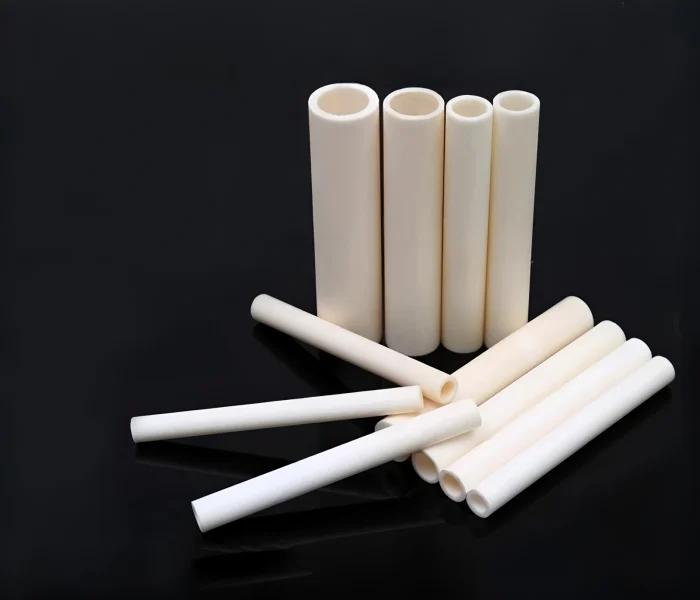

Industrial Ceramic Tubes & Pipes for High-Temperature and Harsh Environments
ADCERAX manufactures industrial, high-temperature ceramic tubes and ceramic pipes for furnaces, heaters, thermocouple assemblies and corrosive or abrasive flow lines, using high-purity alumina, silicon carbide, zirconia and boron nitride. We keep standard sizes for insulating sleeves and furnace tubes in stock, and produce engineered ceramic pipes, protection tubes and lined pipe sections according to your drawings and operating conditions.
Choose ADCERAX as your ceramic tube and pipe partner to stabilize production, protect your equipment and reduce overall running costs.
What Are Ceramic Tubes?
Ceramic tubes are hollow cylindrical components made from engineered ceramic materials such as alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, ZTA and boron nitride. They are used where metals or plastics fail – at high temperature, in aggressive atmospheres, under strong electrical insulation requirements or in highly abrasive flows.

Key Performance Advantages of ADCERAX Ceramic Tubes
ADCERAX designs ceramic pipes for demanding furnace, heater, sensing and process-line environments where ordinary materials fail. The focus is on stable performance over long service life rather than short-term replacement parts.
Reliable at Elevated Temperatures
Engineered alumina, silicon carbide, zirconia and boron nitride bodies retain strength and stiffness at temperatures where metallic tubes creep, deform or scale, keeping heating zones and process chambers dimensionally stable.
Dimensional Accuracy and Shape Stability
Precision grinding and controlled sintering deliver tight OD, ID and straightness tolerances. This ensures a repeatable fit with metal housings, seals and fixtures, reducing assembly time and leakage or misalignment issues.
Clean, Low-Contamination Contact Surfaces
High-purity ceramics with smooth internal and external surfaces minimize contamination of furnace loads, process gases and liquids. This is especially important for heat treatment, laboratory work and clean process applications.
Corrosion and Wear Protection for Process Media
Ceramic pipes resist oxidation, carburization, chemical attack and abrasive particles better than metallic components. They are well suited for aggressive gases, powders and slurries in chemical and energy processes.
Resistance to Thermal Shock and Cycling
Tailored microstructures and controlled firing give the tubes resistance to rapid heating and cooling. This helps prevent cracking in applications such as tube furnaces, burner tiles and thermocouple protection in fluctuating cycles.
High Electrical Insulation in Hot Zones
Oxide and nitride ceramics provide intrinsic dielectric strength, allowing the tubes to act as insulating sleeves, sensor carriers and element supports in high-voltage or high-temperature assemblies without additional insulation layers.
Properties of Ceramic Tube
Ceramic tubes made mainly from high-purity alumina, with options in zirconia, boron nitride and silicon carbide, provide a strong mix of mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, electrical insulation and chemical stability for demanding furnace, heater and process line duties.
Alumina Ceramic Tube
High-purity alumina tube combines strong electrical insulation, mechanical strength and chemical resistance at high temperature, ideal for furnace liners, guides and thermocouple protection.
| Property | Unit | 96% Al₂O₃ | 99% Al₂O₃ | 99.5% Al₂O₃ | 99.6% Al₂O₃ | 99.7% Al₂O₃ | 99.8% Al₂O₃ | 99.9% Al₂O₃ | 99.99% Al₂O₃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina content | % | 96 | 99 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.99 |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.75 | 3.88 | 3.89 | 3.91 | 3.92 | 3.93 | 3.95 | 3.98 |
| Flexural strength | MPa | 330 | 360 | 379 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 320 |
| Hardness | GPa | 11.5 | 13.5 | 14.1 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 20–25 | 30–35 | 35 | 32–37 | 33–38 | 34–39 | 35–40 | 36–42 |
| Thermal shock resistance ΔT | °C | 150 | 200 | – | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 228 |
| Maximum use temperature (no load) | °C | ≤1600 | ≤1700 | ≤1750 | 1755 | 1760 | 1765 | 1770 | 1800 |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 8–10 | 10–12 | 11–13 | 12–14 | 12–15 | 13–16 | 14–17 | 15–18 |
| Volume resistivity (25°C) | Ω·cm | ≥1×10¹³ | ≥1×10¹⁴ | ≥3×10¹⁴ | ≥5×10¹⁴ | ≥1×10¹⁵ | ≥3×10¹⁵ | ≥5×10¹⁵ | ≥1×10¹⁶ |
Zirconia Ceramic Tube
Zirconia tube offers very high toughness and thermal shock resistance, so tubes in stressed positions endure rapid heating and mechanical impact with low risk of cracking.
| Property | Specification |
| Maximum Working Temperature | 1500 °C continuous use |
| Density | 5.65 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 10.3 × 10⁻⁶/K (25–1000 °C) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 2.2 W/m·K at 1000 °C |
| Chemical Stability | 0.08% mass loss after 24 h acid/alkali exposure at 1200 °C |
| Flexural Strength | 900 MPa at room temperature |
| Fracture Toughness | 8 MPa·m½ |
| Hardness (Vickers) | 12 GPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 210 GPa |
Boron Nitride Tube
Boron nitride ceramic tube is non-wetting to most molten metals, with good thermal shock resistance and easy release, reducing sticking and contamination.
| Property | Unit | Pyrolytic Boron Nitride | Hot Pressed Boron Nitride |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | % | 99.99% | 99.50% |
| Density | g/cm³ | 2.15–2.19 | 1.96–2 |
| Hardness | HVO.5 | 651 | 62 |
| Volume resistivity | Ohm·cm | 2×10¹⁴ | 1.2×10¹⁴ |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 55 | 76 |
| Maximum working temperature | °C | 1000 (air), 2300 (vacuum) | 900 (air), 1850 (vacuum) |
| Bending strength | MPa | 173 (A direction) | 310 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 60 (A direction) | 55 |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 112 (A direction) | 110 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | 1/°C | 6×10⁻⁷ | 1.8×10⁻⁶ |
| Compressive strength | MPa | 154 (A direction) | 120 |
Silicon Carbide Tube
Silicon carbide tube for extreme heat and rapid cycling, with excellent thermal shock and corrosion resistance, typically used up to 1,600 °C in burners and radiant heaters.
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material System | RBSiC (80% SiC, 20% free Si) / SSiC (≥99% SiC) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | ≤1380°C (RBSiC) / ≤1600°C (SSiC) |
| Bulk Density | 3.02 g/cm³ (RBSiC) / 3.10 g/cm³ (SSiC) |
| Open Porosity | <0.1% |
| Flexural Strength (20°C) | 250 MPa (RBSiC) / 380 MPa (SSiC) |
| Flexural Strength (1200°C) | 280 MPa (RBSiC) / 400 MPa (SSiC) |
| Compressive Strength | 1000–2200 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 330 GPa (RBSiC) / 420 GPa (SSiC) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 45 W/m·K (RBSiC) / 74 W/m·K (SSiC) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 4.1–4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K |
| Hardness | 2600–2800 kg/mm² |
| Chemical Stability Range | pH 2–12 |
| Oxidation Stability | <1% microstructural oxidation after 50 cycles (1000°C → RT) |
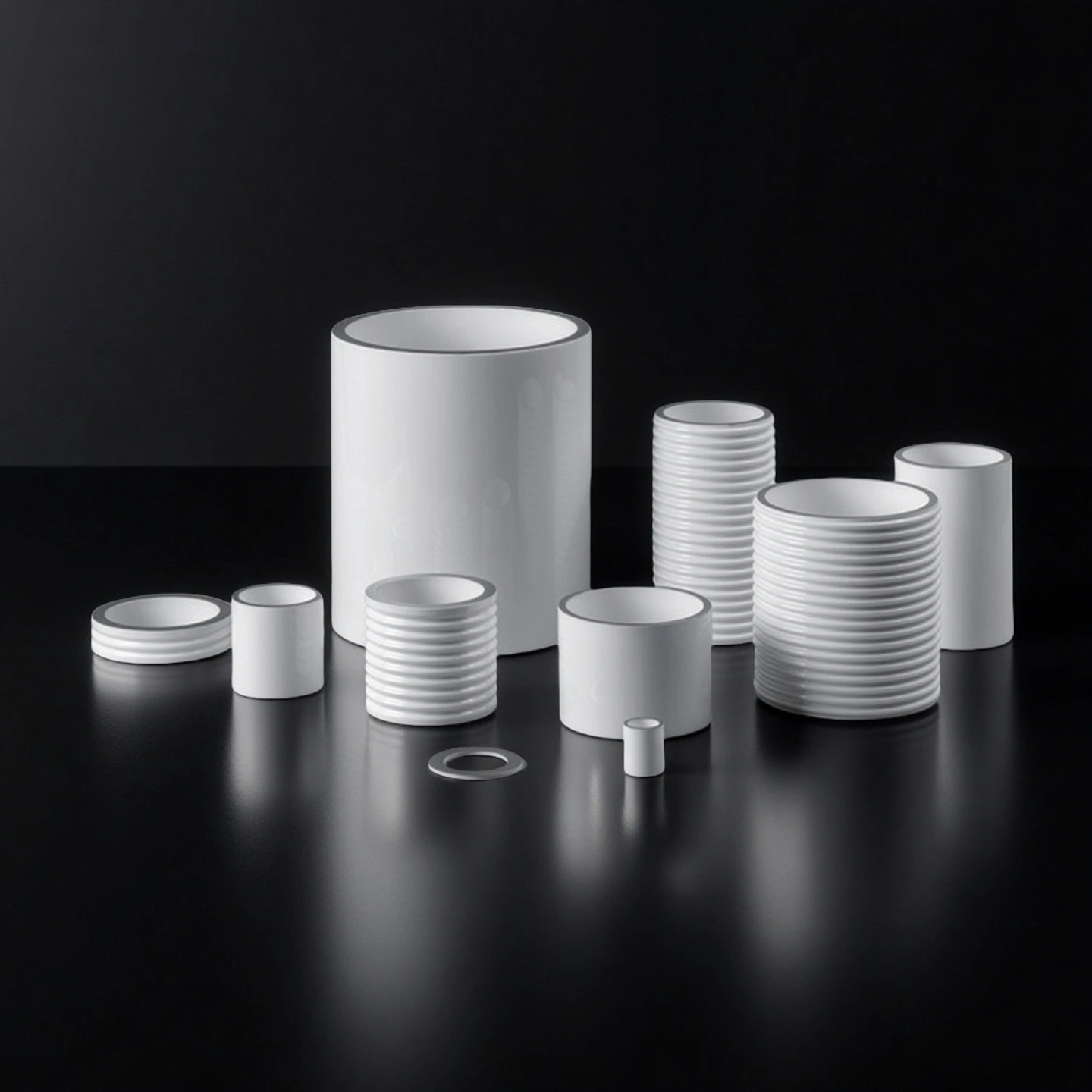
China Ceramic Tube and Pipe Products
Wear-resistant ceramic pipes are selected by material, bore design and application. Here you can compare alumina, zirconia, BN, SiC and other ceramic tubes—single-bore, multi-bore, closed-end, flanged or lined—to match your furnace, sensors, heaters and pipelines.

