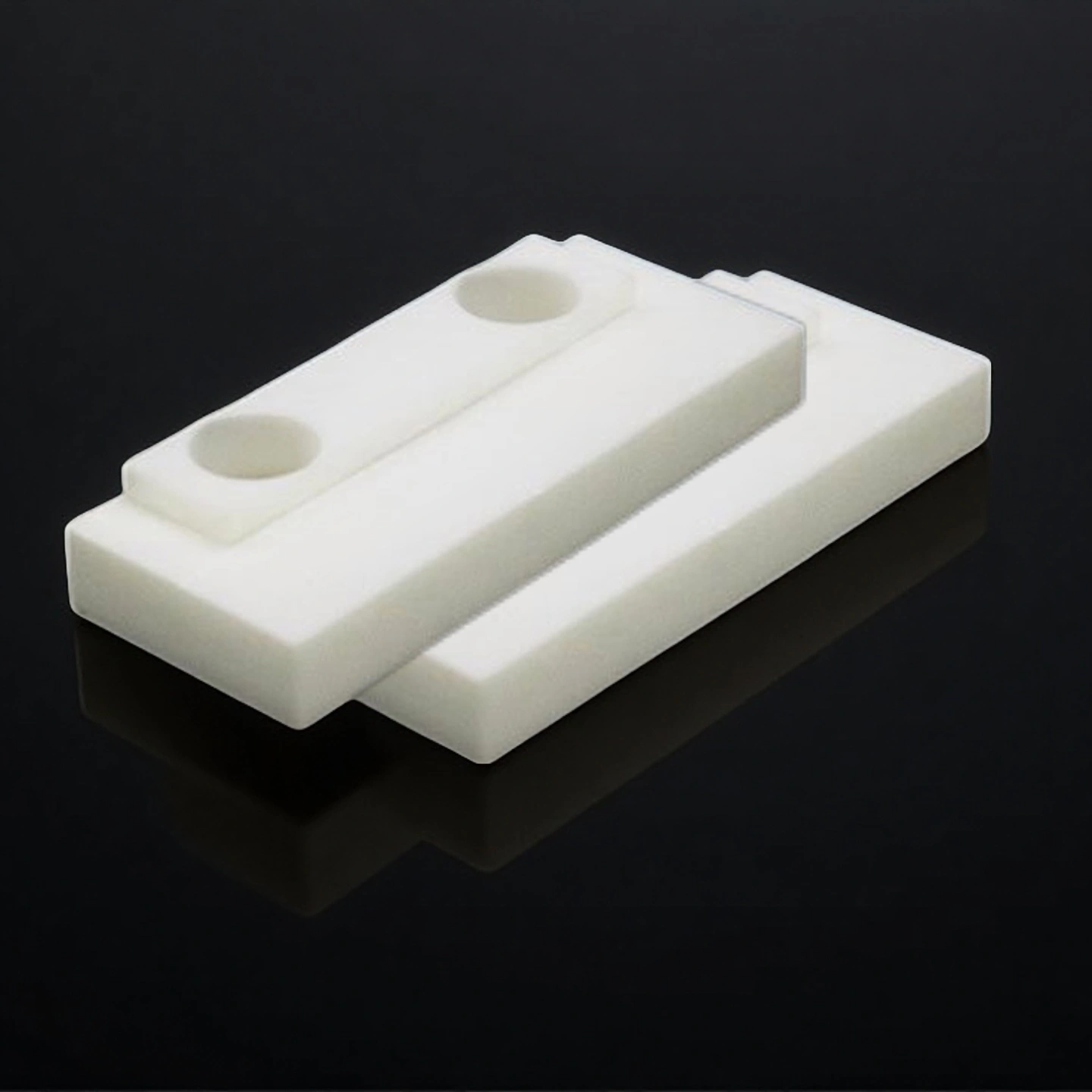
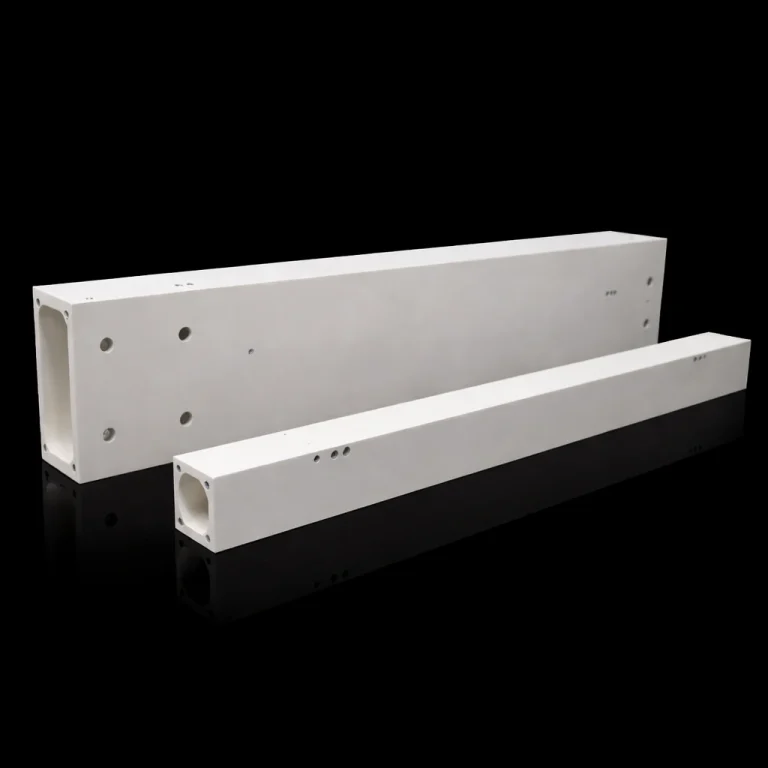
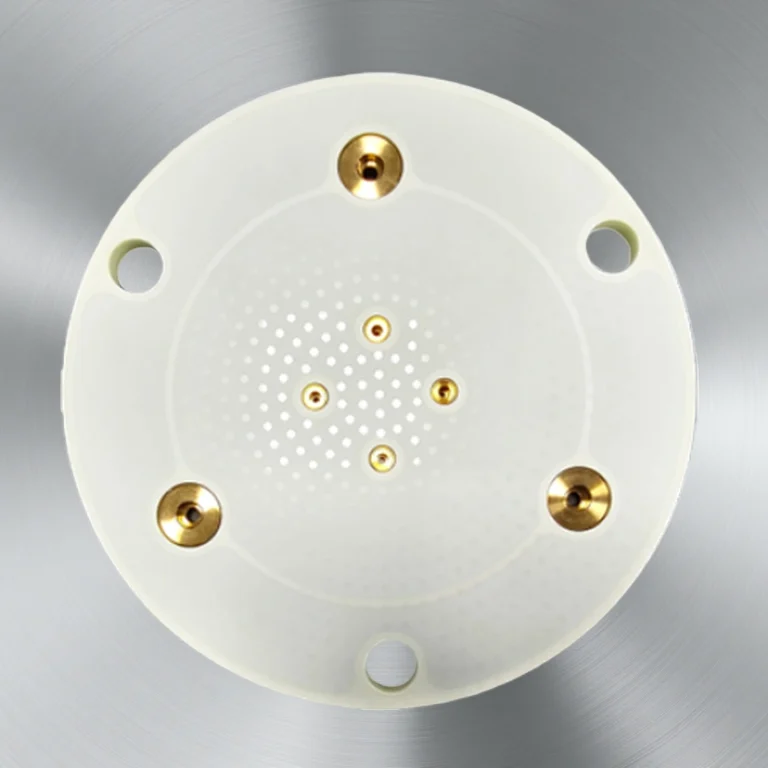
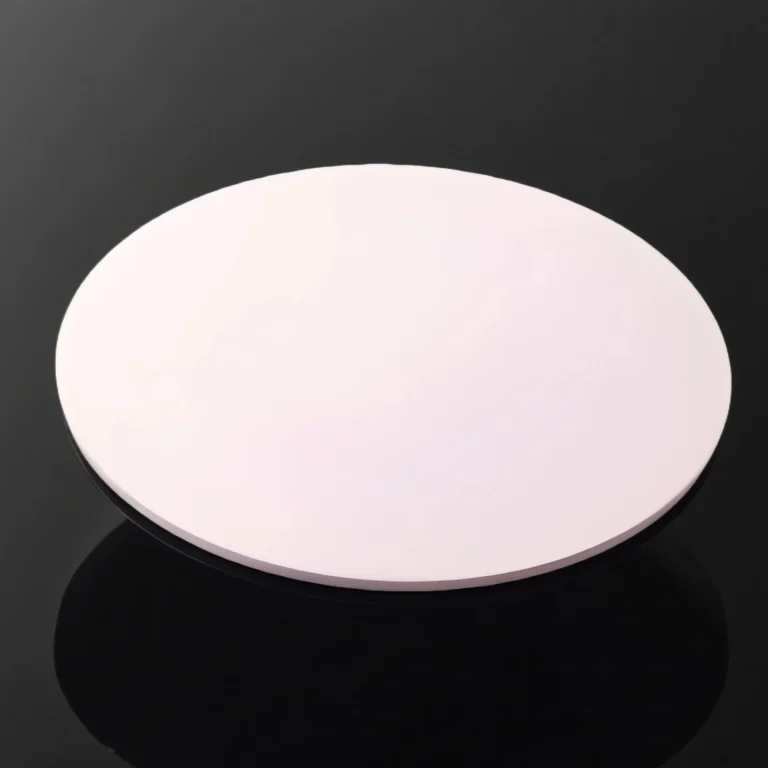
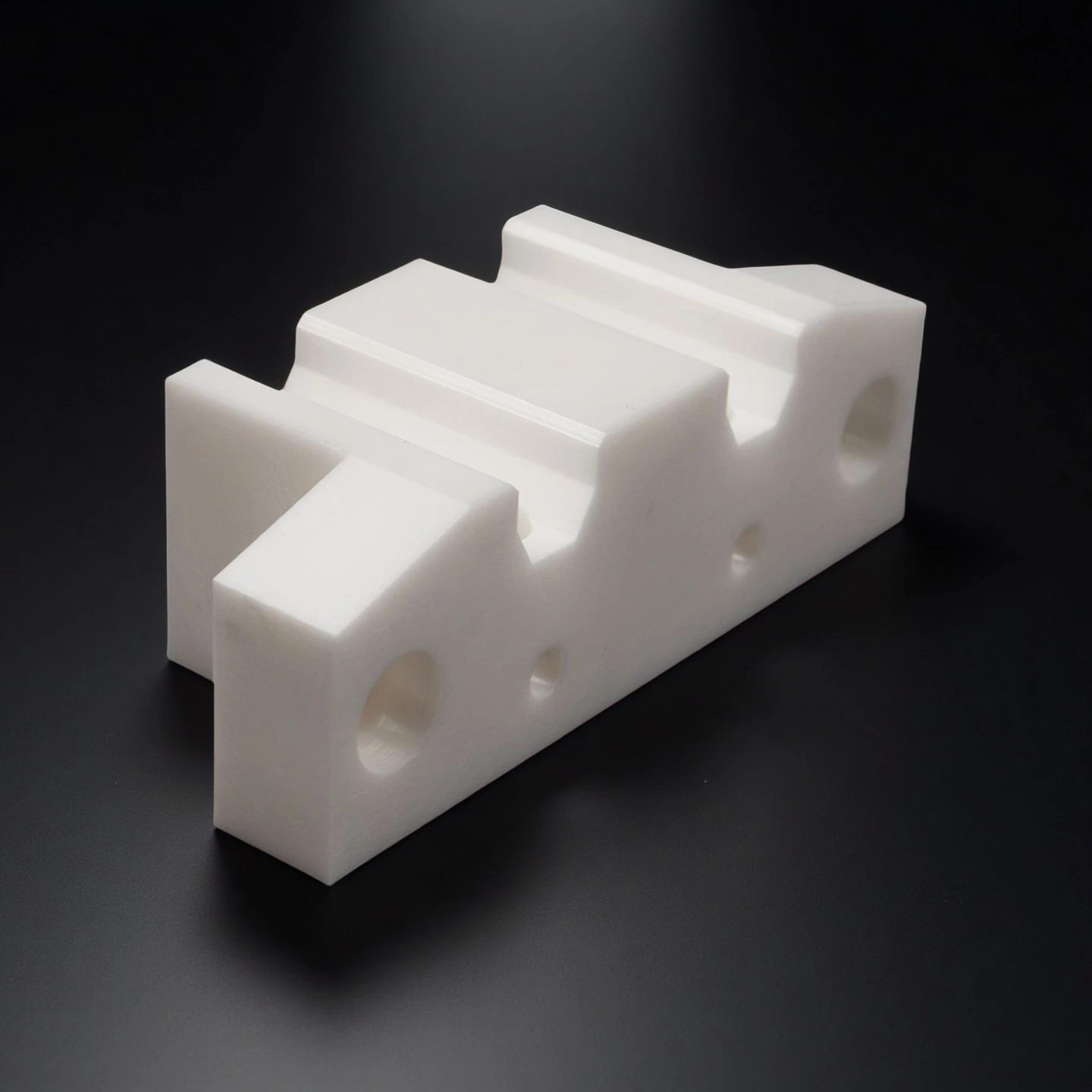
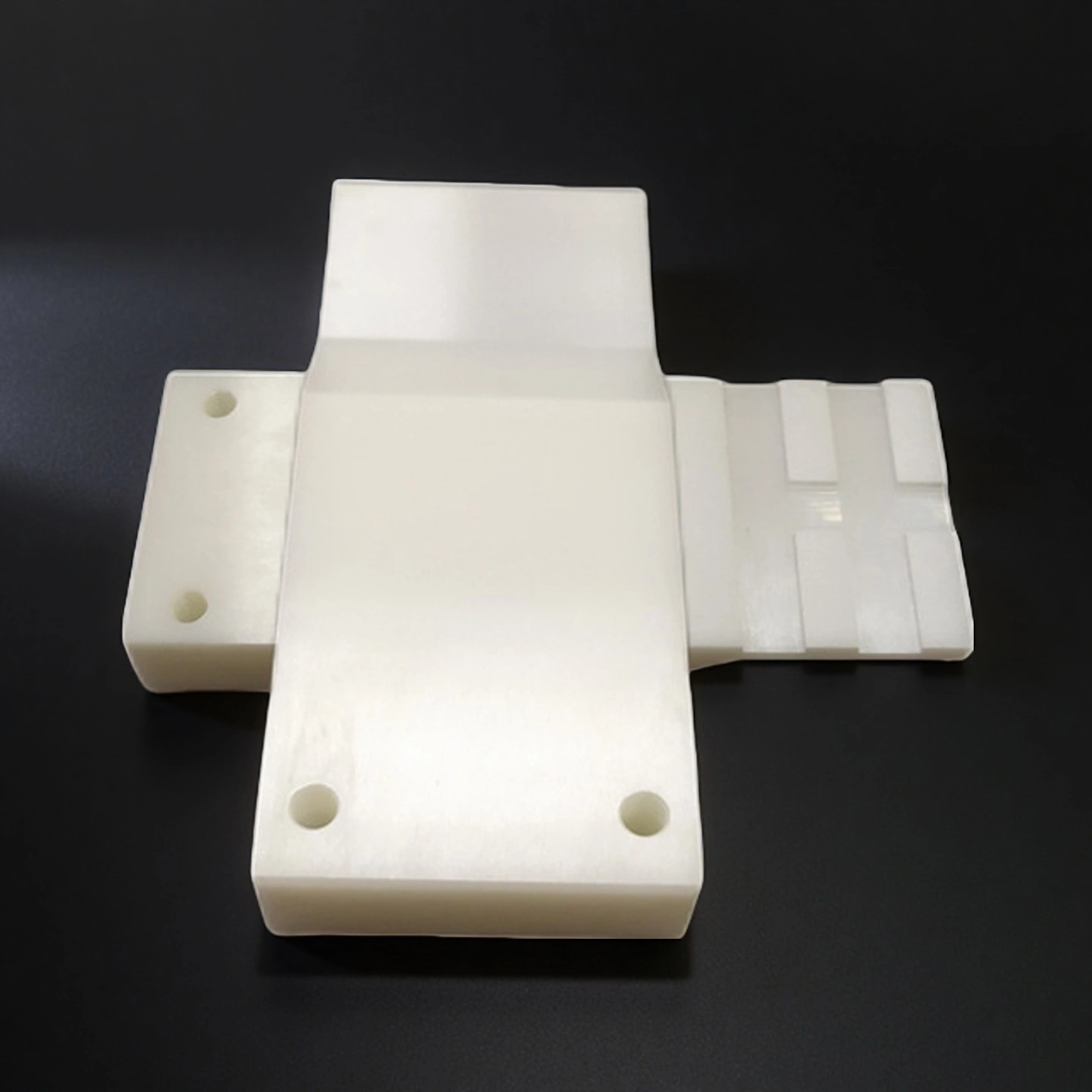
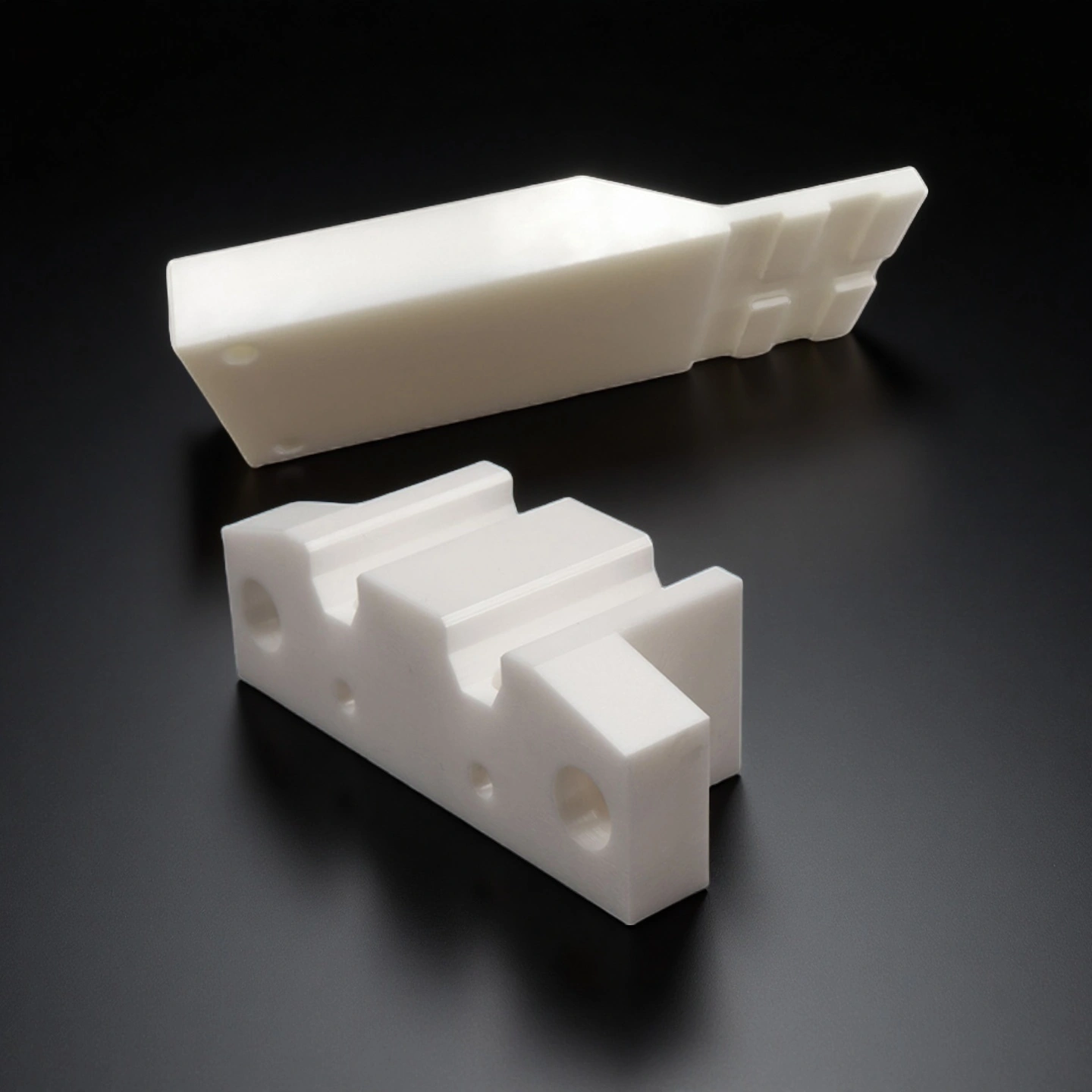
ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Block is a high-strength ceramic part used for precise alignment in industrial molds and fixtures. It withstands mechanical stress, high temperatures, and corrosive environments. Made from yttria-stabilized zirconia, it ensures stable positioning over extended use. Zirconia Positioning Block supports reliable performance in tooling, automation, and optical applications.
Mechanical and Thermal Advantages of Zirconia Positioning Block
