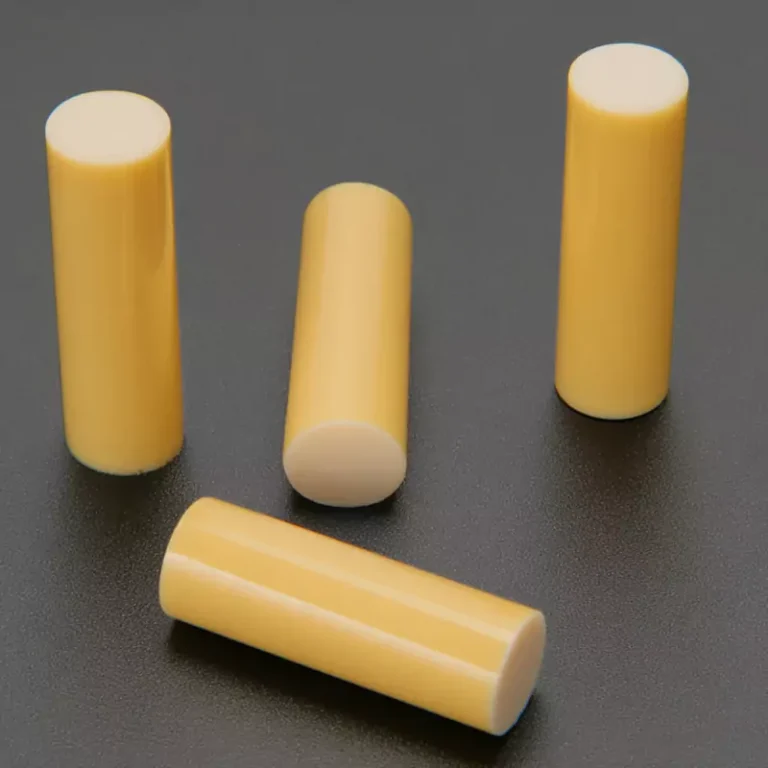
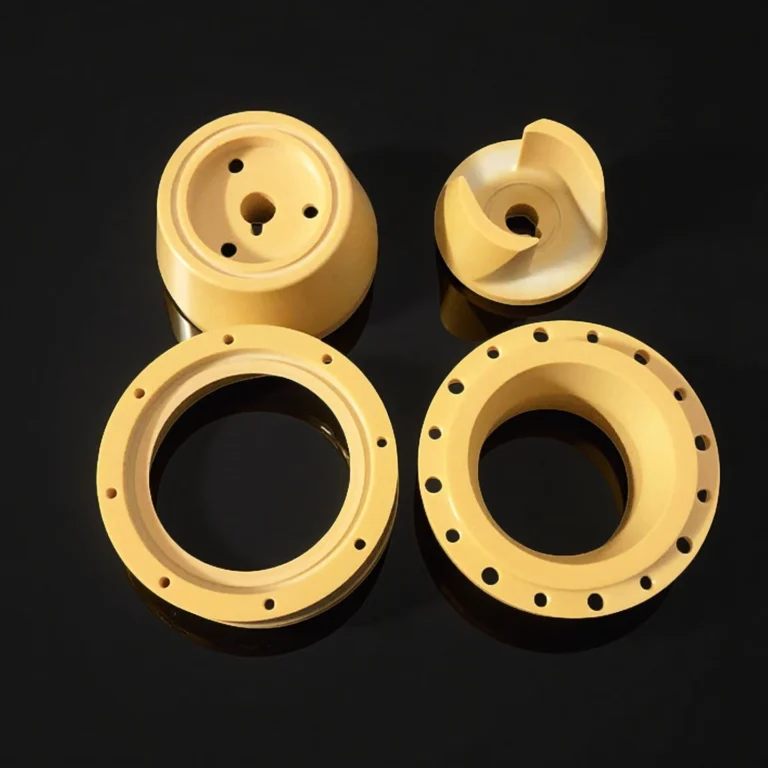
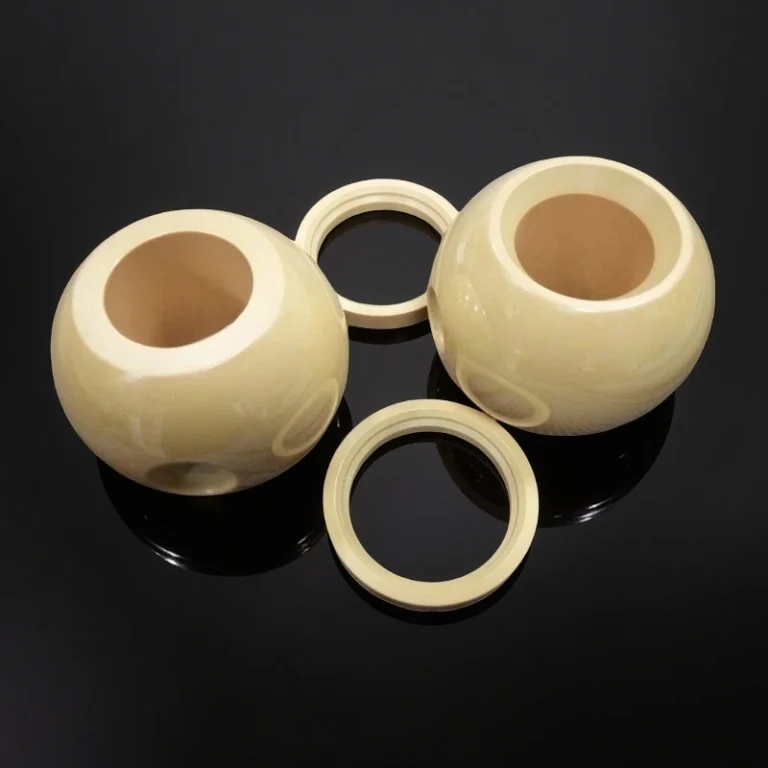
ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring delivers stable mechanical performance under high temperature, corrosive, and abrasive operating conditions where conventional zirconia typically fails. Its MgO‑stabilized cubic structure ensures reliable resistance to thermal shock, enabling long service life in environments involving rapid temperature fluctuations. This material behavior makes the ring suitable for continuous operation in metallurgy, chemical processing, and mechanical systems where wear resistance, electrical insulation, and heat isolation are required simultaneously.
Product Features of Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring
-
Acid–Alkali Stability
Laboratory immersion tests show mass‑loss rates below 0.02% after exposure to strong acids and alkalis for extended cycles. This stability allows the ring to operate in chemical systems where metallic rings typically corrode within 3–6 months.
-
Resistance to Chloride and Solvent Media
Chloride‑containing and solvent environments cause dimensional drift of over 10% in stainless steel components over a one‑year cycle, while MSZ rings show changes below 0.5%. This performance ensures consistent sealing and structural reliability.
-
High Chemical Inertness at Temperature
At 800–1000°C, corrosion progression in MSZ materials remains under 0.01 mm/year, significantly outperforming alloy steels under the same conditions. This enables multi‑year operation without frequent replacement.
-
High Surface Hardness
MSZ materials provide hardness values comparable to HRA 88–90, reducing abrasive wear that causes up to 15% failure rates in metal rings in rotating machinery. This property supports extended service intervals.