alumina ceramic tube
Alumina tube for high-temperature insulation, with stable dimensions, dielectric strength and clean surfaces.

zirconia ceramic tube
Tough Zro2 tube for stressed positions, combining high fracture strength, tight tolerances and thermal stability.

ZTA Ceramic Tube
ZTA tube offering alumina hardness with toughness, resisting chipping and abrasion in cyclic loading.
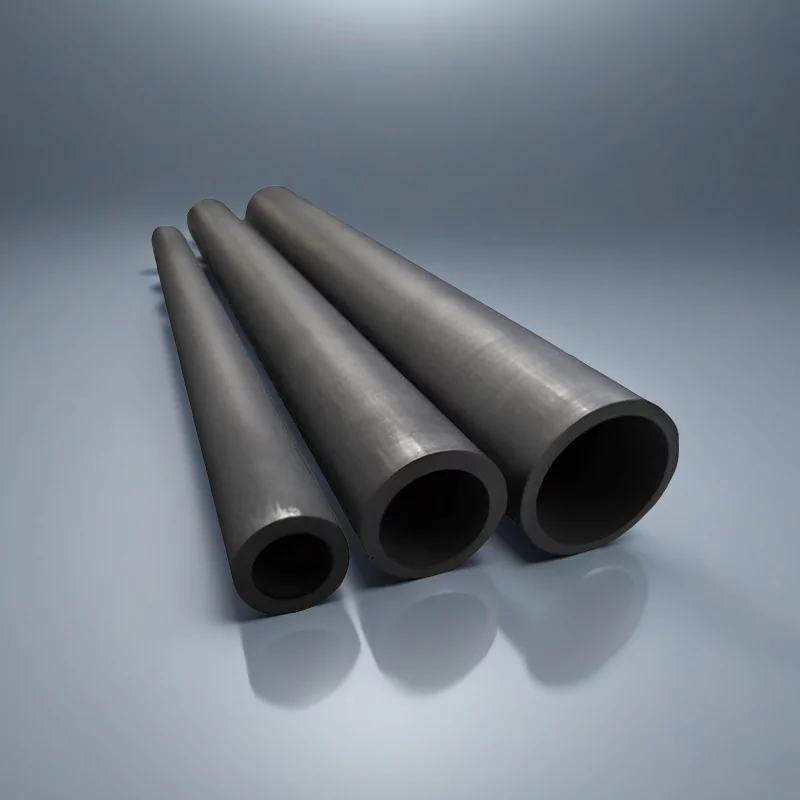

Silicon Carbide Tube
Silicon carbide tube for extreme heat and rapid cycling, with excellent thermal shock and corrosion resistance.
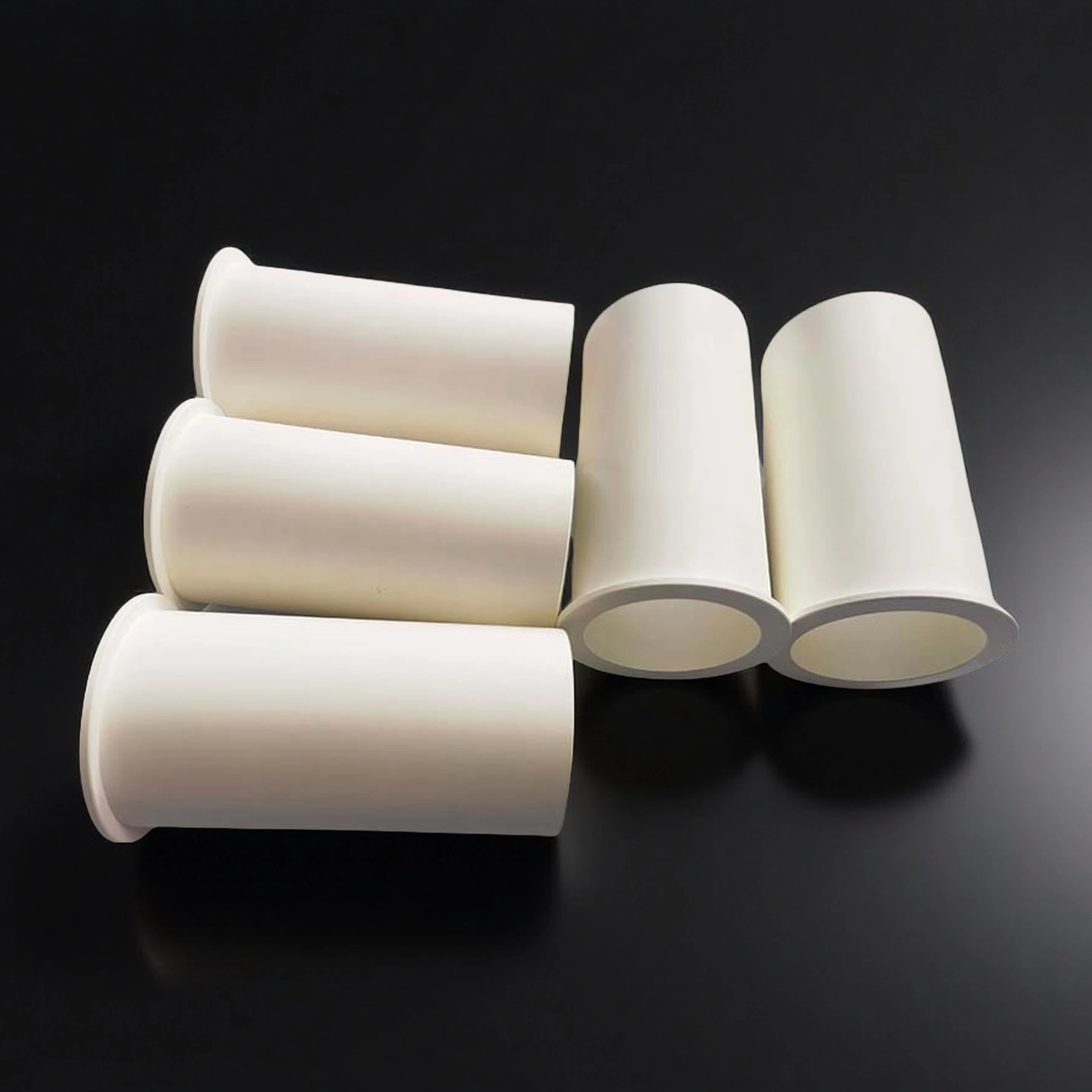

boron nitride tube
Non-wetting BN ceramic tube for molten metals, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and easy release from metal contact.

