ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube is designed for continuous operation in environments where high temperature, corrosive gases, and molten metals place heavy demands on measurement components. Its stable thermal behavior and resistance to oxidation allow sensors to maintain reliable performance during long production cycles. These characteristics make the material suitable for metallurgical plants, chemical processing systems, and industrial furnaces that require consistent monitoring under harsh conditions.
Key Performance Features of Silicon Carbide Protection Tube
-
Dense Microstructure Stability
The SSiC matrix maintains structural density above 3.10–3.15 g/cm³, enabling resistance to gas penetration during long production cycles.
This high density supports measurement systems that require stable barrier protection in molten metal environments.
-
Thermal Conductivity Efficiency
Heat transfer is supported by conductivity values of 90–120 W/m·K, reducing thermal lag for temperature sensors.
This helps maintain accurate readings under variable furnace heating conditions.
-
Thermal Expansion Control
The material’s coefficient of 3.6–4.1 × 10⁻⁶/K minimizes dimensional change under rapid heating.
This reduces shock-related failure during high-frequency thermal cycling.
-
Extended Temperature Endurance
The tube operates at 1,600–1,650 °C in air, supporting measurement applications inside continuous casting lines.
In controlled gas atmospheres, stability extends up to 1,900 °C, allowing protection in advanced furnace systems.
-
Corrosion Resistance to Industrial Gases
The covalent Si–C structure resists SO₂, H₂S, and nitride-forming gases common in chemical plants.
This reduces sensor degradation when exposed to fluorides, alkalis, or combustion by-products.
-
Molten Metal Compatibility
The surface remains unwetted by molten aluminum, copper, and zinc, preventing chemical erosion during immersion.
Lifetimes in these environments often reach 5–10× that of oxide ceramics.
-
Flexural Strength Reinforcement
Strength values above 350 MPa allow stable operation when inserted into high-velocity gas streams or mechanical guide ports.
This prevents breakage when the tube is used in long-span or unsupported configurations.
-
Compressive Load Resistance
The material withstands compressive forces greater than 2,200 MPa, supporting weight-bearing furnace designs.
This ensures integrity when the tube functions as a support or protection barrier in heated zones.
-
Thermal Cycling Stability
The microstructure tolerates gradients exceeding 600 °C/min without cracking.
This performance reduces replacement frequency in rapid-heating furnaces and high-throughput casting systems.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Protection Tube
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube is engineered for use in high-temperature, corrosive, and mechanically demanding industrial systems, where stable thermal behavior, predictable structural strength, and long-term chemical resistance are essential for reliable operation.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Type |
