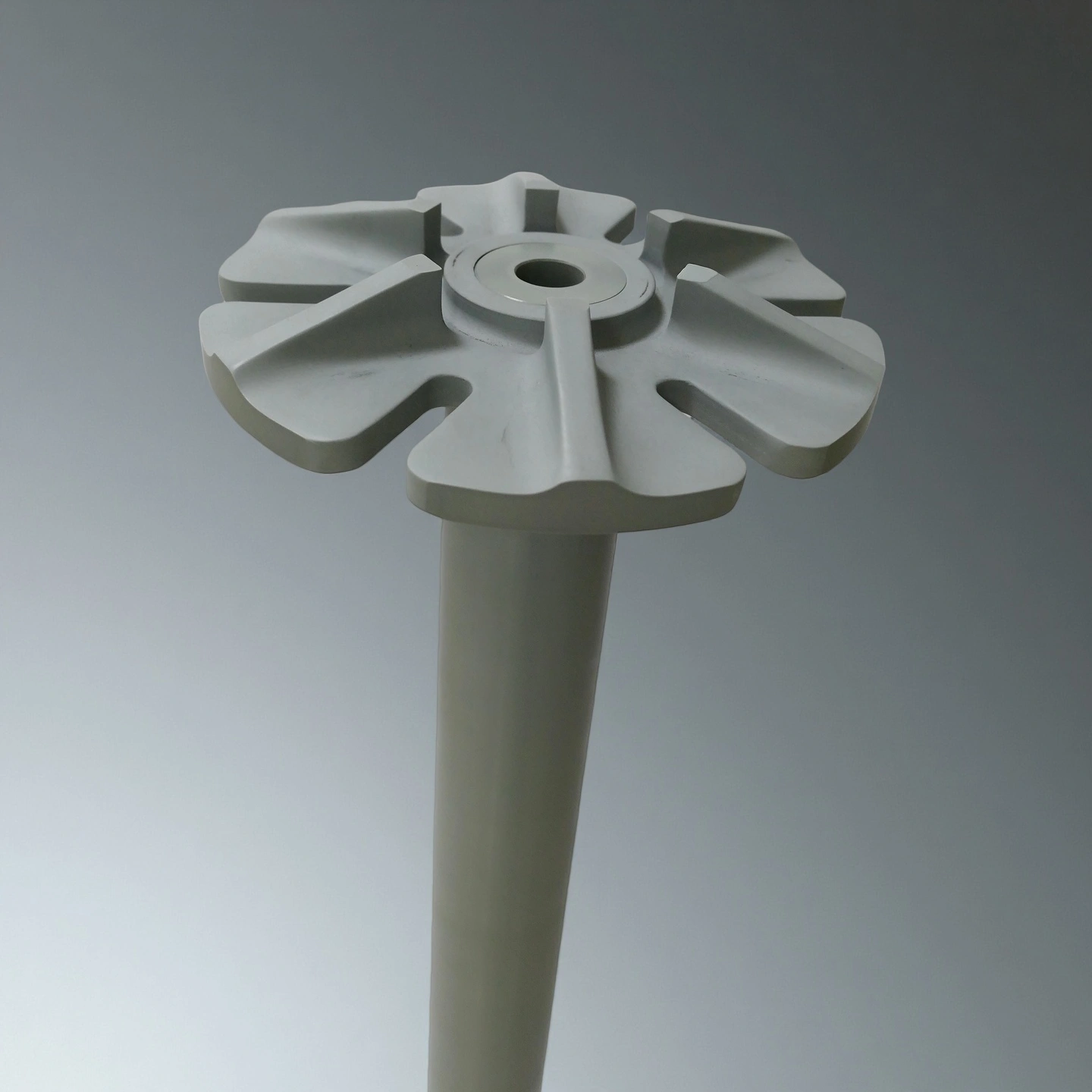
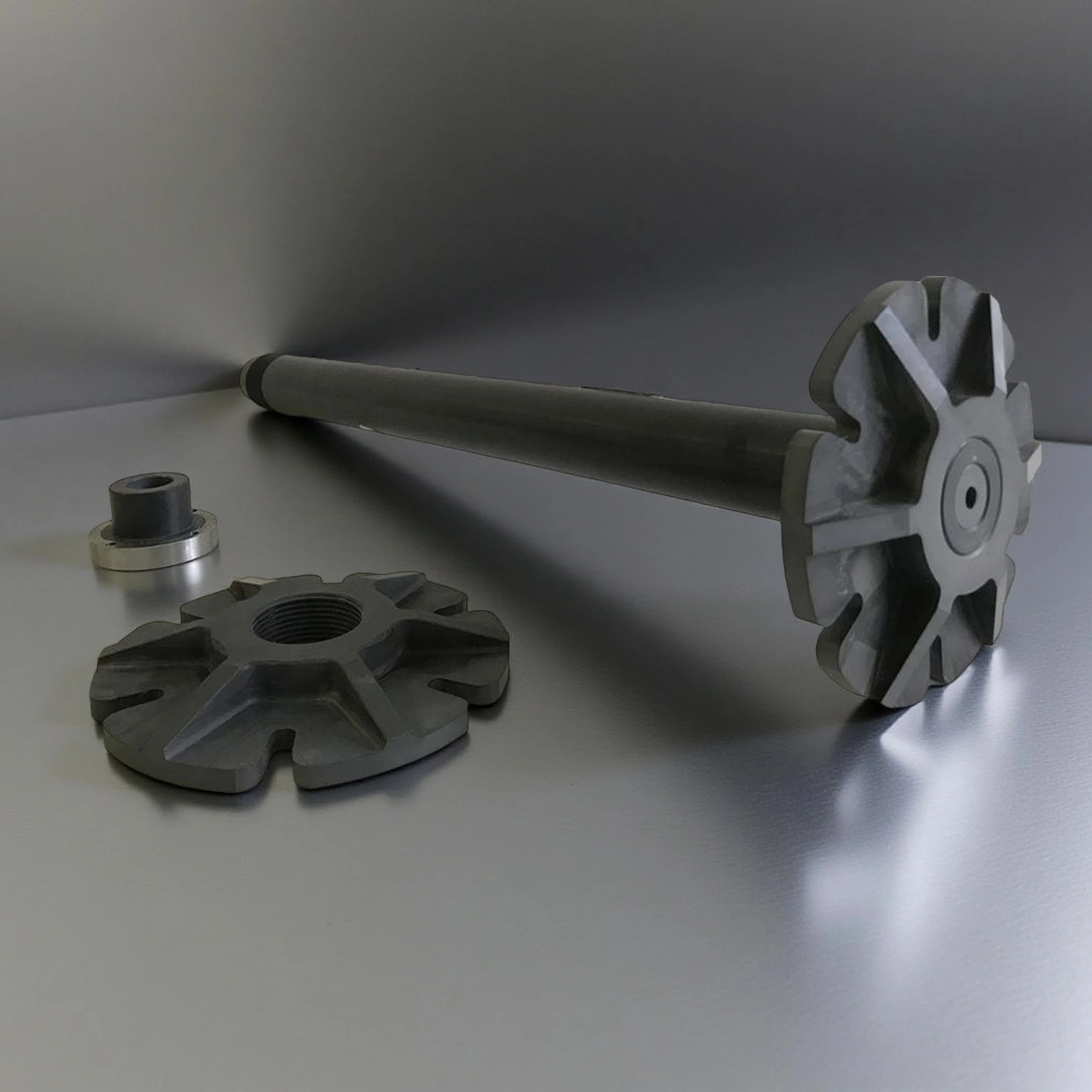
Silicon nitride degassing rotor is a rotating Si₃N₄ ceramic impeller used in molten aluminium to remove dissolved hydrogen and float oxides to the surface. Inert gas (N₂ or Ar) flows through the shaft and is dispersed by the rotor into fine bubbles. These bubbles increase gas–metal contact, allowing hydrogen to diffuse out of the melt and carry inclusions upward for removal.
Silicon Nitride Degassing Rotor Benefits
-
Stable bubble dispersion for consistent hydrogen removal
Optimized rotor vane geometry and Si₃N₄ stiffness ensure uniform gas shearing at 1,200–3,000 rpm. This produces fine bubbles with higher surface-to-volume ratio, enabling hydrogen reduction from ~0.18 mL/100 g Al to ≤0.10 mL/100 g Al in typical melt treatment. -
Low-wetting Si₃N₄ surface minimizes oxide adhesion and melt contamination
Silicon nitride maintains a contact angle >90° with molten aluminium, meaning the melt does not spread or attach to the rotor surface. This reduces dross build-up, keeps gas outlets unobstructed, and prevents particle shedding that may cause inclusions in castings. -
High mechanical integrity under rotation and thermal cycling
With flexural strength of 600–900 MPa and fracture toughness around 6 MPa·m¹ᐟ², the rotor withstands cyclic loading from rotation and immersion in 700–750 °C aluminium without warping or cracking. This prevents vibration issues and extends service life compared to graphite. -
Oxidation resistance during preheating and standby
Unlike graphite that oxidizes at ~500 °C in air, Si₃N₄ forms a thin SiO₂ protective layer that remains stable up to 1000–1200 °C. This allows repeated preheating without material loss, avoiding dimensional changes and surface powdering before immersion into the melt. -
Dimensional stability ensures proper sealing and alignment with the well block or shaft coupling
The low thermal expansion coefficient (~3.0×10⁻⁶ /K) keeps tolerances steady during heating and immersion. This helps maintain shaft alignment, seal clearances, and gas flow channel accuracy, improving rotor balancing and reducing wear on mechanical interfaces.