magnesia tube
Mgo tube with good basic slag resistance and thermal stability, suited to high-temperature alkali or lime-bearing environments.

metalization ceramic tube
Metalization ceramic tube with metallized layers for brazing, enabling vacuum-tight ceramic-to-metal joints.
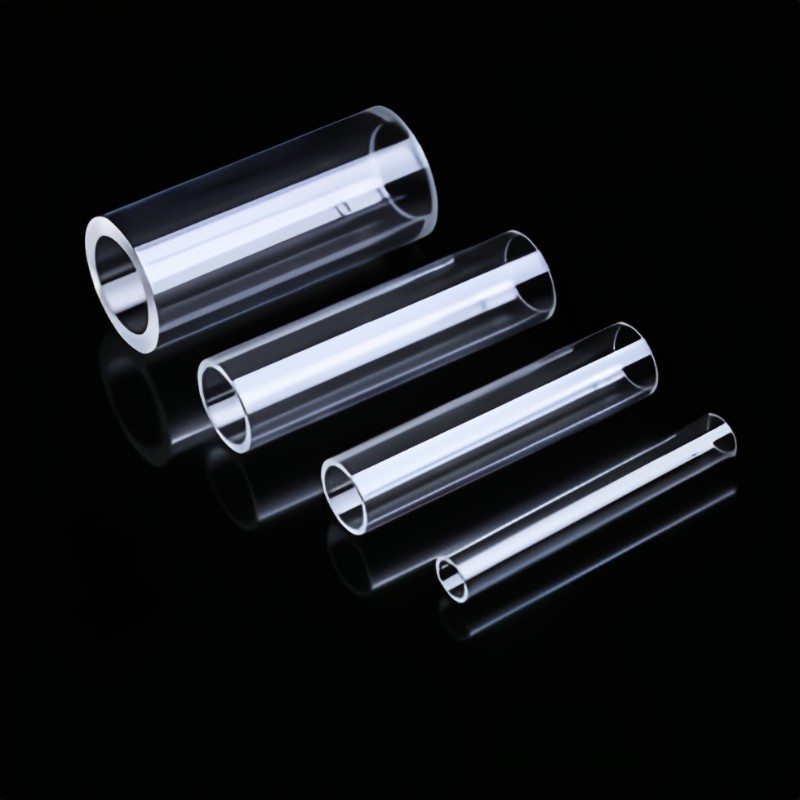

transparent ceramic tube
Transparent ceramic tube providing clarity, heat resistance and insulation for ports, sensor housings and light guides.
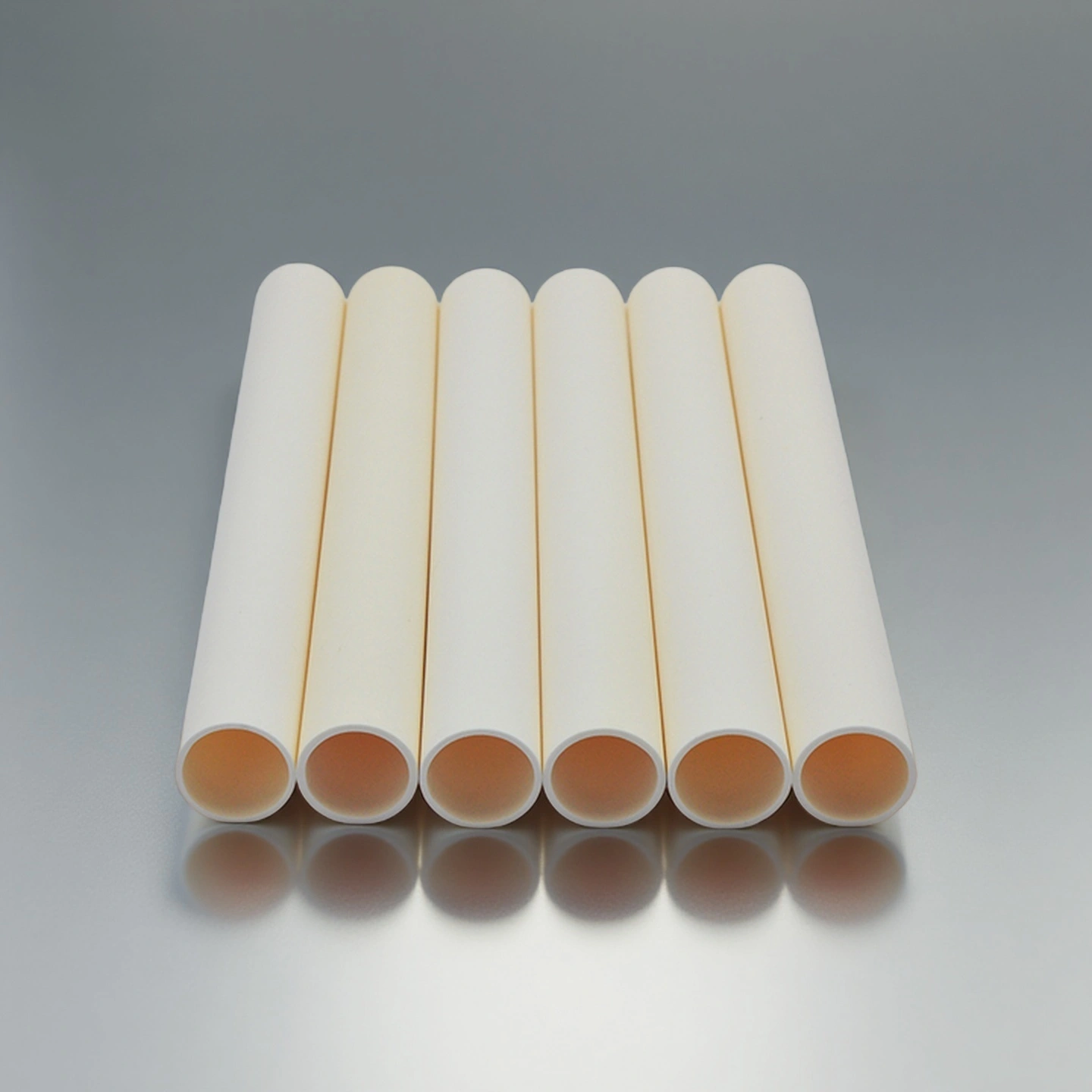

Ceramic Pipe, Open Both Ends
Open-both-ends ceramic pipe for heating gas paths, offering alignment, contamination control and integration into furnace lines.