SSiC / RBSiC |
| Density |
3.10–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Apparent Porosity |
<0.1% |
| Hardness |
HV > 2200 |
| Flexural Strength |
>350 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
>2200 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity |
90–120 W/m·K |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
3.6–4.1 ×10⁻⁶/K |
| Maximum Service Temperature (Air) |
1600–1650 °C |
| Maximum Service Temperature (Controlled Atmosphere) |
Up to 1900 °C |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
Stable under 600 °C/min gradients |
| Corrosion Resistance |
Stable in SO₂, H₂S, alkali vapor, molten Al/Cu/Zn |
| Oxidation Resistance |
High stability at elevated temperatures |
| Electrical Resistivity |
High, non-conductive ceramic |
| Microstructure |
Fine-grain, high-density SiC matrix |
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Protection Tube
Type 1-SIC Protection Tube One End Closed
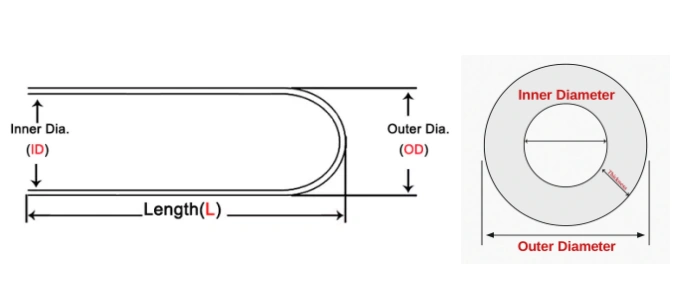
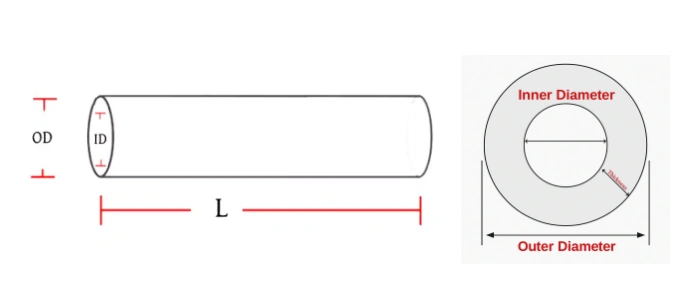
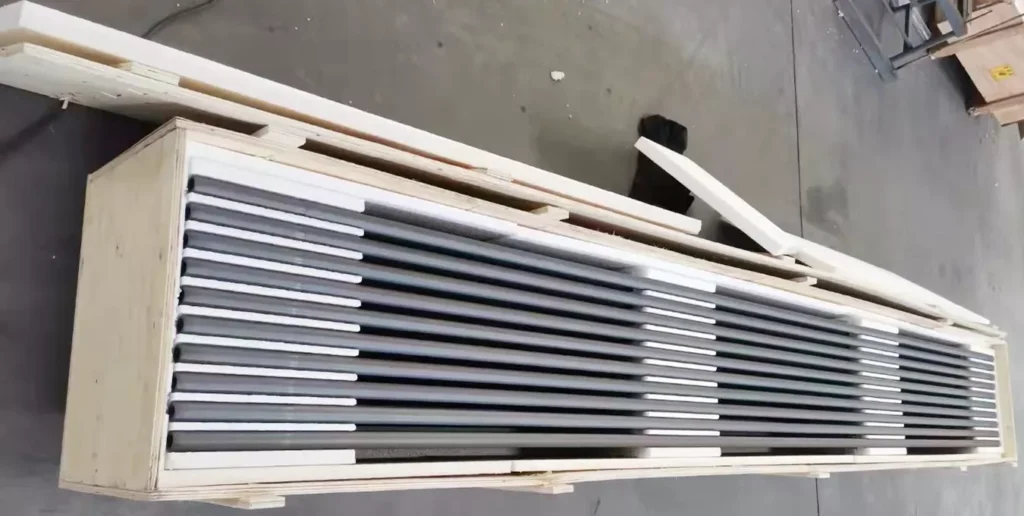
Packaging for Silicon Carbide Protection Tube
Silicon Carbide Protection Tube is packed in reinforced wooden crates with internal foam cushioning to prevent vibration and contact damage during transport. Each tube is separated by protective spacers to maintain alignment and surface integrity. The crate structure supports long-distance international shipping and ensures the tubes arrive in stable, inspection-ready condition.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube for Solving High-Temperature Industrial Measurement Challenges
The ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube supports continuous and reliable temperature monitoring in harsh industrial environments where molten metals, corrosive gases, and fast thermal cycling create conditions that significantly strain conventional protection components. Its material stability, chemical resistance, and thermal performance address application-specific challenges that typically cause measurement drift, early sensor failure, or costly production interruptions.
-
Silicon Carbide Protection Tube in Molten Aluminum Degassing and Refining Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Non-Wetting Performance in Molten Aluminum
The dense SSiC surface of ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube shows negligible wetting when immersed in molten aluminum at 700–750 °C for extended periods. This reduces metal adhesion and chemical attack, extending tube lifetime by 5–10× compared with conventional oxide-based tubes in the same refining line.
2. Stable Heat Transfer for Accurate Degassing Control
With thermal conductivity in the range of 90–120 W/m·K, the tube supports fast heat transfer between molten aluminum and the sensor core. In practice this helps process engineers maintain temperature control within ±2 °C, which is critical for consistent hydrogen removal efficiency and refining quality.
