Engineering Communication Ceramics in Industrial Systems
Industrial ceramics used in communication systems are functional materials selected to control signals, heat flow, and mechanical stability rather than to replace metals structurally.
In engineering communication ceramic components, dielectric stability and dimensional consistency directly affect RF transmission accuracy and optical alignment reliability.
Consequently, communication equipment ceramic parts are applied where long-term electrical insulation and thermal balance must remain predictable across varying environments.
As a result, advanced communication ceramic solutions are now integral to RF modules, optical interfaces, and outdoor communication infrastructure.
maintains heat balance under continuous power loads
withstands humidity corrosion and aging exposure
preserves signal integrity at high frequencies
retains geometry under vibration and assembly stress
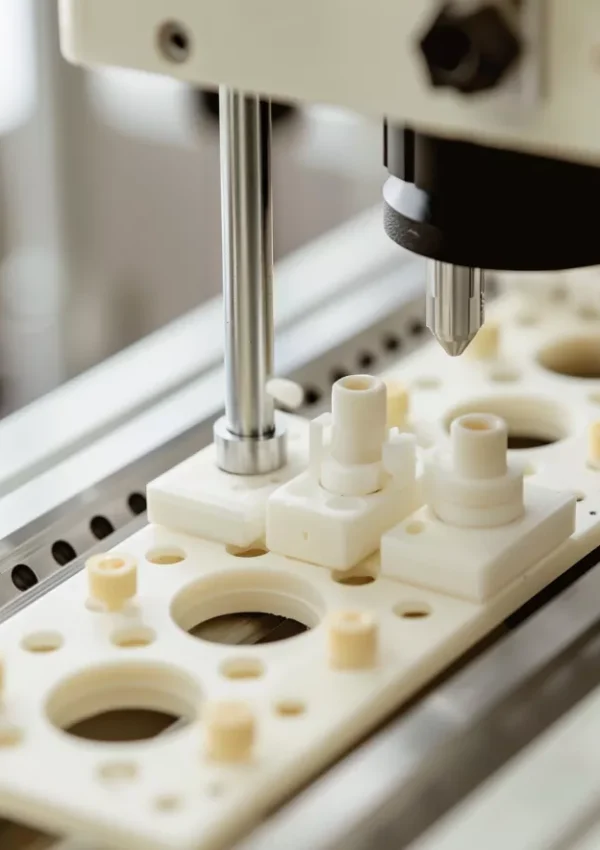