ceramic tube, one end closed
One-end-closed ceramic tube for sealed hot zones, protecting sensors or media from flame, molten metal and aggressive gases.
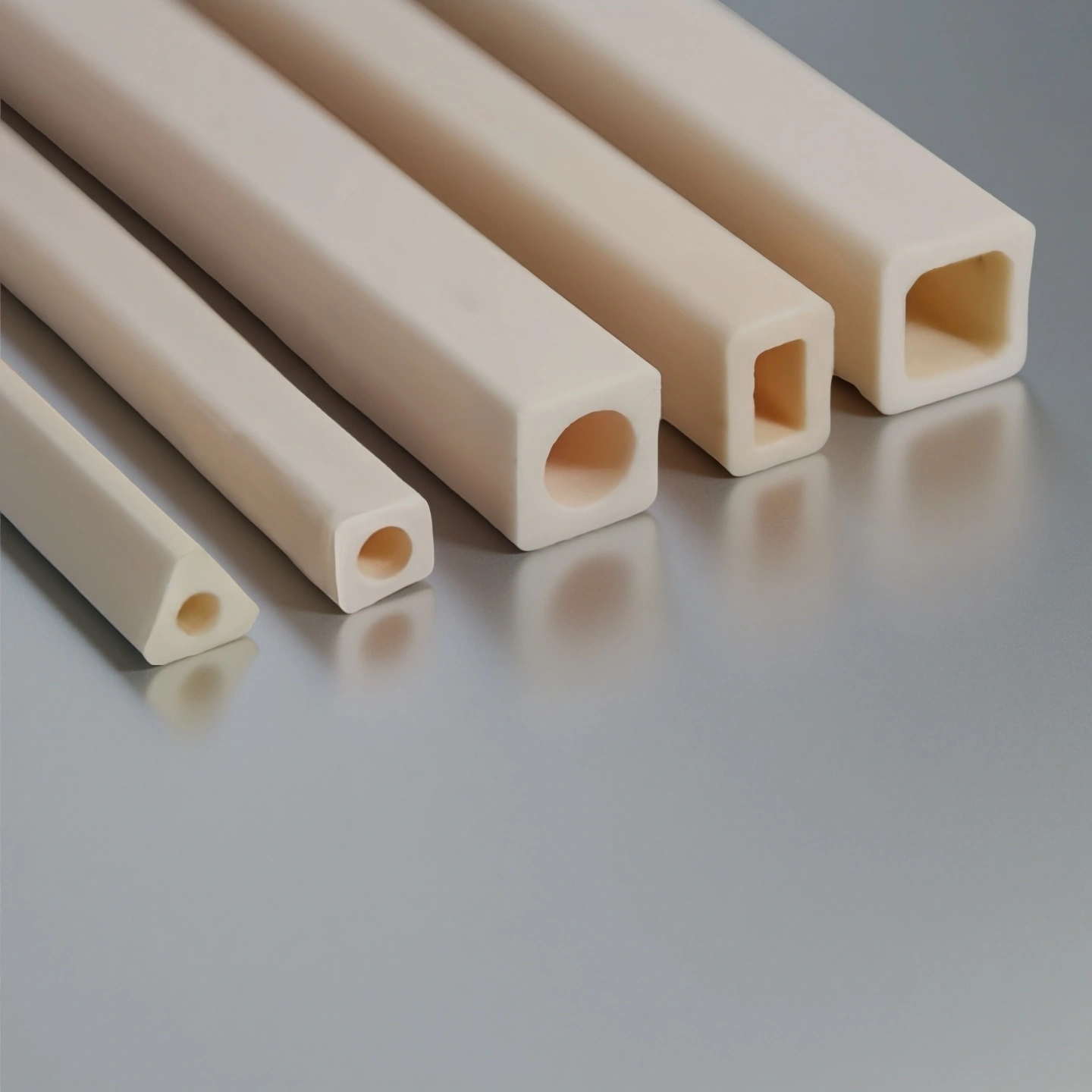
Square Ceramic Tube
Square ceramic tube with flat faces for anti-rotation mounting, easy fixturing and uniform contact in heater, support or guide assemblies.
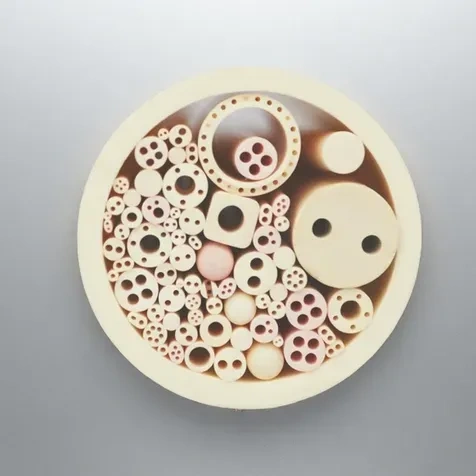

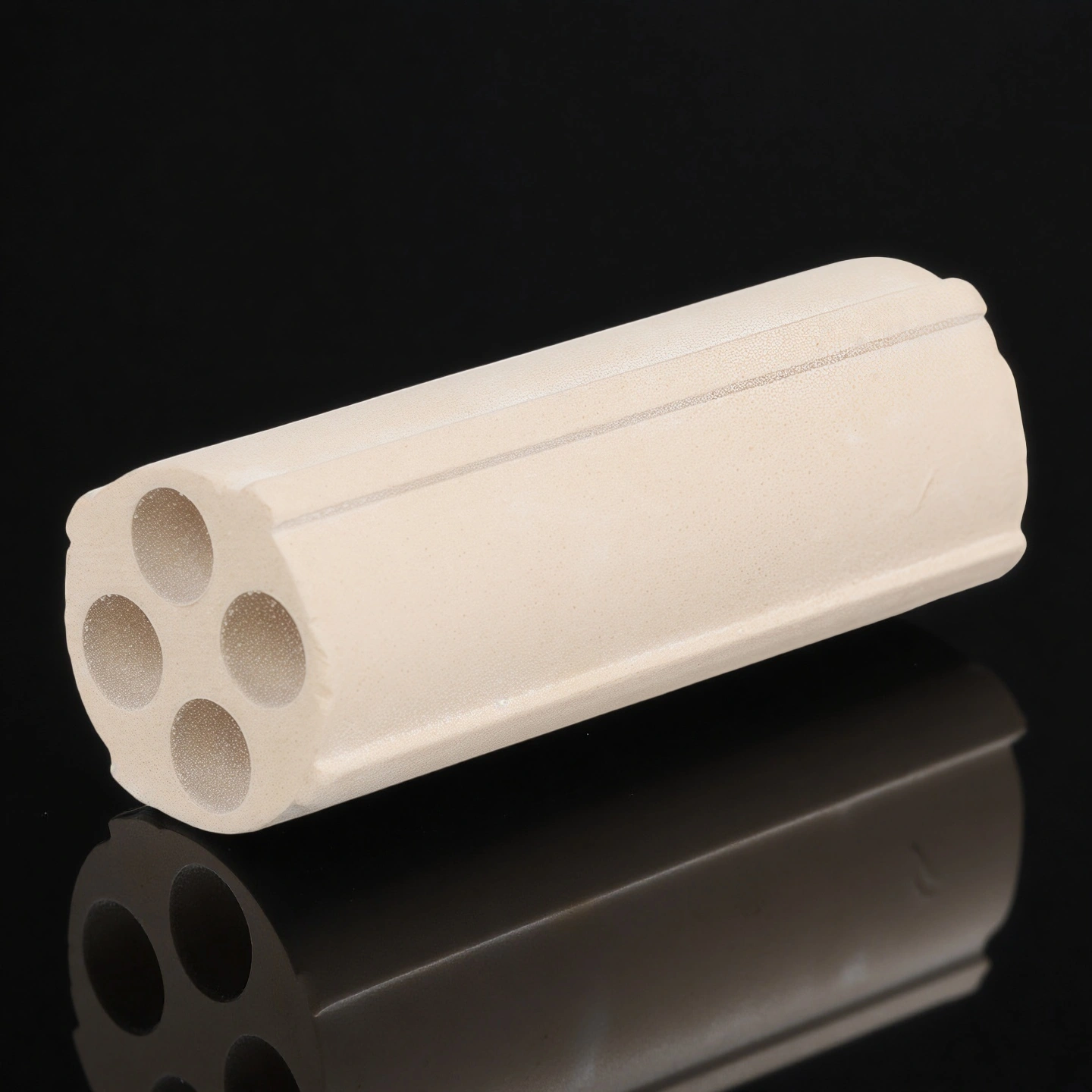
Multi-Bore Ceramic Tube
Multi-bore ceramic tube routes multiple wires or media in one compact part, giving precise spacing, improved insulation and easier assembly in tight spaces.

ceramic tube with flange
Ceramic tube with flange allows direct bolting to metal housings, improving alignment, sealing and replacement speed in furnaces, heaters and process lines.

threaded ceramic tubes
Threaded ceramic tubes provide screw-in mounting, adjustable positioning and insulation where components stay fixed under heat and vibration.
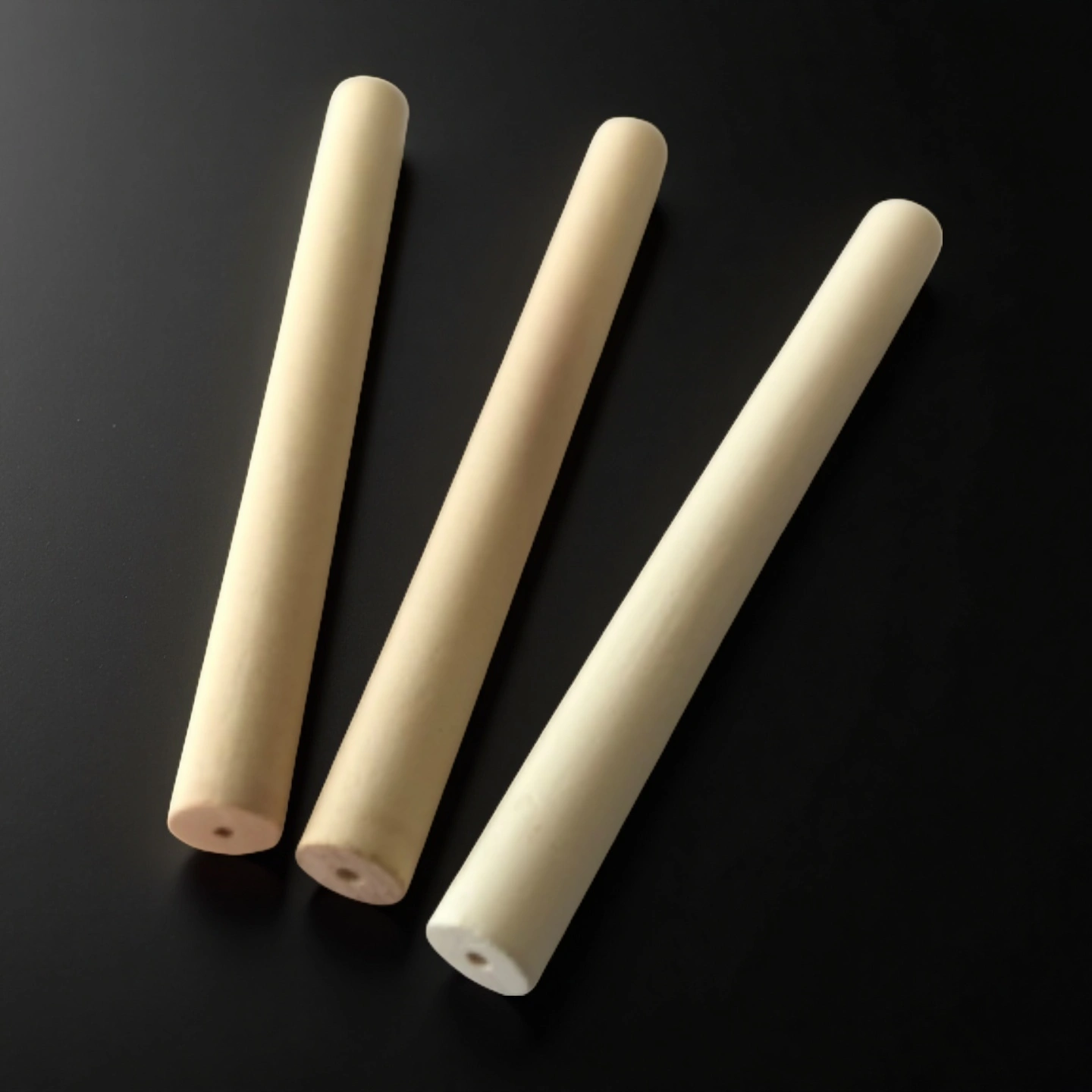

