ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter is engineered for molten steel and iron applications where stable flow control and reliable inclusion removal are required. Its three‑dimensional SiC foam structure supports consistent metallurgical cleanliness by reducing slag transfer, oxide films, and micro‑impurities throughout the pouring process. This performance makes the filter suitable for steel foundries, automotive casting operations, and heavy machinery production where predictable casting quality and thermal stability are essential.
Advanced Performance Characteristics of Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
-
High Thermal Endurance for Molten Metal Stability
The Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter maintains structural reliability under extreme temperatures, supporting casting processes that operate close to 1500°C.
Its ceramic matrix withstands rapid temperature changes above ΔT 1200°C, ensuring continuous filtration without cracking during pouring transitions.
This stability supports long casting cycles in large foundry operations, where extended exposure above 1400°C is common.
-
Consistent PPI Structure for Predictable Filtration Efficiency
Each Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter offers controlled pore distribution across 10/20/30/40 PPI, supporting predictable flow resistance in automated casting systems.
The filter’s porosity range of 80–90% enhances laminar flow formation and reduces turbulence that contributes to inclusion entrapment.
This uniformity directly supports scrap‑rate improvements, with documented reductions of 30–60% in typical iron and steel foundries.
-
Mechanical Strength and Low Clogging Behavior in Industrial Casting Lines
The Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter provides compressive strength above 1.0 MPa, maintaining shape integrity under metal head pressure in pouring cups and gating systems.
Its open‑cell structure reduces clogging frequency during melts with high impurity loads, retaining filtration capacity across pours exceeding 10–12 kg/s flow rate.
This mechanical stability supports consistent casting output, contributing to surface finish improvements of 15–40% in downstream machining.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter is engineered with stable thermal behavior, controlled pore architecture, and reliable structural performance suitable for molten steel and iron filtration in industrial environments. Its material characteristics support consistent inclusion control, predictable flow modulation, and dependable behavior under rapid thermal cycling.
| Property |
Specification |
| Base Material |
Silicon Carbide (SiC) >80% |
| Porosity |
80–90% open‑cell structure |
| Pore Density |
10 / 20 / 30 / 40 PPI |
| Density |
0.35–0.50 g/cm³ |
| Maximum Operating Temperature |
up to 1500°C |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
withstands ΔT >1200°C |
| Thermal Expansion |
low expansion ceramic matrix |
| Compressive Strength |
≥1.0 MPa |
| Chemical Stability |
non‑reactive in molten steel |
| Flow Rate Capacity |
2–12 kg/s depending on PPI |
| Slag Capture Efficiency |
reduces inclusions by 40–70% |
| Surface Finish Improvement |
15–40% enhancement range |
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
Type 1 -Round SIC Ceramic Foam Filter

|
Item |
Diameter*Thickness(mm) |
PPI |
Fractional hole area (%) |
|
AT-SIC-PM001 |
40*12 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM002 |
50*15 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM003 |
60*15 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM004 |
70*15 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM005 |
80*20 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM006 |
100*22 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM007 |
200*25 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM008 |
300*25 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
|
AT-SIC-PM009 |
360*30 |
8/10/15/20/25/30 |
80~90 |
Type 2 -Square SIC Ceramic Foam Filter
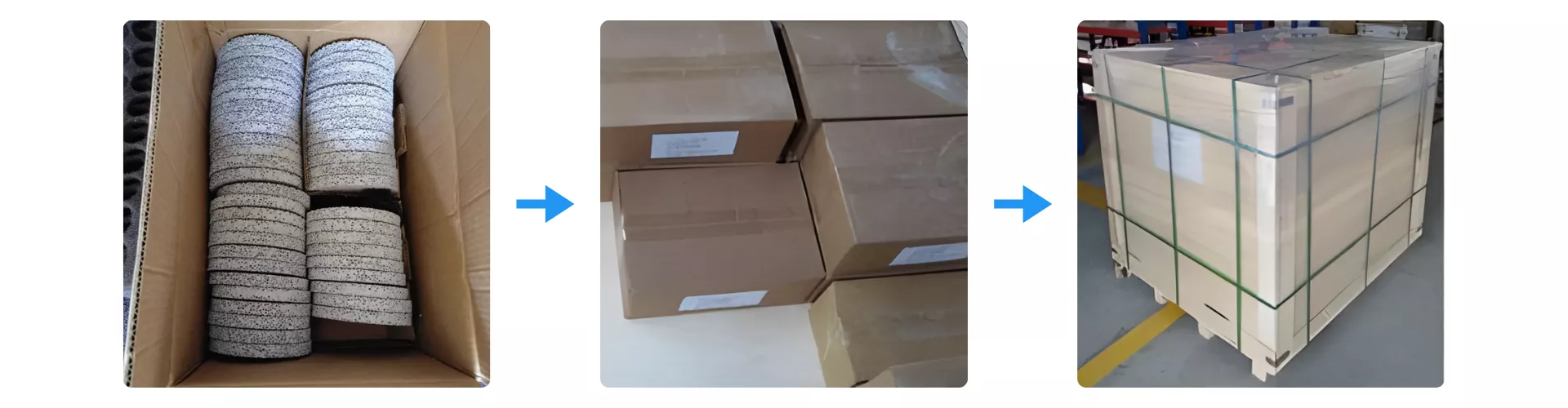
Packaging Method of Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter products are packed in reinforced cartons with protective cushioning to prevent abrasion during transit. Each carton is securely sealed and labeled before being stacked onto pallets for stable handling. The palletized load is then fully wrapped and banded to ensure safe international shipment and consistent product integrity upon arrival.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter Enhances Reliability in Demanding Casting Environments
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter supports stable molten‑metal processing in operations where flow control, impurity capture, and temperature endurance directly influence casting reliability. Its engineered pore structure and thermal integrity help industrial plants resolve defects, stabilize production cycles, and maintain melt cleanliness across continuous or heavy‑load casting conditions.