- Vickers hardness exceeds 12.5 GPa, enabling prolonged service under high-friction contact.
- Material loss rate remains below 0.02 mm per 1000 cycles, based on internal wear testing.
- Flexural strength surpasses 1200 MPa, resisting deformation during clamp or load-bearing operation.
- Stable structure up to 1000 °C under ambient oxidation, without mechanical property loss.
- Acid corrosion rate below 0.1 mg/cm²/day in H₂SO₄ exposure (per ISO 9290).
- No dimensional degradation after 200 thermal cycles between −20 °C and 800 °C.
- Elastic modulus reaches 210 GPa, reducing deflection under mechanical stress.
- Poisson’s ratio maintained at 0.3, limiting transverse strain in compression.
- Observed displacement error < 5 µm in simulated mold closure after 10,000 cycles.
Technical Properties of Zirconia Positioning Block
Zirconia Positioning Block exhibits a rare combination of mechanical strength, thermal endurance, fracture resistance, and chemical inertness, making it a reliable choice for high-load, high-temperature, and corrosion-prone applications in industrial tooling and alignment systems.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Type |
Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (3Y-TZP) |
| Density |
> 6.0 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength |
> 1200 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
> 2000 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness |
≥ 10 MPa·m½ |
| Elastic Modulus |
200–210 GPa |
| Hardness |
> 12.5 GPa (Vickers HV1) |