porous ceramic tube
Porous ceramic tube for gas diffusion, aeration and filtration in chemical systems where controlled permeability and heat resistance matter.

ceramic thermocouple tubes
ceramic thermocouple protection tubes shield wires from flame, molten metal and gases, giving insulation and stable readings in furnaces and process lines.
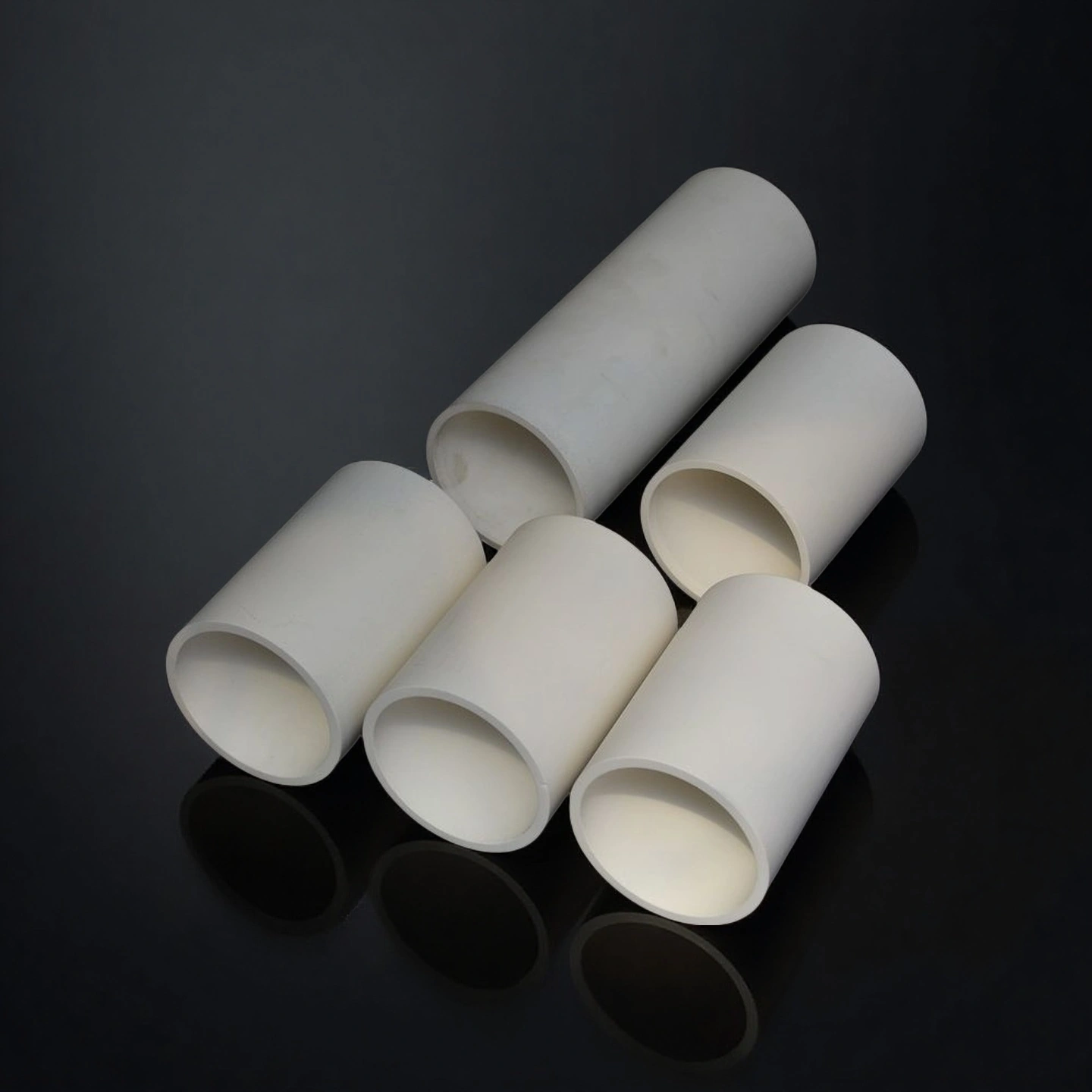

ceramic tube for furnace
Ceramic tube for furnace service used as process tube, burner tube or support in industrial heat-treatment, sintering and firing equipment.
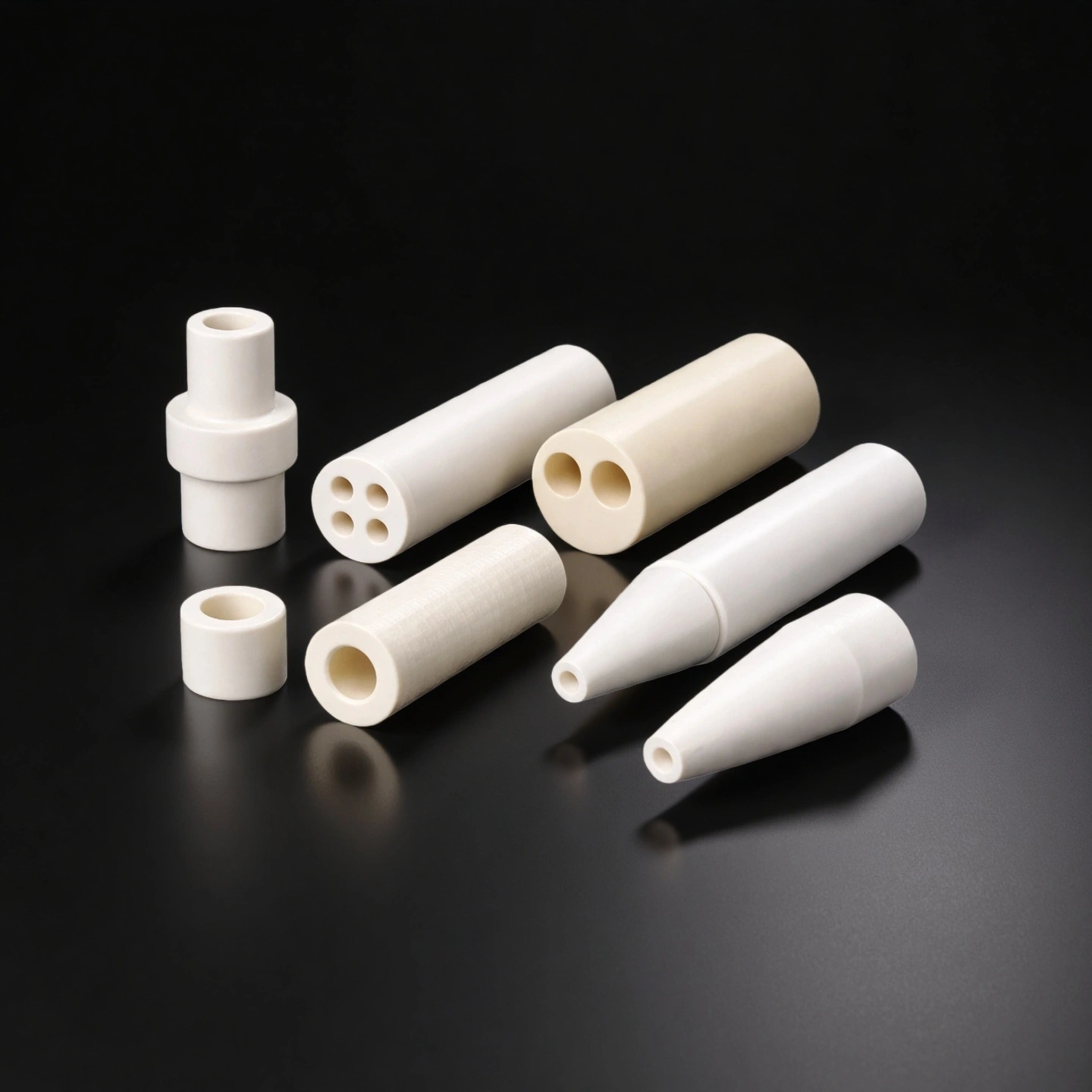

