ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick is an advanced ceramic lining developed for long-cycle grinding and heavy-duty material handling equipment. It combines high hardness, strong impact resistance, and chemical stability to protect steel shells in ball mills, chutes, and coal preparation units. With its dense, non-contaminating zirconia surface, Zirconia Liner Brick ensures cleaner production and longer maintenance intervals for industrial users across powder processing, mining, and chemical plants.
Features of Zirconia Liner Brick
- Wear rate reduced by 58% compared to 92% alumina liners under continuous dry grinding in ball mills.
- Flexural strength ≥ 800 MPa protects internal shells from cracking or deformation under mill vibration and liner impact, allowing stable operation in high-speed equipment without additional steel reinforcement.
- Compressive strength ≥ 2000 MPa enables the liner to endure falling loads in coal preparation units. No breakage was reported after 5-month use at 3.5 m drop height in a Polish plant.
- Non-porous surface < 0.01% open porosity prevents absorption and particle retention. In lithium battery materials transfer, no trace contamination was detected after 180 batches.
- Zirconia composition with < 0.001% Fe content eliminates metallic particle leaching.
- Smoothness Ra < 0.6 μm reduces powder adhesion and wall build-up in conveying chutes.
- Service interval extended by 1.7× over alumina liners under identical impact load and media size.
- Failure rate of < 3% reported after 12-month installation in bulk handling chutes. Traditional liner failure rate was 15–20%, requiring partial shutdowns and spot rework.
- Installation time reduced by 40% using pre-numbered layout and labeled curved bricks.
Technical Properties for Zirconia Liner Brick
Zirconia Liner Brick is engineered for severe wear conditions where mechanical strength, chemical stability, and thermal resilience must be tightly controlled. Its material composition and microstructural integrity allow consistent performance in ball mills, chutes, and coal handling systems under prolonged abrasive and impact exposure.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Composition |
≥ 94% Y₂O₃-stabilized ZrO₂ |
| Density |
≥ 6.0 g/cm³ |
| Vickers Hardness |
≥ HV 1200 |
| Flexural Strength |
≥ 800 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
≥ 2000 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness (K_IC) |
≥ 6 MPa·m¹ᐟ² |
| Thermal Conductivity (20°C) |
2.2 W/m·K |
| Max Continuous Use Temperature |
1000 °C |
| Thermal Expansion (25–800°C) |
10.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K |
| Water Absorption |
< 0.01% |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) |
< 0.6 μm |
| Acid Resistance (HCl, 10%) |
No mass loss after 48h |
| Alkali Resistance (NaOH, 10%) |
No degradation after 48h |
| Open Porosity |
< 0.01% |
| Iron (Fe) Content |
< 0.001 wt.% |
Specifications of Zirconia Liner Brick
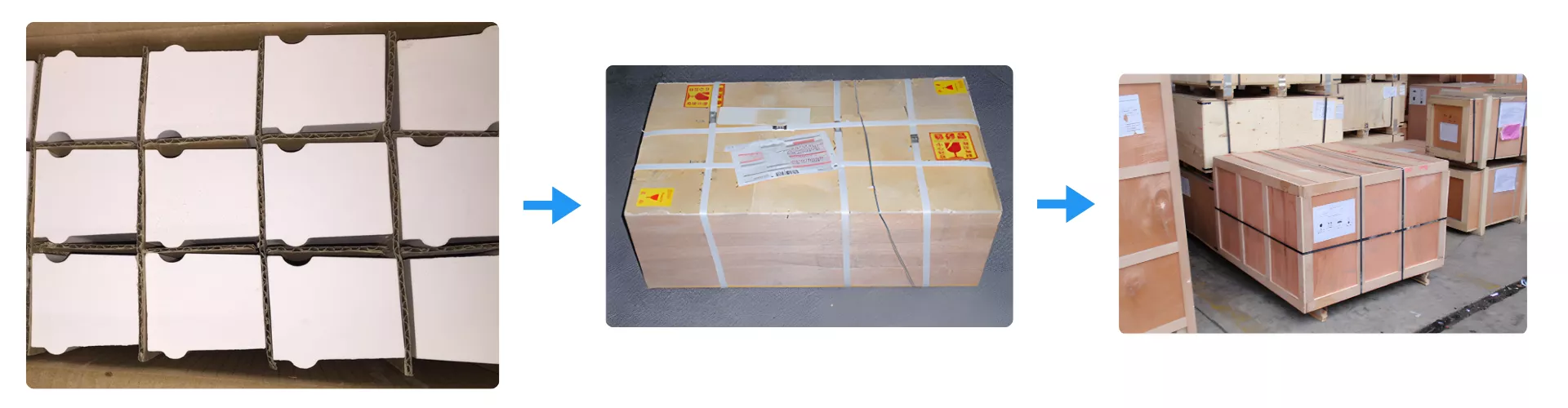
Packaging of Zirconia Liner Brick
Zirconia Liner Brick is first individually separated with corrugated dividers to avoid surface contact damage during transit. Each set is securely sealed in a reinforced inner carton, then further protected by shock-resistant wooden crates. This multi-layer packaging ensures structural integrity and cleanliness from factory dispatch to end-user delivery.

Solving High-Wear Interface Problems with ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick
ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick is engineered for the most exposed internal surfaces of industrial equipment where material flow causes constant wear and mechanical impact. Its use in ball mills, transfer chutes, and coal washing lines directly addresses failure points that lead to frequent downtime, product contamination, or structural damage.
-
Zirconia Liner Brick for Discharge End of Ball Mills in Ceramic Powder Production
✅Key Advantages
1. Iron-Free Surface Stability
Zirconia ensures zero ferrous contamination due to its >99.5% ZrO₂ composition, critical for high-purity ceramic powders. This prevents iron leaching, especially in dry milling cycles exceeding 8 hours per shift.