3. Thermal Shock Resistance Under Immersion Cycles
The material tolerates temperature gradients above 600 °C/min when transferring from preheat zones into molten metal. This reduces cracking risk during immersion cycles and allows repeated insertion and extraction without sudden tube failure in continuous degassing operations.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In one aluminum casting facility, conventional protection tubes required replacement every 2–3 weeks due to wetting, erosion, and cracking during degassing, causing several hours of cumulative downtime each month. Temperature drift of more than ±5 °C led to inconsistent refining quality and elevated scrap rates. After switching to ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube with non-wetting SSiC material, immersion life extended to 3–4 months under the same operating schedule. Unplanned tube-related stoppages were cut by more than 60%, and the process maintained tighter temperature control, reducing scrap and rework cost across the refining line.
-
Silicon Carbide Protection Tube in Sulfur-Bearing Gas Heating Lines for Chemical Processing
✅Key Advantages
1. Resistance to SO₂ and H₂S Penetration
The ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube combines a porosity of <0.1% with a chemically stable SiC matrix, limiting gas penetration in ducts carrying SO₂ and H₂S at temperatures above 800 °C. This structure slows internal damage mechanisms that typically shorten the life of porous refractory-based tubes in sulfur-bearing lines.
2. Stable Operation at Elevated Oxidizing Temperatures
The tube maintains mechanical integrity and surface stability up to 1600–1650 °C in oxidizing atmospheres. This supports long-term installation in preheaters and reaction zones where gas temperature routinely operates in the 900–1200 °C range without rapid scale formation or spalling on the tube surface.
3. Controlled Expansion for Long Cycle Service
With a thermal expansion coefficient of 3.6–4.1 ×10⁻⁶/K, dimensional change during load variations and start–stop cycles is minimized. This reduces stress at sealing interfaces and supports multi-month campaigns without the sealing failures often seen in more expansive materials subjected to fluctuating gas temperatures.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A chemical processing line using sulfur-bearing gas previously relied on conventional ceramic protection tubes that showed heavy surface degradation after 1–2 months of service, leading to increasing noise in temperature readings and unscheduled shutdowns. Inspection revealed gas-driven microcracking and internal contamination of the sensor assembly, forcing early replacement to maintain safety margins. After adopting ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube in the same ducts and preheater sections, service life extended beyond 6 months under identical SO₂/H₂S conditions. Recorded drift in process temperature dropped significantly, and shutdown frequency related to protection tube failures decreased by approximately 50%, improving overall line availability.
-
Silicon Carbide Protection Tube for High-Velocity Burner Zones in Industrial Furnaces
✅Key Advantages
1. High Hardness Against Particle Erosion
The ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube provides hardness above HV 2200, which resists abrasion from high-velocity combustion particles and scale carried in burner streams. In furnace zones where gas velocities exceed 30–40 m/s, this hardness level reduces wall loss and dimensional change compared with softer refractory components.
2. Mechanical Strength Under Dynamic Burner Loads
Flexural strength greater than 350 MPa and compressive strength above 2200 MPa allow the tube to withstand flame impact and vibration in burner tiles and measurement ports. This mechanical stability helps maintain alignment and structural integrity over thousands of heating cycles in steel treatment and ceramics firing furnaces.
3. Thermal Cycling Robustness in Rapid-Fire Profiles
The material’s ability to tolerate temperature swings exceeding 600 °C/min enables reliable operation in furnaces that ramp between idle and peak temperatures multiple times per shift. This reduces the risk of microcracking and sudden tube fracture during aggressive firing schedules, supporting long campaign lengths without tube replacement.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In a heat-treatment furnace handling steel components, burner-zone protection tubes made from standard ceramics required replacement every 4–6 weeks due to erosion and cracking from high-velocity flames and thermal cycling. These failures disturbed temperature uniformity and forced unplanned outages, reducing furnace availability by an estimated 8–10% per quarter. After installing ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube in the same burner ports, inspection over a 6-month period showed only minor surface wear and no structural failures under identical firing profiles. Furnace operators reported a reduction of burner-related tube changeouts by more than 70%, with temperature control in the burner region becoming more stable and predictable across each production campaign.
