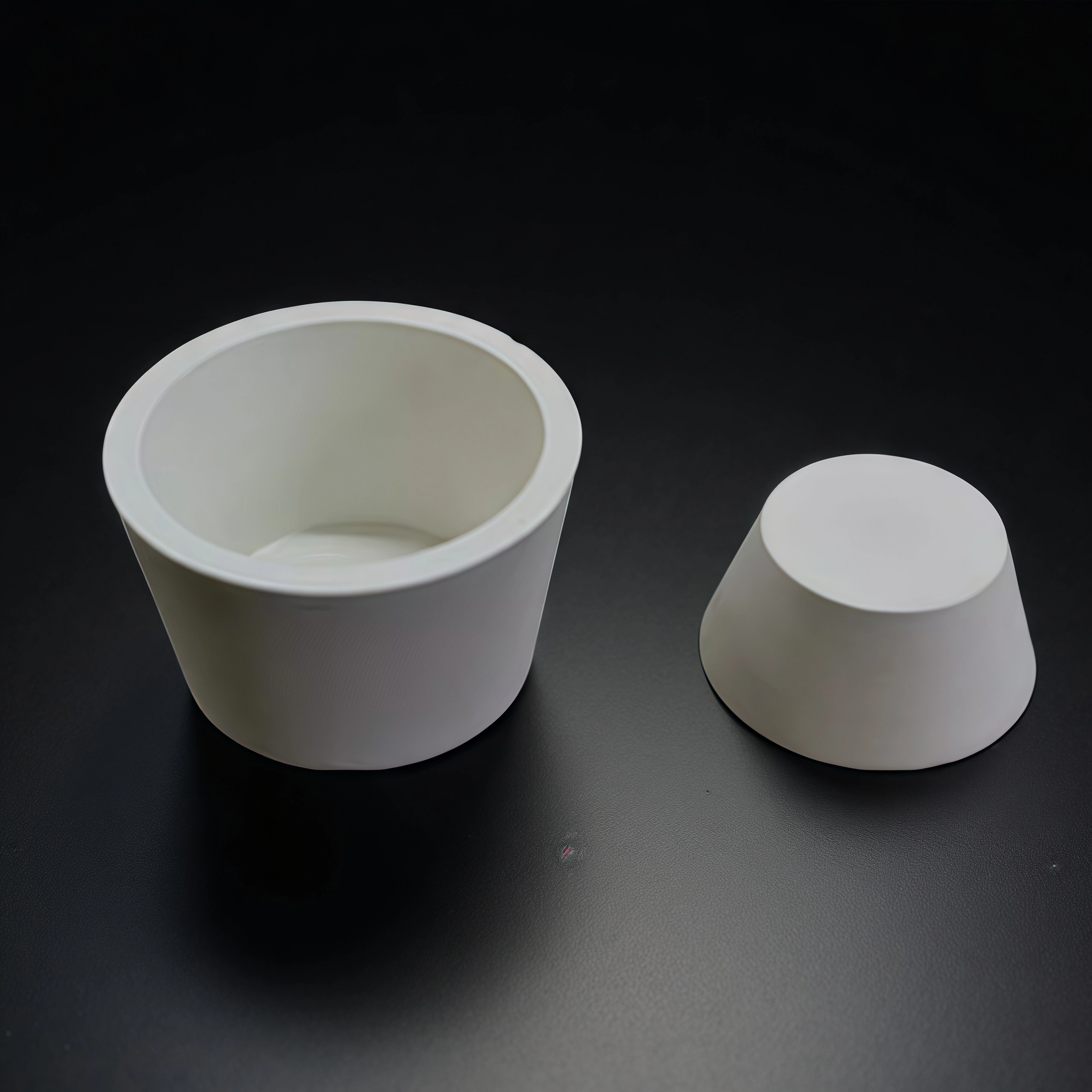
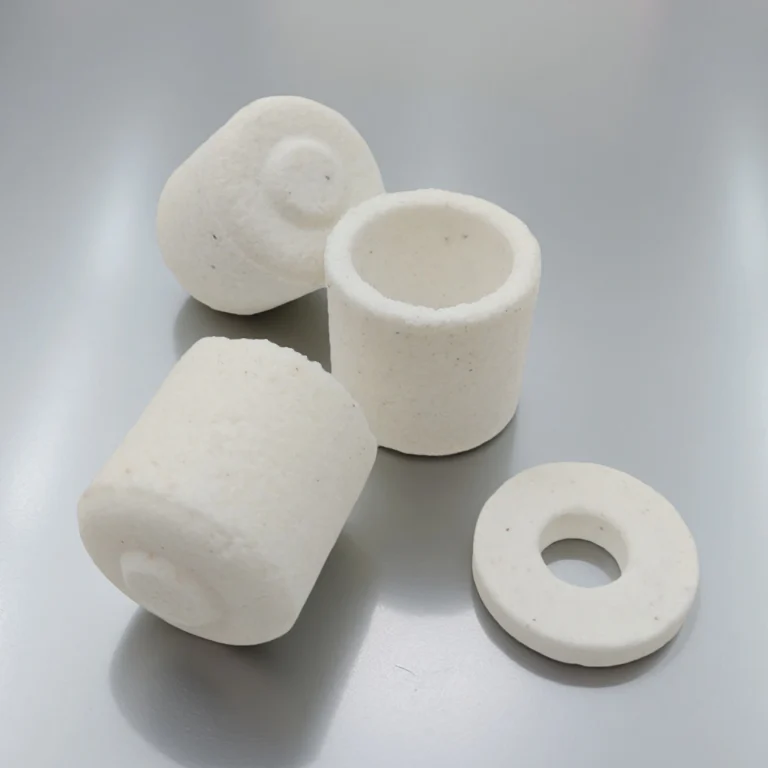
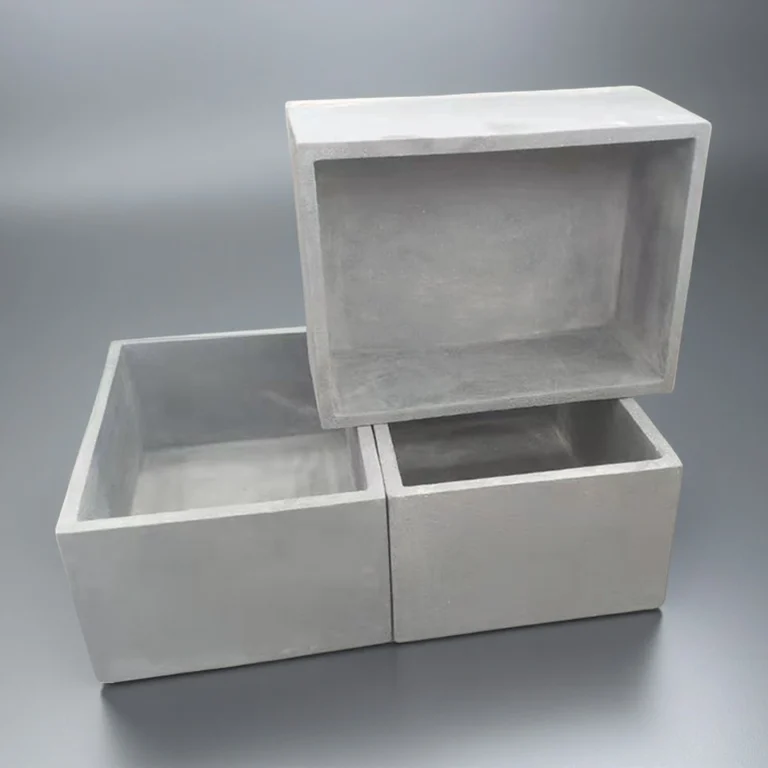
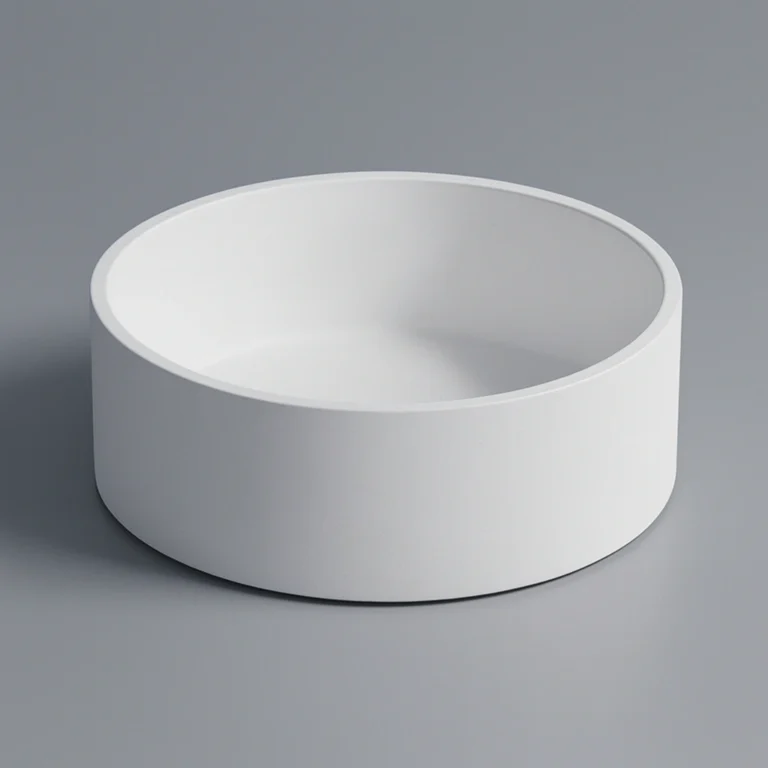
Custom boron nitride crucible is a high-temperature container made by machining hot-pressed boron nitride (BN) blocks to the exact size, shape, and features required by the user. Unlike standard furnace crucibles that come in fixed dimensions, these are produced according to technical drawings or application needs—such as stepped rims for lids, holes for thermocouples, drainage channels, or extra-thick walls in high-stress areas.
Custom Boron Nitride Crucible Technical Advantages
-
Non-Wetting to Molten Metals
BN has very low surface energy (~0.03–0.04 N/m), so molten Al, Mg, Zn and precious metals do not adhere to the crucible wall. This reduces dross buildup, improves alloy purity, and enables cleaner pouring without release coatings.
-
Electrical Insulation at High Temperature
Volume resistivity remains above 10¹¹ Ω·cm even at >1000 °C, allowing the crucible to be placed near induction or resistance heaters without electrical interaction. Suitable for processes requiring both thermal containment and dielectric isolation.
-
CNC Machinability with Tight Tolerances
Hot-pressed BN can be machined to ±0.05–0.20 mm, enabling stepped rims, thin walls (1–2 mm), vent holes, or complex lid interfaces. No secondary sintering is required, ensuring accurate fit in vacuum furnaces or alloy casting fixtures.
-
Low Contamination & Stable in Vacuum
High-purity BN has negligible vapor pressure under high vacuum and does not release alkali impurities. This prevents coating defects, alloy contamination, and makes it suitable for PVD/CVD precursors or reactive metal melts.