ADCERAX® Ceramic Properties for Communication Systems
To ensure predictable system behavior, engineering communication ceramic materials are evaluated through quantifiable thermal, electrical, chemical, and mechanical performance parameters rather than nominal material labels.
Thermal Properties
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Max Continuous Service Temp (°C) | CTE (×10⁻⁶/K) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (96–99.5%) | 24–30 | 1600 | 7.5–8.0 | 25–1000°C, air |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 2.2–3.0 | 1000 | 10.0–10.5 | 25–800°C, air |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 120–180 | 1400 | 4.0–4.5 | 25–1000°C, inert |
| Boron Nitride (Hot-Pressed) | 60–120 | 900 | 1.0–2.0 | In-plane, 25–500°C |
| Beryllium Oxide | 250–330 | 1000 | 7.0–8.0 | 25–500°C, air |
Electrical Properties
| Material | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Dielectric Loss (tan δ) | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (96–99.5%) | 9.4–9.9 | ≤2×10⁻⁴ | ≥10¹⁴ | 25°C, dry |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 25–30 | ≤1×10⁻³ | ≥10¹² | 25°C, dry |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 9.7–10.2 | ≤5×10⁻⁴ | 10⁵–10⁷ | 25°C |
| Boron Nitride (HPBN) | 3.8–4.2 | ≤1×10⁻⁴ | ≥10¹⁴ | 25°C |
| Beryllium Oxide | 6.5–6.9 | ≤3×10⁻⁴ | ≥10¹⁴ | 25°C |
Chemical Stability
| Material | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Water Absorption (%) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | <0.1% mass loss | <0.2% mass loss | <0.02 | 24 h immersion, 25°C |
| Zirconia | <0.05% mass loss | <0.1% mass loss | <0.01 | 24 h immersion, 25°C |
| Silicon Carbide | <0.01% mass loss | <0.01% mass loss | 0 | 24 h immersion, 25°C |
| Boron Nitride | <0.5% mass loss | <0.5% mass loss | <0.1 | 24 h immersion, 25°C |
| Beryllium Oxide | <0.05% mass loss | <0.1% mass loss | <0.02 | 24 h immersion, 25°C |
Mechanical Properties
| Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (96–99.5%) | 300–380 | 1300–1600 | 300–380 | 3-point bend, RT |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 900–1200 | 1200–1300 | 200–210 | 3-point bend, RT |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 400–550 | 2500–2800 | 410–450 | 3-point bend, RT |
| Boron Nitride (HPBN) | 30–60 | 200–300 | 20–40 | 3-point bend, RT |
| Beryllium Oxide | 250–300 | 1000–1200 | 330–360 | 3-point bend, RT |
Functional Application Domains Across Communication Systems
Across modern communication equipment, engineering ceramics are deployed according to functional roles such as signal control, precision alignment, thermal regulation, and structural insulation rather than by individual part geometry.
RF and Microwave Signal Control Systems
In RF and microwave architectures, engineering ceramics are selected to stabilize electromagnetic behavior while maintaining structural and thermal reliability under continuous signal load.
- Dielectric stability reduces frequency drift and signal attenuation in RF paths.
- Thermal balance supports consistent performance under sustained power input.
- Mechanical rigidity preserves geometry during vibration and outdoor exposure.
Dielectric control for antenna signal shaping
Electrical insulation for RF assembly mounting
High strength insulation in RF structures
High power RF thermal substrate solution
Optical Fiber Precision Alignment Systems
Optical communication systems depend on ceramic precision parts to maintain micron-level alignment stability throughout long service cycles.
- Dimensional consistency ensures repeatable optical axis positioning.
- Surface integrity minimizes optical loss at connection interfaces.
- Wear resistance supports repeated mating and adjustment operations.
Precision fiber alignment geometry control
Concentric guidance for fiber connectors
Stable optical fiber termination interface
Thermal Management in Communication Equipment
As power density increases, communication equipment requires ceramics that combine thermal conductivity with electrical insulation.
- Heat dissipation efficiency protects sensitive electronic components.
- Electrical isolation prevents leakage under high voltage conditions.
- Thermal stability maintains performance during long duty cycles.
High conductivity ceramic heat spreading plate
Thermal conduction with electrical insulation
Compact high power thermal management base
Insulation Structures in Communication System
Mechanical fastening and structural insulation in communication equipment rely on ceramics to separate electrical, thermal, and mechanical functions.
- Electrical insulation enables safe separation of conductive assemblies.
- Mechanical strength supports fastening under load and vibration.
- Environmental resistance ensures long-term outdoor reliability.
Electrical insulation for structural fastening
High strength fastening with insulation
Antenna and Resonator Performance Systems
Antenna and resonator systems employ ceramics to control electromagnetic boundaries while maintaining structural and thermal stability.
- Dielectric control shapes radiation patterns and resonance behavior.
- Material uniformity supports repeatable antenna performance.
- Weather resistance extends service life in exposed installations.
Electrical insulation for structural fastening
Signal reflection and pattern shaping element
Application-Oriented Ceramic Solutions for Communication Systems
Engineering communication ceramic components are selected based on functional roles across RF, optical, and thermal subsystems.
Clear application mapping enables predictable integration and repeatable production outcomes.
ADCERAX® Ceramic Categories for Communication Systems
To support diverse communication system requirements, ADCERAX® organizes engineering communication ceramic components by material behavior and functional role.

Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics provide stable dielectric and insulating performance in communication assemblies.
- Stable dielectric properties for RF systems
- Reliable insulation for structural fastening
- Cost-effective consistency in batch supply

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics enable precision alignment and mechanical stability in optical communication.
- Micron-level dimensional stability for alignment
- High strength under repeated assembly
- Long service life in optical interfaces
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide ceramics support heat dissipation and structural rigidity in communication equipment.
- High thermal conductivity for power modules
- Structural stiffness under thermal cycling
- Reliable performance in harsh environments

Boron Nitride Ceramics
Boron nitride ceramics balance thermal conductivity with electrical insulation in communication systems.
- Efficient heat transfer with electrical isolation
- Stable performance under continuous power loads
- Reduced thermal stress on sensitive components

Beryllia Ceramics
Beryllium oxide ceramics serve high-power RF and microwave communication substrates.
- Exceptional thermal conductivity for RF substrates
- Low dielectric loss at high frequencies
- Suitable for compact high-power designs
Integrated Manufacturing Services for Communication Ceramics