ceramic insulating tube
Ceramic insulating tubes sleeve hot conductors and heater leads, providing high-temperature insulation and shielding to prevent tracking, short circuits and damage to nearby parts.
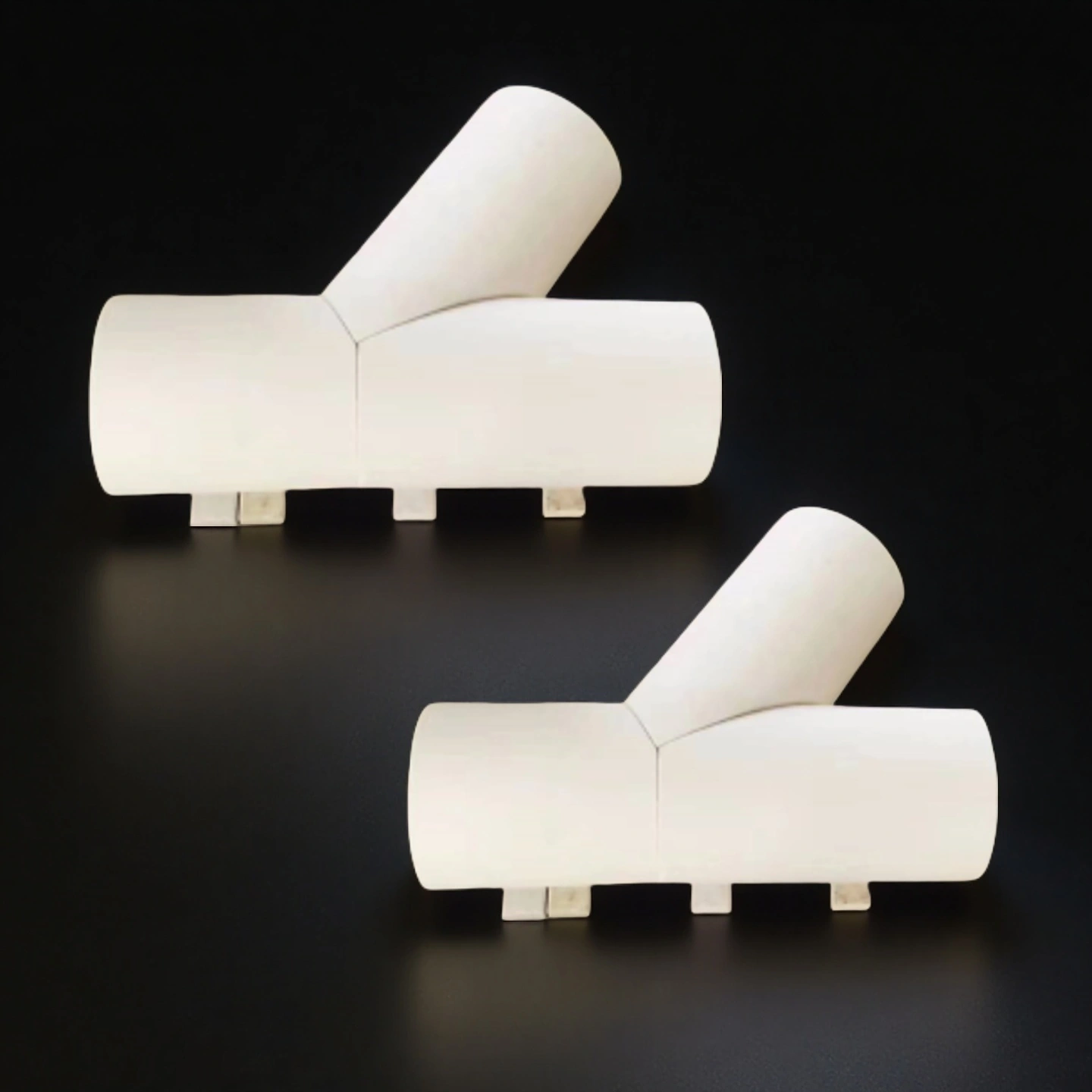

ceramic lining tube
Ceramic-lined tube and pipe for corrosive flow, combining a steel shell with a wear-resistant bore to extend service life and reduce shutdowns.
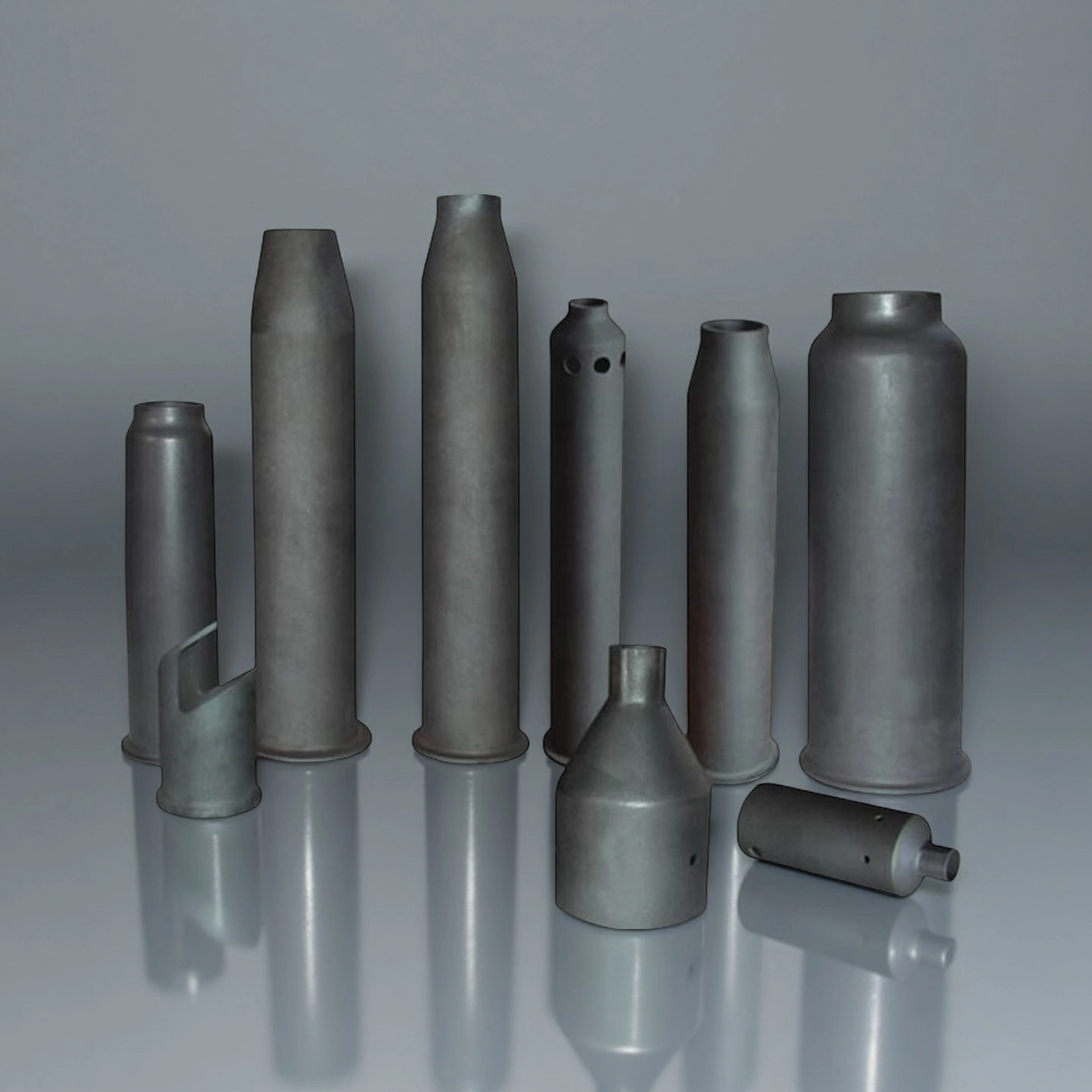

ceramic burner tube
Ceramic burner tubes form a heat-resistant throat for gas or oil burners, shaping the flame, shielding metal parts from direct fire and thermal shock, and helping maintain stable combustion.
Not Sure Which Ceramic Tube Fits Your Furnace or Equipment?
Share your drawing and key conditions—temperature, atmosphere, media and duty cycle—and we’ll recommend the best ceramic tube or pipe material and design, ready for repeatable production.
What are Ceramic Pipes Used for?
Ceramic pipes are engineering components used wherever metal or plastic pipe cannot survive high temperature, aggressive chemistry or intense abrasion. In industrial plants they act as stable flow channels, protective liners and insulating sleeves that keep processes clean and equipment running longer.