-
High‑Load Brake Disc Casting with Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
✅Key Advantages
1. Enhanced Turbulence Dampening
The interconnected SiC foam network reduces metal velocity fluctuations by 25–40% in wide gating regions where brake disc molds are most sensitive.
2. High Efficiency Inclusion Capture
The controlled 30–40 PPI pore structure captures slag clusters that typically bypass coarse filtration, improving melt cleanliness during extended tapping sequences.
3. Thermal Integrity During Continuous Pouring
The SiC matrix maintains structure under repeated temperature swings above 1400°C, ensuring filter reliability during long production runs.
✅ ️Problem Solved
High‑volume brake disc plants often experience unstable melt quality during prolonged tapping cycles, where oxide concentration can rise by 20–35% during peak shift output. This leads to elevated micro‑porosity levels and inconsistent machining allowances on braking surfaces. ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter reduces turbulence at the gating entrance and captures oxide fragments before cavity entry, helping stabilize melt cleanliness across entire production blocks. Foundries using ADCERAX® have reported a measurable drop in surface‑related defects, with rework frequency decreasing by 15–30% during heavy‑load casting phases.
-
Pump Body and Valve Housing Casting with Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
✅Key Advantages
1. Long‑Pour Thermal Stability
The SiC matrix remains structurally reliable during extended pouring sequences that maintain high temperatures for 35–60 seconds or longer.
2. Reduced Slag Accumulation at Gating Transitions
The open‑cell structure with 80–90% porosity slows molten metal flow at transition points where suspended slag tends to accumulate.
3. Improved Density in Heavy Cross‑Sections
Flow modulation provided by the filter lowers turbulence that disrupts feeding behavior in large castings, reducing shrinkage tendencies by 20–40%.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Large pump and valve castings often encounter internal voids when turbulence disrupts metal feeding in thick cross‑sections, particularly when slag content peaks during long pours. Plants report that melt instability can increase shrinkage‑related scrap by 20–35%, especially in geometries with deep cavities or complex channels. ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter maintains thermal rigidity under prolonged heat exposure and slows slag‑laden flow at critical gating transitions. Foundries adopting ADCERAX® have documented improved internal density uniformity and a decline in shrinkage‑related defects across extended fill cycles.
-
Stainless Steel Precision Component Casting with Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter
✅Key Advantages
1. High‑Temperature Oxide Film Suppression
The SiC ceramic framework withstands stainless steel’s elevated melt range near 1500°C, reducing oxide film re‑entry risk at the pouring stage.
2. Flow Stabilization for Narrow Geometry Tolerance
The uniform 20–30 PPI structure moderates flow rate at cavity entrances, lowering turbulence amplitude by 20–30%.
3. Reduced Surface Roughness Variation
Consistent impurity capture prevents micro‑defects that lead to variations in roughness, which machining teams often identify as 15–25% fluctuations without proper filtration.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Stainless steel casting environments struggle with oxide film regeneration at high temperatures, which introduces surface inconsistencies and micro‑defects during solidification. Manufacturers report increased finishing workload when inclusion levels rise, often resulting in roughness variation of 15–25% across batches. ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter supports stable flow behavior and limits oxide re‑entry during the initial pour, helping maintain consistent metallurgical cleanliness. Plants implementing ADCERAX® have seen reduced surface‑related rework and improved machining efficiency on stainless components with sensitive finish requirements.
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter User Guide for Reliable Casting Performance
The ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter requires proper handling, preparation, and operation control to achieve stable melt filtration results. This guide helps casting engineers and operators understand the essential precautions and best‑practice steps that ensure consistent performance, long service life, and predictable behavior in demanding molten‑metal environments.
-
Preparing the Silicon Carbide Ceramic Foam Filter Before Casting
1. Inspect the filter packaging and ensure it remains fully intact before opening, as clean and uncontaminated pores support more consistent melt flow.
2. Keep the filter in a controlled environment away from moisture or dust to maintain stable pore functionality during preheating.
3. Position the filter correctly within the gating layout, confirming full surface contact so that metal flow enters evenly across the entire filter face.
-
Preheating Procedures for Stable Melt Flow
1. Gradually warm the filter to prevent sudden thermal exposure, as smooth temperature transitions help reduce thermal stress during the first pour.
2. Use a heating range that aligns with the casting process so the filter reaches a thermally balanced state before molten metal arrives.
3. Maintain proper ventilation around the heating zone to protect workers and ensure consistent air‑to‑surface temperature equilibrium on the filter.
-
Operating Guidelines During Molten Metal Pouring
1. Control the metal head height so that no excessive pressure compromises filtration uniformity or impacts pore performance.
2. Monitor impurity load in the molten metal, adjusting flow rate when necessary to maintain effective slag interception across prolonged pouring cycles.
3. Keep the pouring rhythm stable, as significant fluctuations can disrupt flow consistency and reduce the filter’s inclusion‑capture efficiency.
-
Post‑Casting Handling, Cleaning, and Storage
1. Allow the filter to cool naturally after casting so thermal gradients do not cause structural shock or affect repeatable performance.
2. Dispose of used filters according to plant safety protocol, especially when accumulated slag may still retain residual heat.
3. Store unused filters in sealed cartons placed on elevated racks to prevent moisture absorption and maintain pore stability for future batches.


![]()