-
Thermal Stability & Low Expansion
BN remains structurally stable up to 1800–1900 °C in vacuum or inert gas. Its low thermal expansion coefficient (~1–2 × 10⁻⁶/K) reduces cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Customize HPBN Crucible Properties
|
Property |
Unit |
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride |
Hot Pressed Boron Nitride |
|
Purity |
|
99.99% |
99.50% |
|
Density |
g/cm3 |
2.15-2.19 |
1.96-2 |
|
Hardness |
HV0.5 |
651 |
62 |
|
Volume resistivity |
Ohm*cm |
2*1014 |
1.2*1014 |
|
Dielectric strength |
kV/mm |
55 |
76 |
|
Maximum working temperature |
℃ |
1000 (air), 2300 (vacuum) |
900 (air), 1850 (vacuum) |
|
Bending strength |
MPa |
173 (A direction) |
310 |
|
Thermal conductivity |
W/m*K |
60 (A direction) |
55 |
|
Tensile strength |
MPa |
112 (A direction) |
110 |
|
Thermal expansion coefficient |
/℃ |
6*10-7 |
1.8*10-6 |
|
Compressive strength |
MPa |
154 (A direction) |
120 |
Customize BN Crucible Specifications
Type 1: Boron Nitride Cylindrical Crucible

Type 2: Boron Nitride Rectangular Crucible

Type 3: Boron Nitride Arc-Shape Crucible

|
Boron Nitride Arc-Shape Crucible |
|
Item No. |
Outer diameter of the upper port(mm) |
Height(mm) |
|
AT-BN-GG3001 |
30 |
17 |
|
AT-BN-GG3002 |
32 |
17 |
|
AT-BN-GG3003 |
35 |
17 |
|
AT-BN-GG3004 |
37 |
15 |
|
AT-BN-GG3005 |
40 |
20 |
|
AT-BN-GG3006 |
42 |
22 |
|
AT-BN-GG3007 |
50 |
25 |
|
AT-BN-GG3008 |
55 |
25 |
|
AT-BN-GG3009 |
60 |
30 |
Type 4: Boron Nitride Conical Crucible

|
Boron Nitride Conical Crucible |
|
Item No. |
Capacities(ml) |
|
AT-BN-GG5001 |
0.25 |
|
AT-BN-GG5002 |
0.5 |
|
AT-BN-GG5003 |
1 |
|
AT-BN-GG5004 |
2 |
|
AT-BN-GG5005 |
3 |
Custom Boron Nitride Crucible Packaging
- Clean handling: parts dust-blown and bagged; lid and cup packaged as a set.
- Unit protection: each crucible seated in a foam cavity with full rim and base support.
Custom Boron Nitride Crucible Applications
Custom boron nitride crucibles are used where metal wetting, atmospheric contamination, or dimensional shift cannot be tolerated. They function not only as containers but as part of the thermal system—often integrated into vacuum chambers, induction coils, or coating fixtures.
-
Vacuum Furnace & High-Temperature Thermal Processing
Typical Uses: Brazing fixtures, heat treatment, sintering of reactive alloys, thermal evaporation crucibles in vacuum or inert gas.✅Key Advantages
1. Dimensional accuracy for sealed fixtures — stepped rims or flat sealing surfaces ensure reliable contact with graphite or molybdenum hot zones.
2. Low outgassing (<10⁻⁵ Pa) — prevents pressure instability and contamination inside high-vacuum chambers.
3. Thermal stability up to 1800–1900 °C — no grain swelling or softening in prolonged high-temperature cycles.
✅ Problem Solved
A German furnace builder adopted BN crucibles with 0.10 mm lid step tolerance for titanium alloy annealing. Gas leakage dropped by 35%,and furnace restart time shortened by 20% due to reduced chamber contamination and easier cleaning.
-
Molten Aluminum /Magnesium/Precious Metal Handling
Typical Uses: Alloy sampling cups, casting crucibles, melt holding vessels, refining containers.
✅Key Advantages
1. Non-wetting to Al/Mg alloys — contact angle > 120°, reducing slag adhesion and improving pour yield.
2. Prevents iron and silica contamination — unlike steel or silica crucibles, BN does not dissolve into molten metals.
3. Electrical insulation for induction melting — isolates molten metal from induction coils without eddy current loss.
✅ Problem Solved
An Italian die-casting workshop replaced Al₂O₃ crucibles with BN for Mg alloy sampling. Metal residue decreased by 40%,sampling time reduced by 1.5 minutes/pour, and sample surface clarity improved significantly for spectrographic analysis.
-
PVD/CVD Coating, Thin Film Deposition & Semiconductor Adjacent Processes
Typical Uses: Crucibles for evaporation materials, target melting, protective containers for precursor chemicals, coating batch holders.