ADCERAX® delivers a vertically integrated manufacturing model for communication ceramics, aligning material science, precision forming, and advanced machining into a single engineering workflow.
Through this processing chain, ADCERAX operates as a technical ceramic manufacturer for battery equipment and communication platforms alike, supporting projects where ceramic geometry and performance are tightly coupled to system behavior.
alumina, zirconia, SiC, BN, BeO purity controlled ≥99.5%
dry pressing, isostatic pressing, extrusion up to 600 mm
sintering capability up to 1700–2200 °C range
CNC grinding tolerance maintained within ±0.01 mm
polishing achieves Ra 0.2–0.4 µm surfaces
CAD-to-process conversion completed within 48 hours
ADCERAX® Core Manufacturing Capabilities Behind Communication Ceramics
Forming and Sintering Control
Dimensional stability and dielectric consistency in engineering communication ceramic components begin with tightly controlled forming and sintering processes.
uniform green density up to ±1.5% variation
controlled firing range 1700–2200 °C atmospheres
linear shrinkage deviation limited within ±0.3%
High-Accuracy
CNC Ceramic Machining
Final geometry and functional interfaces are achieved through precision machining tailored to hard and brittle ceramic materials.
profile tolerances maintained within ±0.01 mm
complex grooves and slots machined in single setup
chamfer radii controlled to 0.05–0.2 mm
Surface Finishing
and Functional Interfaces
Surface condition directly influences dielectric behavior, optical alignment, and thermal contact in communication systems.
surface roughness reduced to Ra 0.2–0.4 µm
planar deviation limited below 5 µm per 100 mm
contact surfaces optimized for stable assembly
Custom Ceramic Solutions Aligned With Communication Systems
ADCERAX® develops custom ceramic components for communication where geometry, material behavior, and system interfaces are tightly coupled.
As a technical partner, the company supports RF, optical, thermal, and structural requirements through drawing-based customization and application-oriented manufacturing.
ADCERAX® invites communication equipment manufacturers to initiate a focused technical discussion and translate system requirements into manufacturable ceramic solutions.
ADCERAX® Technical FAQs for Engineering Communication Ceramic
Dielectric stability determines how consistently signals propagate across RF and microwave frequencies. In engineering communication ceramic parts, stable permittivity prevents frequency drift and impedance mismatch during long-term operation. This stability directly reduces tuning loss and requalification cycles in communication equipment. As a result, system performance remains predictable across temperature and load variations.
Low dielectric loss ceramic for communication minimizes energy dissipation during high-frequency transmission. Engineering communication ceramic materials with controlled loss tangent reduce signal attenuation in RF paths. This characteristic is especially critical in antenna feeds and resonator structures. Lower loss translates into higher system efficiency and reduced power compensation requirements.
Ceramic vs metal for communication equipment is primarily determined by electromagnetic behavior rather than strength alone. Engineering communication ceramic components avoid eddy current formation and signal distortion common in metallic structures. Ceramics also maintain electrical insulation while withstanding thermal stress. This combination enables cleaner signal boundaries and simplified system design.
High thermal conductivity ceramic with insulation dissipates localized heat without introducing electrical leakage. In engineering communication ceramic applications, this balance protects RF amplifiers and power modules from thermal degradation. Stable heat transfer reduces temperature gradients across sensitive components. Consequently, long-term reliability and output stability are improved.
Optical systems depend on micron-level alignment that cannot drift over time. Engineering communication ceramic components such as zirconia alignment parts maintain geometry under thermal cycling and mechanical stress. This stability prevents signal loss caused by misalignment. It also supports repeatable assembly in high-volume production.
Communication infrastructure ceramic parts are exposed to humidity, temperature changes, and environmental stress. Engineering communication ceramic materials resist corrosion, UV exposure, and aging better than polymer alternatives. These properties preserve electrical and mechanical behavior over extended service life. As a result, maintenance intervals are significantly reduced.
Surface finish directly affects dielectric interfaces, optical contact, and thermal coupling. Engineering communication ceramic parts with controlled roughness reduce scattering and contact resistance. This improves signal consistency and heat transfer efficiency. Proper surface preparation also enhances assembly repeatability.
No single ceramic material optimizes all communication functions. Engineering communication ceramic selection depends on whether dielectric control, thermal management, or mechanical strength dominates system requirements. Aligning material behavior with application roles prevents overdesign and cost inefficiency. This approach shortens development cycles and improves system integration.
Ceramic materials for RF thermal management combine heat conduction with electrical insulation. Engineering communication ceramic substrates maintain thermal pathways without compromising signal integrity. Polymers often degrade or deform under sustained RF heat loads. Ceramics therefore provide more stable long-term thermal performance.
Ceramic fasteners electrically isolate structural connections within communication equipment. Engineering communication ceramic bolts prevent current leakage and electromagnetic interference across assemblies. They also retain strength under temperature variation. This improves system safety and layout flexibility.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