| Thermal Expansion (25–800 °C) |
~10.3 × 10⁻⁶ /K |
| Maximum Service Temperature |
1000 °C (in air) |
| Electrical Resistivity |
> 10¹² Ω·cm |
| Surface Finish (Polished) |
Ra ≤ 0.8 µm |
Specifications of Zirconia Positioning Block
|
Zirconia Positioning Block |
|
Model |
Size |
|
AT-YHG-DW1001 |
Customized |
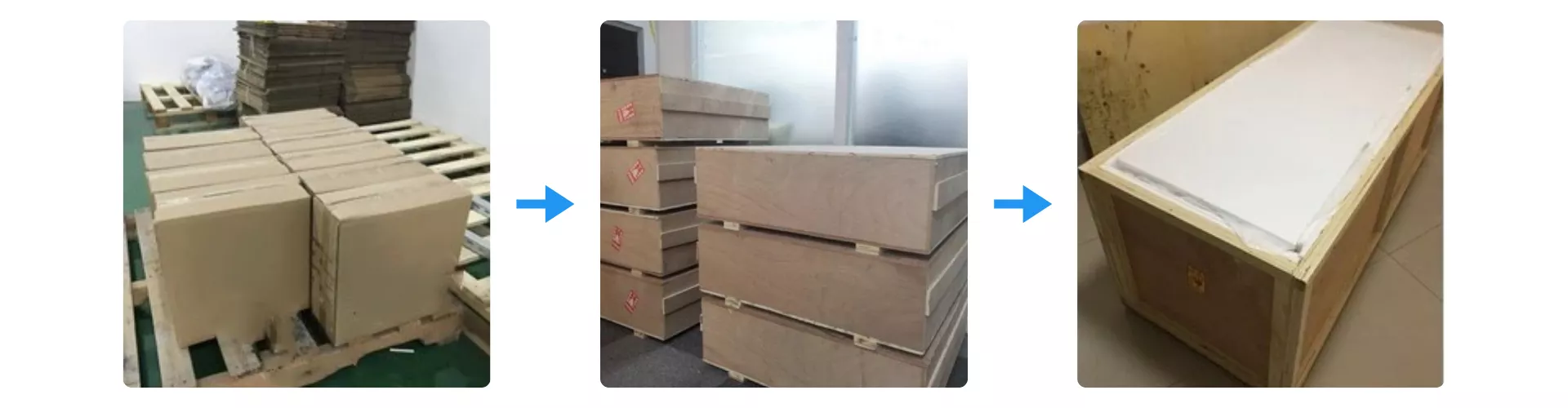
Packaging of Zirconia Positioning Block
Zirconia Positioning Block is packed using multilayer protection including foam padding, inner cartons, and reinforced plywood crates. Each crate is sealed and secured on fumigation-free pallets to prevent damage during international transit. Packaging complies with export safety standards for industrial ceramic components.