✅Key Advantages
1. Low vapor pressure & chemical inertness — prevents BN material evaporation into chambers <10⁻⁶ Torr.
2. No alkali/alkaline contamination — avoids Na⁺, K⁺ ion pollution that commonly damages optical coatings or hard films.
3. Complex geometry for fixture integration — ports for thermocouples, angled grooves for vapor flow, lid alignment pins all machinable in BN.
✅ Problem Solved
A Korean PVD tool manufacturer used BN crucibles to load Ti/Al/Cr targets. Chamber particle count dropped by 28%,coating uniformity improved from ±6% to ±3.5%,and chamber cleaning interval extended from 60 hours to 96 hours.
Custom BN Crucible Usage Instructions
This guide helps users correctly install, operate, maintain and extend the service life of custom boron nitride crucibles in vacuum, inert, or molten metal applications.
-
Installation & Pre-Use Preparation
1. Check fit and geometry: Verify ID/OD, mating lid, step height, and sealing surfaces match the furnace fixture or support plate before heating.
2. Pre-bake to remove moisture: Heat slowly to 200–300 °C in air or inert gas for 1–2 hours to remove adsorbed water. This prevents microcracking and outgassing under vacuum.
3. Avoid excessive force: BN is machinable but brittle; do not press-fit or hammer into holders. Use graphite, molybdenum, or BN support rings if required.
4. Lid alignment: Ensure orientation marks match. If a stepped or tongue-and-groove lid is used, check for smooth engagement without binding.
-
Operating Guidelines
1. Heating rate: For wall thickness ≤3 mm, limit ramp rate to ≤5 °C/min; thicker walls can handle 5–10 °C/min. Rapid heating can cause internal stress cracking.
2. Atmosphere control: Use under vacuum or inert gas (Ar/N₂). Continuous exposure to air above 900–1000 °C leads to oxidation of BN and surface whitening.
3. Molten metal contact: Preheat crucible before adding metal to avoid thermal shock. For Al/Mg melts, maintain crucible temperature within ±20 °C of the melt to stabilize non-wetting behavior.
4. Induction or resistance heating: BN is electrically insulating—safe for contact near coils. However, ensure metal does not overflow and form a conductive bridge.
-
Cooling & Post-Processing
1. Controlled cooling: Cool under inert atmosphere or in furnace chamber. Avoid forced air cooling or cold plate contact that creates thermal gradients.
2. Do not quench: Direct immersion into water/oil or rapid gas cooling causes cracking due to low thermal expansion mismatch.
3. Lid removal: Allow crucible to reach <100 °C before attempting to remove the lid; residual thermal expansion may cause binding.
-
Cleaning & Maintenance
1. Residue removal: Use soft brush or compressed air. For metal residues, gently scrape using a plastic or BN tool; avoid steel tools.
2. Chemical cleaning: Use only non-reactive solvents. Avoid acids or alkalis that can attack BN or leave ionic contamination.
3. Surface reconditioning: Slight surface glazing or metal films can be sanded with 600–1000 grit SiC paper; remeasure dimensions if tolerance is critical.
4. Storage: Store in a dry cabinet or sealed PE bag with desiccant. Keep lids paired with corresponding crucibles to avoid mismatch.
-
Common Issues & Solutions
| Issue |
Possible Cause |
Solution |
| micro-cracks after first use |
heated too fast, no pre-bake |
use preheating cycle, reduce ramp rate |
| lid stuck or warped |
thermal expansion mismatch, uneven heating |
increase lid clearance by 0.05–0.1 mm or refine heating profile |
| metal wetting or sticking |
crucible too cold, contaminated surface |
preheat crucible; clean or polish inner surface |
| vacuum level instability |
residual moisture or surface dust |
pre-bake at 200–300 °C; clean surface before chamber entry |
| brittle edge breakage |
direct tooling contact |
use graphite or ceramic-handling tools |