Silicon Nitride Ceramic Degassing Rotor
| Si3N4 Type | Gas pressure sintering Si3N4 | Hot pressing sintering Si3N4 | High thermal conductivity Si3N4 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.25 |
| Flexture strength (MPa) | 700 | 900 | 600~800 |
| Young Modulus (GPa) | 300 | 300 | 300~320 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 2500 | 3000 | 2500 |
| Hardness (GPa) | 15 | 16 | 15 |
| Fracture toughness (MPa*m1/2) | 5~7 | 6~8 | 6~7 |
| Maximum working temperature (℃) | 1100 | 1300 | 1100 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m*K) | 20 | 25 | 80~100 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (/℃) | 3*10-6 | 3.1*10-6 | 3*10-6 |
| Thermal shock resistance (ΔT ℃) | 550 | 800 | / |
Si3N4 Degassing Rotor Specifications
Type 1: Silicon Nitride Degassing Shaft
| Silicon Nitride Degassing Shaft | ||||
| Item No. | Outer Diameter (mm) | Inner Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) |
 |
| AT-DHG-G3001 | 50 | 30 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3002 | 68.5 | 38 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3003 | 75 | 55 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3004 | 85 | 64.5 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3005 | 105 | 84 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3006 | 135 | 110 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3007 | 150 | 136 | 400-1500 | |
| AT-DHG-G3008 | 200 | 174 | 400-1500 | |
Type 2: Silicon Nitride Degassing Rotor Disc
| Silicon Nitride Degassing Rotor Disc | |||
| Item No. | Outer Diameter (mm) | Inner Diameter (mm) |
 |
| AT-DHG-G3009 | 180 | 35 | |
| AT-DHG-G3010 | 200 | 40 | |
| AT-DHG-G3011 | 210 | 40 | |
| AT-DHG-G3012 | 220 | 40 | |
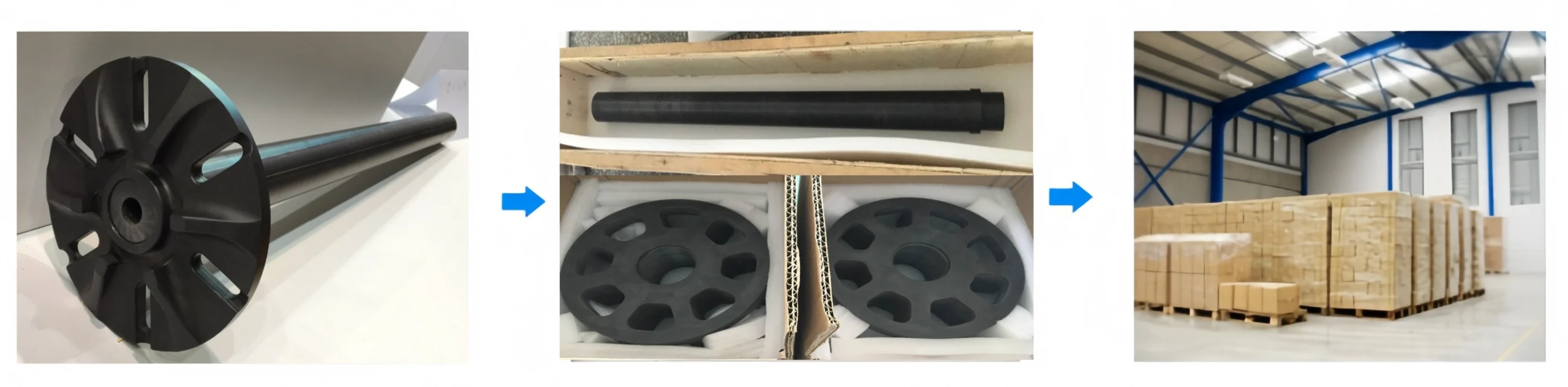
Si3N4 Degassing Rotor Packaging
- Each rotor is individually packed in foam-padded wooden boxes to prevent damage during transit.