High-Temperature Furnace and Heater Lines
– ceramic tubes for stable process gas paths and burner assemblies.
🧩Where industrial ceramic tubes are used:
Industrial ceramic pipes carry hot process gases, combustion products or protective atmospheres in furnaces, kilns and tube heaters. They hold their shape and stiffness at temperatures where steel pipes creep or scale, helping to stabilise heat-treatment and firing conditions.
🧩ADCERAX ceramic pipes help prevent tube sagging, wall thinning and flaking scale that destabilise temperature profiles and contaminate loads, so heat-treatment and firing processes stay consistent with fewer emergency tube changes.

Abrasive and Corrosive Process Media
– ceramic pipes and ceramic lined pipes for long-life, wear- and corrosion-resistant conveying and process sections.
🧩Where industrial ceramic tubes are used:
In pneumatic conveying, ash handling and slurry systems, ceramic pipes and ceramic lined pipes protect against particle erosion and chemical attack. They are used for powders, granulates and corrosive gases or liquids in power plants, cement, mining and chemical processing.
🧩ADCERAX ceramic tubes reduce rapid wall wear, pinhole leaks and frequent replacement of carbon-steel spools and elbows, cutting unplanned shutdowns, maintenance labour and spare-part consumption in harsh transport lines.
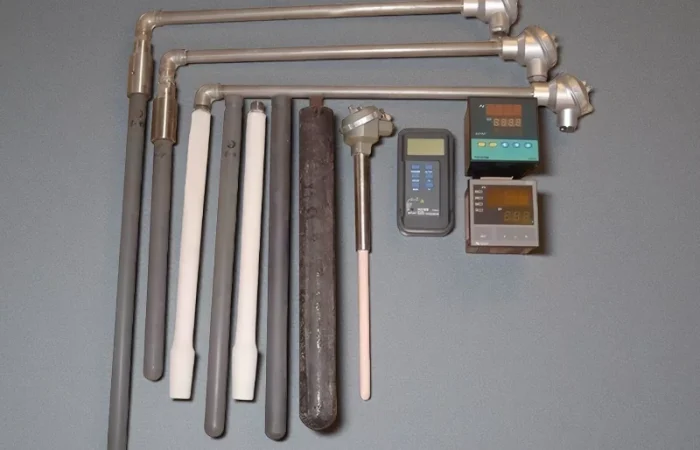

Electrical Insulation Around Hot Conductors
– ceramic sleeves and spacers for high-temperature electrical isolation of heaters, electrodes and busbars.
🧩Where industrial ceramic tubes are used:
Where conductors or heater elements run through hot zones, ceramic pipes serve as insulating sleeves and spacers. They maintain clearances and dielectric strength at elevated temperature, for example in resistance heaters, busbar tunnels and electrode guides.
🧩ADCERAX ceramic tubes help eliminate insulation breakdown, flashover and short circuits caused by overheated polymer or mica parts, maintaining safe clearances and dielectric strength at elevated temperature while keeping assemblies compact.

Clean, Low-Contamination Flow Paths in Lab and R&D
– high-purity ceramic tubes for inert, low-outgassing gas paths in laboratory furnaces, reactors and analytical equipment.
🧩Where industrial ceramic tubes are used:
In laboratory furnaces, pilot plants and analytical equipment, high-purity ceramic pipes provide clean, low-outgassing flow paths for gases and test atmospheres. They reduce cross-contamination and make it easier to maintain stable, repeatable test conditions.
🧩ADCERAX ceramic tubes reduce rapid wall wear, pinhole leaks and frequent replacement of carbon-steel spools and elbows, cutting unplanned shutdowns, maintenance labour and spare-part consumption in harsh transport lines.
Custom Ceramic Tube Supplier
ADCERAX is a China ceramic tube manufacturer specialising in custom-made tubes and pipes for industrial equipment and laboratory furnaces. We tailor length, bore design, wall thickness, material grade and end features to your drawings, while keeping key standard ceramic tube sizes in stock for urgent maintenance and small projects.
Customization Options
Extra-large / Extra-small diameters, non-standard thicknesses, and ultra-long / ultra-short lengths.
Provide higher - level dimensional accuracy and concentricity control than the standard.
Flanges, steps, threads, drilling holes, grooves, etc.
Adjust the material according to the application requirements.
Polish and grind the surface to achieve a specific surface roughness.
Customization Process
Send us your drawing, CAD file, or physical sample with material grade, dimensions, tolerances, and quantity. Our engineers will evaluate the design and provide a detailed quotation with lead time and pricing.
Once the quote is approved, we proceed with sample prototyping (1–50 pcs) if needed, for testing and validation.
After sample approval or direct confirmation, we begin batch manufacturing using CNC machining, sintering, and polishing. All parts undergo dimensional checks, material purity testing, and surface finish inspection.
Finished products are securely packed and shipped via DHL/FedEx/UPS or your preferred method. We support global delivery with full documentation.
ADCERAX: A Reliable Source for Ceramic Tubes
ADCERAX is a ceramic tube wholesaler and manufacturer, supplying custom and standard tubes with controlled materials and tight tolerances. Engineering support, fast sampling and reliable export logistics make ceramic tube sourcing efficient and predictable.
Competitive pricing with strict quality control from raw material sourcing to final delivery
Professional team providing comprehensive technical support and collaborative design
Small batch orders to large-scale production with complex geometries and tight tolerances
24-hour response and 24-hour dispatch for standard items, 3-7 weeks for custom orders.
China Industrial Ceramic Pipes Factory-ADCERAX

ADCERAX has been engaged in advanced ceramics for over 20 years and has developed more than 2,000 types of high-temperature components, with a strong focus on wear resistant ceramic pipes and tubes made from high-purity alumina, zirconia, boron nitride, silicon carbide and other engineering ceramics.
We supply both custom and standard ceramic tubes for laboratory equipment, tube furnaces, thermocouple protection, burner systems and high-temperature process lines, exporting to more than 50 countries and supporting industrial users and OEMs that require stable, low-contamination and long-life ceramic tube performance.
Ceramic Tube Processing Strength
ADCERAX controls every step, from forming to finishing, to keep the ceramic tube ID, OD, wall thickness and straightness consistent. Tuned sintering profiles and 100% visual checks for cracks deliver strong, thermal-shock-resistant ceramic tubes and pipes that run reliably over many furnace and process cycles.
CNC Forming Stability & Wall Thickness Control
Dimensional accuracy for ceramic tubes is achieved through CNC-assisted forming and machining, keeping wall thickness, inner diameter, outer diameter and straightness within tight, repeatable tolerances for secure fits and stable heating paths.
Holding ceramic tube wall variation within narrow limits for uniform heating, insulation and mechanical strength along the full length.
Controlling inner and outer diameters so ceramic tubes slide smoothly into metal housings, seals and fixtures without binding or leakage.
Managing bow and end squareness so tubes align properly in furnaces, heaters and pipelines, improving assembly, sealing and service life.

Clean, Low-Contamination Surface Finishing
Internal and external ceramic tube surfaces are refined to reduce residue build-up, minimize contamination and limit micro-cracks, helping each heating or process cycle stay stable and easy to maintain.
Optimised bore roughness reduces powder adhesion and gas turbulence while maintaining good flow and clean contact with media.
Removing sharp rims and micro-chips at tube ends and holes to lower breakage risk during handling and installation.
Applying selected finishes where lower porosity, easier cleaning or reduced reaction with process atmospheres is required.

High-Temp Sintering for Service Life & Thermal Shock Resistance
Microstructure density and strength in ceramic tubes are developed through controlled high-temperature sintering cycles, tuned to each material system for long life under repeated heating and cooling.
Managing ramp and cool-down rates to balance strength, residual stress and resistance to cracking in rapid-cycle service.
Matching soak times and peak temperatures to alumina, zirconia, BN or SiC tube bodies so each grade reaches its designed properties.
Low open porosity improves chemical stability and cuts gas or slag penetration over many cycles, helping ceramic tubes keep strength and tightness.