Solving Industrial Alignment and Support Challenges with ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Block
ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Block plays a critical role in high-precision industrial systems where dimensional accuracy, mechanical integrity, and thermal resilience are essential. By replacing metal-based positioning components, it helps address failure modes caused by wear, corrosion, and thermal distortion across demanding production environments.
-
Zirconia Positioning Block in Progressive Die Mold Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Deformation-Free Performance
Zirconia Positioning Block maintains shape integrity under loads exceeding 1,200 MPa without yielding.
Unlike metals, it shows no creep or indentation after 100,000 stamping cycles at 60 kN press force.
2. Stable Contact Interface at Elevated Temperature
With thermal expansion ~10.3×10⁻⁶/K, the block resists mismatch during prolonged high-speed runs.
Even under continuous die heating to 180 °C, alignment shift remains under 0.01 mm.
3. Wear-Resistant Contact Longevity
Its hardness >12.5 GPa reduces surface erosion from repeated tool contact.
In automotive stamping trials, wear depth was <0.015 mm after 150,000 cycles.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A Tier-1 automotive supplier faced die misalignment after 60,000 cycles due to soft steel locating pins.
ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Block was integrated into their progressive mold system, resulting in <0.01 mm misalignment after 200,000 cycles and reducing press rework stoppage by 93% within the first 3 months of use.
-
Zirconia Positioning Block in Optical Equipment Baseplates
✅Key Advantages
1. Elastic Rigidity for Structural Stability
With elastic modulus up to 210 GPa, deflection under lens loads is minimized.
Long-term platform tilt deviation was <3 arc seconds under 10 kg load for 48 hours.
2. Surface Stability Against Vibration and Humidity
Surface roughness ≤0.8 µm prevents micro-slip and positioning drift.
In thermal chambers (±5 °C swings), movement remained under 0.002 mm.
3. Non-Contaminating Inert Material
Zirconia is chemically inert and oxide-free, ideal for optical-grade assemblies.
After 120 days in UV/IR active enclosures, no particulate shedding or oxidation film was detected.