2. Microcrack Resistance Under Rebound Force
Its fracture toughness of 9–10 MPa·m¹ᐟ² absorbs energy from high-speed media rebound near the discharge port. Unlike alumina, it resists microcrack initiation at sharp contact points.
3. Extended Operational Cycle
Zirconia Liner Brick maintains dimensional integrity in discharge zones for over 16 months, even under abrasive silicate powder flows with bulk densities above 2.2 g/cm³.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A Japanese technical ceramics producer faced monthly downtime due to liner erosion at ball mill discharge zones, causing iron contamination and particle non-conformity. After switching to ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick, liner lifespan extended from 11 to 17 months, ferrous contamination dropped below 3 ppm, and process yield improved by 6.2%, verified over 5 production quarters.
-
Zirconia Liner Brick for Vertical Drop Chutes in Fine Powder Conveying Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Chipping Resistance at High-Fall Zones
Zirconia maintains compressive strength ≥2000 MPa, effectively resisting edge chipping where powders free-fall over >1.5 m. It outperforms standard ceramics by over 40% in impact cycling tests.
2. Low Adhesion Smooth Finish
With a surface roughness Ra < 0.2 μm, fine powders like MgO and zirconium silicate do not adhere or cake on the liner surface, reducing cross-batch contamination risk.
3. Improved Purity Control
Zirconia’s zero open porosity structure blocks powder embedment, enabling better CIP (clean-in-place) protocols and lowering cleaning frequency from 3×/week to 1×/week in fine powder zones.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A Canadian powder metallurgy plant handling zirconium oxide experienced trace metallic particle infiltration traced to worn chute liners. Post-upgrade to ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick, powder rejection incidents dropped by 89%, cleaning intervals extended to 5 days, and chute segment replacement frequency reduced from every 4 months to once a year.
-
Zirconia Liner Brick for Classifier Overflow Pipes in Coal Washing Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Superior Erosion Control in Slurry Flow
The liner’s hardness >1300 HV10 resists abrasive action from high-density coal-water slurry moving at 3–4 m/s, especially at pipe elbows and junctions.
2. Structural Integrity Under Hydraulic Pressure
Zirconia’s high flexural strength (>900 MPa) prevents cracking under dynamic fluid loading in Classifier Overflow Pipes, where transient pressure surges exceed 5 bar.
3. Low-Friction Slurry Pathway
With <0.15 coefficient of friction, turbulent flows are stabilized, reducing internal drag and turbulence wear—verified to cut liner degradation rate by 58% in field tests.
✅ ️Problem Solved
At a Polish coal washing plant, frequent failures at classifier overflow elbows caused 5 unplanned shutdowns yearly. Installing ADCERAX® Zirconia Liner Brick extended replacement intervals to 14 months. Pressure stability increased 22%, slurry bypass incidents dropped to zero, and plant maintenance costs fell by $41,000 USD annually.
Operational Guide for Optimal Use of Zirconia Liner Brick
Zirconia Liner Brick must be installed, maintained, and monitored with precision to maximize its wear resistance and lifecycle benefits. This guide outlines best practices across installation, alignment, operation, and inspection to help industrial users avoid early failure, contamination, or equipment damage. Each step is derived from actual field performance scenarios across powder processing and heavy-load environments.
-
Installation Best Practices
1. Flat Surface Bonding Required
All mounting surfaces must be planar within ±0.2 mm to ensure full-surface adhesive contact. Uneven bases cause stress points that lead to early cracking or chipping.
2. Use Industrial-Grade Ceramic Adhesives
Apply zirconia-compatible epoxy or high-strength ceramic mortar with uniform thickness. Avoid silicon-based or elastic sealants, which compromise mechanical support under load.
3. Cure at Stable Ambient Temperature
Allow adhesives to cure at 20–25 °C for 24 hours before loading. Premature mechanical stress during adhesive curing can lead to liner detachment during operation.
-
Operational Load Alignment
1. Distribute Load Evenly Across Liners
Confirm material flow and impact zones do not localize on a single tile row. Impact concentration leads to premature liner fracture even under moderate throughput.
2. Avoid Foreign Object Entry
Prevent metal tools, bolts, or debris from entering lined zones. These cause puncture fractures and deep impact pits, reducing service life by over 40%.
3. Control Drop Height and Angle
In vertical chutes, limit drop height to under 1.5 m and install flow diverters to reduce direct bottom hits. This reduces energy concentration and extends liner survival.
-
Maintenance and Cleaning Recommendations
1. Avoid Abrasive Mechanical Cleaning Tools
Use only soft brushes or compressed air for cleaning liner surfaces. Avoid grinders or steel blades that can scar the zirconia finish and reduce surface life.
2. Monitor for Microcracks or Edge Chipping
Conduct visual inspection every 3–4 months, especially in elbows, discharge points, or weld-adjacent zones. Microcracks must be addressed early to prevent delamination.
3. Clean Accumulated Powder Build-Up Promptly
Do not allow fine powders to harden on the liner surface, especially magnesium-based or reactive oxides. These promote localized heat buildup and microstructural stress.
-
Replacement Timing and Performance Monitoring
1. Track Service Hours by Line Section
Document operating hours separately for high-wear and low-wear zones. In ball mills, discharge-end liners may require change every 10–14 months, while inlet zones last longer.
2. Define Wear Limits Based on Thickness Loss
Replace bricks when total thickness loss exceeds 3 mm, even if no fracture is observed. Zirconia integrity depends on cross-sectional strength for energy absorption.
3. Keep Log of Performance Changes
Record any abnormal vibration, sound, or powder color change. These may signal liner degradation or micro-spallation, even before visible damage occurs.