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Protection Tube User Guide for Safe and Efficient Operation
The Silicon Carbide Protection Tube requires proper handling, installation, and maintenance to ensure stable performance in high-temperature and corrosive industrial environments. This user guide provides clear operational recommendations so engineers can maintain measurement accuracy, extend service life, and prevent preventable equipment downtime during continuous production cycles.
-
Pre-Installation Handling Requirements
1. Initial Inspection Protocol
Before installation, each tube should be checked for surface integrity, ensuring no microcracks or impact marks are present. Visual evaluation is recommended under adequate lighting to detect early defects that may worsen during heating cycles. Documentation of incoming inspection helps maintain traceability for long-term operational records.
2. Storage Environment Conditions
Tubes should be stored in a dry indoor area with stable ambient temperature to avoid moisture absorption in surrounding equipment structures. Protection from accidental impact is essential, and crates should remain closed until installation. Maintaining stable storage conditions helps reduce startup thermal stress during first use.
3. Handling and Transport Protection
Manual handling must avoid point impacts, and lifting should be performed using padded supports. Contact with hard metallic surfaces should be minimized to prevent unintended chipping. Controlled movement during internal transport preserves tube geometry prior to installation.
-
Installation Guidelines for High-Temperature Systems
1. Gradual Heating Recommendations
A controlled warm-up sequence should be applied, limiting initial temperature rise to avoid abrupt thermal gradients. Gradual heating stabilizes internal structures and reduces the likelihood of thermal shock. This step is especially important when systems operate above 1000 °C.
2. Correct Positioning in Furnaces and Reactors
The tube must be aligned vertically or horizontally according to system design to maintain even heat distribution. Misalignment may introduce bending forces that reduce service life, especially in long-length configurations. Ensuring proper seating also improves sensor accuracy in continuous monitoring systems.
3. Sensor Assembly Fitment
Instrumentation inserted into the tube should be centered to avoid wall contact during thermal expansion. Secure but non-abrasive mounting prevents internal wear and contamination. Maintaining adequate insertion clearance helps ensure stable long-term measurement performance.
-
Operation in Molten Metal and Corrosive Gas Environments
1. Immersion Depth and Stability
When used in molten aluminum or copper baths, immersion depth should remain consistent to ensure homogeneous temperature exposure. Excessive oscillation in molten metal may increase surface stress and shorten lifetime. Stable immersion minimizes mechanical load and preserves consistent thermal transfer.
2. Gas Atmosphere Considerations
In SO₂, H₂S, or oxidizing atmospheres, stable airflow around the tube prevents local overheating. Corrosive gas buildup should be avoided by maintaining clean flow paths within ducts. Maintaining adequate clearance ensures predictable chemical interaction across the tube’s surface.
3. Thermal Cycling Control
When operating in systems that cycle between high and low temperatures, ramp rates should be moderated to prevent repeated shock. Excessive temperature fluctuation reduces operational life even in SiC materials. Controlled cycling slows cumulative fatigue in long-duration furnace campaigns.
-
Maintenance, Inspection, and Service Life Extension
1. Routine Inspection Intervals
Tubes should be inspected at planned intervals for early signs of wear, such as surface roughness or localized discoloration. Regular inspection supports predictive maintenance and reduces unexpected downtime. Recording these observations helps identify furnace or gas-flow imbalances.
2. Cleaning and Surface Preservation
Mechanical cleaning should only be performed with non-abrasive tools to avoid micro-etching of the SiC surface. Avoid chemical cleansers that react with high-temperature ceramics. Proper cleaning helps preserve surface density, reducing infiltration in corrosive environments.
3. End-of-Service Indicators
Indicators such as reduced thermal response or visible erosion suggest approaching service limits. These signals should trigger planned replacement to maintain process stability. Early recognition of these markers helps prevent processing irregularities and protects downstream equipment.


![]()