✅ ️Problem Solved
An optical metrology OEM reported lens alignment shift >0.04 mm after 3 months of operating in a ±3 °C lab.
By switching to ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Blocks, vertical drift dropped to <0.005 mm, eliminating monthly recalibration and extending instrument uptime by 22%.
-
Zirconia Positioning Block in Robotic Plasma Welding Fixtures
✅Key Advantages
1. High-Temperature Geometry Retention
Service temperature rating of 1000 °C supports thermal stability in weld zones.
Post 150 hours at 950 °C, dimensional loss was <0.01 mm across all surfaces.
2. Molten Spatter Resistance
Zirconia forms no adhesion layer with molten metal droplets.
In spatter-rich environments, surface erosion remained under 0.02 mm after 200 h of continuous exposure.
3. Chemical Inertness in Reactive Atmospheres
Corrosion rate in Ar + H₂ + O₂ mixed plasma stayed below 0.05 mg/cm²/day.
Unlike oxidizing stainless fixtures, zirconia showed no pitting or discoloration post 50 cycles.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A Korean robotic welder integrator reported fixture distortion and weld misplacement every 2 weeks due to Inconel blocks oxidizing above 800 °C.
After adopting ADCERAX® Zirconia Positioning Blocks, they achieved 10-week uninterrupted operation, reducing fixture rebuild frequency by 80% and cutting downtime-related labor costs by 35%.
Handling and Application Guidelines for Zirconia Positioning Block
Zirconia Positioning Block is designed for high-performance alignment in demanding equipment setups. To maximize its operational life and maintain alignment accuracy, users should follow these usage guidelines covering installation, handling, storage, and maintenance across various industrial environments.
-
Installation Best Practices
1. Ensure flat and clean contact surfaces during mounting to avoid uneven stress distribution. Debris or misalignment during installation may lead to concentrated pressure points and early fatigue. Always verify fixture flatness using certified precision gauges.
2. Avoid excessive torque or mechanical impact when fastening components near the Zirconia Positioning Block. Ceramic materials are highly rigid but sensitive to sudden force. Use torque-limited tools and apply pressure gradually.
3. Align with precision jigs or fixtures during assembly to minimize stress accumulation at contact interfaces. Improper alignment during equipment setup may reduce long-term positional stability. Visual or laser alignment systems are recommended.
-
Handling Precautions
1. Use non-metallic tools when positioning or removing Zirconia Positioning Block from its housing. Steel implements may chip ceramic edges upon contact. Use polymer-tip tweezers or rubber-faced clamps for contact safety.
2. Minimize vibration and shock exposure during transport within the facility. Dropping from a height of just 10 cm can cause microcracks in dense ceramics. Always move blocks with padded trays or foam inserts.
3. Wear clean gloves when handling to avoid introducing oils or particles to the block surface. Contamination may affect downstream precision assembly or cause thermal stain spots under load.
-
Storage and Environmental Control
1. Store in dry, temperature-stable conditions, ideally between 15 °C and 25 °C. High humidity or condensation can initiate surface degradation over time. Avoid placing crates near HVAC outlets or windows.
2. Keep Zirconia Positioning Block isolated from metal tooling or abrasive materials during storage. Contact with rough surfaces may compromise polish quality. Use dedicated foam compartments or anti-static pouches.
3. Label all containers with orientation indicators to prevent stacking in the wrong direction. Inversion of precision-ground surfaces can lead to warping or edge damage if pressure is applied unevenly.
-
Maintenance and Inspection Recommendations
1. Inspect surface finish and edges regularly for signs of chipping, abrasion, or wear. A surface roughness increase of >0.2 µm indicates premature degradation. Replace if dimensional consistency is compromised.
2. Perform contact fit verification every 6–12 months depending on operational frequency. Use dial indicators or laser systems to detect cumulative alignment shifts beyond ±0.01 mm.
3. Clean with non-abrasive solvents and lint-free wipes to remove residues or environmental buildup. Avoid ultrasonic cleaning unless explicitly validated for ceramic substrates in your system.