FAQs About Ceramic Tubes & Pipes
When choosing a ceramic tube, it helps to break the decision into clear steps instead of one long sentence.
You should first define:
Maximum operating temperature
Atmosphere: oxidizing, reducing, vacuum or inert
Mechanical loads: bending, axial loads, vibration, shock
Internal pressure or flow conditions
Media type: gas, powder, slurry, molten metal, etc.
Required electrical insulation level
Bore structure: single bore, multi-bore or one-end-closed
Dimensional requirements: ID, OD, wall thickness, length and tolerances
Target service life and maintenance strategy
Then align these requirements with:
Material data: alumina, zirconia, SiC, BN and other ceramics
Feasible manufacturing routes: extrusion, pressing, isostatic pressing, machining
This matching process is essential to achieve a reliable ceramic tube design that can be produced consistently and perform as expected in service.
Ceramic tubes maintain stiffness, dimensional stability and electrical insulation far above the service limit of most alloys, and they are more resistant to oxidation, carburization and many corrosive gases. However, ceramics are brittle and less tolerant of impact or bending, so correct support, installation clearances and controlled thermal gradients are required to avoid fracture.
For industrial tubes, typical as-fired wall-thickness tolerances are around ±0.3–0.5 mm, while ground or machined tubes can reach ±0.05–0.1 mm on OD or ID depending on size and length. Straightness and ovality are controlled through extrusion tooling, sintering supports and post-grinding, and should be specified together with length and fit requirements in the drawing.
Raw Material Preparation
Fine alumina, zirconia, BN or SiC powders are milled, blended and conditioned to achieve the particle size, purity and flow needed for extrusion or pressing.Forming the Ceramic Pipe
The prepared body is extruded or isostatically pressed into ceramic tubes and pipes, controlling inner diameter, outer diameter and wall thickness along the full length.Drying and Pre-Firing
Formed tubes are slowly dried and may be pre-fired to remove moisture and binders, reducing the risk of cracking or distortion during high-temperature sintering.High-Temperature Sintering
Tubes are fired in programmable kilns at carefully controlled ramp rates and soak times so the ceramic microstructure densifies and develops strength and thermal-shock resistance.Finishing and Machining
After sintering, ceramic tubes are ground or machined to final ID, OD and length, and special features such as flanges, threads or closed ends are added where required.Inspection and Packaging
Each ceramic tube and pipe is visually inspected for cracks and chips, key dimensions are checked, and parts are packed in protective sleeves and crates for export.
If you share your drawing and operating conditions, ADCERAX can recommend a manufacturable ceramic tube design and guide you on the most suitable production route and inspection level.
1. Match the pipe to the application
Choose a ceramic pipe with suitable material (e.g. alumina, SiC), inner diameter, wall thickness and length based on temperature, atmosphere, media (gas, powder, slurry) and any internal pressure.2. Design proper supports and housings
Mount the ceramic pipe in cradles, sleeves or frames that support its weight along the length, avoid point loads and allow free thermal expansion relative to metal parts.3. Use compatible seals and fittings
Select gaskets, packing and end fittings rated for the same temperature and chemistry as the ceramic pipe, and avoid excessive tightening that could create local stress or bending.4. Control heating and cooling rates
Bring the system up to temperature and cool it down gradually so the ceramic pipe is not exposed to sudden temperature shocks or large gradients between inside and outside.5. Avoid impact and misalignment
Protect the pipe from mechanical impact, vibration and misaligned connections, and do not use it as a lever or support for other components.6. Inspect and maintain regularly
During shutdowns, check ends and accessible sections for cracks, chips and erosion. Replace damaged ceramic pipes before they are returned to high-temperature or high-stress service.
In most cases you should avoid thermal shock and aggressive mechanical tools, and combine dry cleaning, compatible chemistry and controlled rinsing. A typical maintenance approach is:
Start with dry cleaning if possible
Use compressed air, soft brushes or non-metallic scrapers to remove loose dust, scale and powder. Avoid hitting or levering on the ceramic to prevent chipping.Select a compatible cleaning medium
Choose solvents or cleaners based on the deposits, not on habit:For oils and organic residues, use suitable industrial detergents or solvents approved for your process.
For inorganic scale or oxide deposits, use mild acidic or alkaline cleaners that are compatible with the ceramic and any metallic fittings.
Always check that the chemistry will not attack glazes, metallised layers or seals.
Control temperature and thermal shock
Never flush a hot ceramic pipe with cold liquid or vice versa. Allow the pipe to cool to a safe, moderate temperature, then apply cleaning fluids, or preheat the fluid if needed to reduce temperature gradients.Use moderate mechanical action
If brushing or swabbing inside the ceramic pipe, use soft or medium-bristle tools with plastic or fibre heads, not metal wire brushes that can scratch or create stress risers.Rinse and dry thoroughly
After chemical cleaning, rinse the ceramic pipe with compatible clean water or solvent to remove residues. Dry slowly with warm air or by controlled heating so moisture does not remain trapped, especially in closed-end or multi-bore sections.Inspect before putting back into service
Check ends, flanges and any threaded sections for chips, cracks or glaze damage. If you see radial cracks, deep scoring or large chips, replace the component rather than returning it to high-temperature or high-pressure service.
If cleaning cycles are frequent, it is worth discussing deposit type, temperature and gas or liquid composition with the ceramic supplier so material selection, surface finish and geometry can be optimised to reduce build-up and make future cleaning easier.
Yes, industrial ceramic pipes are generally safe when the material is correctly matched to the temperature, atmosphere and media. High-purity ceramics are chemically inert and low-contamination; the main safety point is to install and support them properly, as ceramics are brittle and must not be overloaded or subjected to severe impact or thermal shock.
Cutting a ceramic tube must be done carefully to avoid cracking or chipping. In many cases, it is safer and more economical to order tubes to finished length, but if cutting on site is unavoidable, follow these principles:
1. Choose the right tool
Use diamond tooling only: a diamond cut-off wheel on an angle grinder or tile saw, or a diamond-coated tube cutter designed for ceramics and glass. Avoid standard metal saw blades, which can shock or chip the tube.2. Support the tube properly
Support the ceramic tube along its length and close to the cut line using soft pads or V-blocks. Do not allow the tube to hang freely or rest on a single hard point; this concentrates stress and encourages cracking.3. Mark and score the cut line
Mark the cut position clearly. Where possible, lightly score around the full circumference with a diamond scribe or the edge of the wheel so the cut starts evenly and does not wander.4. Use light pressure and steady feed
Start the cut slowly, with low to moderate pressure. Let the diamond do the work; forcing the tool increases vibration and shock. Rotate the tube gradually (if possible) to cut from multiple sides rather than sawing straight through one point.5. Control dust and temperature
Use water cooling or dust extraction where allowed to reduce dust and local heating. Avoid rapid heating and cooling of the tube section; excessive thermal shock can cause radial cracks.6. Deburr and smooth the edges
After cutting, lightly grind or sand the cut edge with a fine diamond file or pad to remove sharp chips and micro-cracks, which could act as starting points for failure in service.
Whenever possible, define the required finished length, tolerances and quantity in your drawing so the ceramic tube manufacturer can supply parts already cut and finished under controlled conditions.
Alumina ceramic tubes are the default choice for general high-temperature, electrically insulating duties up to roughly 1,600–1,700 °C in suitable atmospheres. Zirconia tubes are preferred where small diameters must carry mechanical load or impact (bushings, guide sleeves), thanks to higher toughness. Silicon carbide pipes and radiant tubes are selected when extreme thermal shock, high heat flux or severe abrasion and corrosive flue gases are present.
Ceramic thermocouple tubes create a stable barrier between the sensing wires and the furnace atmosphere or molten metal, reducing chemical attack, grain growth and mechanical damage. This extends sensor life, reduces drift, and allows maintenance teams to replace thermocouples without disturbing refractory linings, which improves calibration consistency and reduces downtime.
Single-bore tubes are used as process tubes, guide sleeves or general insulating components. Multi-bore tubes route several conductors, thermocouple legs or small fluid channels in one compact, electrically isolated component. One-end-closed tubes are chosen when the hot end must be sealed—for example, thermocouple protection in molten metal, burner nozzles or gas sampling lances.
Standard ceramic tube sizes held in stock can usually be shipped within a short time after order confirmation and packaging. Custom tubes require tooling, process validation and sintering cycles, so lead times depend on length, quantity, material and machining complexity; prototype batches are often produced first, followed by scheduled series production once the design is frozen.
Large diameter ceramic pipes are usually not off-the-shelf retail items; they are supplied by specialized industrial ceramic tube manufacturers. ADCERAX is a China ceramic tube manufacturer that produces large diameter ceramic pipes and ceramic lined pipes in alumina and other engineering ceramics for furnaces, burners and abrasive or corrosive process lines.
You can buy large diameter ceramic pipes by sending ADCERAX your basic requirements—material, inner and outer diameter, length, operating temperature, media and expected quantity—so the engineering team can confirm a feasible design, quote pricing and define lead time for production and export.
Yes. ADCERAX is a China ceramic tube manufacturer supplying industrial ceramic pipes and ceramic tubes for sale in alumina, silicon carbide, zirconia and other engineering ceramics. We offer stocked standard sizes for maintenance and small projects, and custom ceramic tubes and pipes produced to your drawings for OEM and high-temperature industrial applications.
Industrial thermocouple ceramic tubes are not sold from a fixed ceramic tubes pricelist, because price depends on material (alumina grade, etc.), tube size (ID, OD, length), wall thickness, bore structure (single or multi-bore), quantity and inspection level.
Instead, ADCERAX prepares a tailored quotation for each specification. If you share your thermocouple tube sizes, material requirement, expected quantity and working temperature, we can quickly provide itemized pricing and recommended options rather than a generic price table that may not match your real application.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
info@adcerax.com
Telephone: +(86) 0731-74427743
WhatsApp: +(86) 19311583352
Within 24 hours
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