-
Low Wear Volume Loss
Pin‑on‑disk test data show wear volume loss below 1.0 × 10⁻⁶ mm³/N·m, whereas hardened steels often exceed 25 × 10⁻⁶ mm³/N·m. This reduction directly lowers maintenance frequency in continuous‑operation systems.
-
Stable Strength Over Long Cycles
After 500+ mechanical loading cycles, MSZ rings retain more than 95% of their original bending strength. Comparable alumina components can fall below 70%, indicating reduced reliability.
Technical Specifications of Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring
ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring exhibits stable thermal performance, mechanical durability, and corrosion resistance in high-demand industrial environments involving repeated thermal cycling and chemically aggressive media.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Composition |
ZrO₂ + 8–10 mol% MgO |
| Crystalline Phase |
Cubic / Partially Stabilized |
| Density |
≥ 5.60 g/cm³ |
| Vickers Hardness |
≥ 1200 HV |
| Flexural Strength |
≥ 300 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
≥ 2000 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness (K₁c) |
≥ 5 MPa·m¹ᐟ² |
| Thermal Conductivity (RT–1000°C) |
2.0–2.5 W/m·K |
| Maximum Working Temperature |
≥ 1000°C, stable under thermal cycling |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
> 100 cycles (1000°C → RT) |
| Volume Resistivity @1000°C |
≥ 10¹⁰ Ω·cm |
| Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) |
26–28 |
| Chemical Resistance |
Excellent in HCl, H₂SO₄, NaOH environments |
| Open Porosity |
≤ 0.2% |
| Magnetic Permeability (μ) |
≈ 0, non-magnetic |
Dimensions of Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring
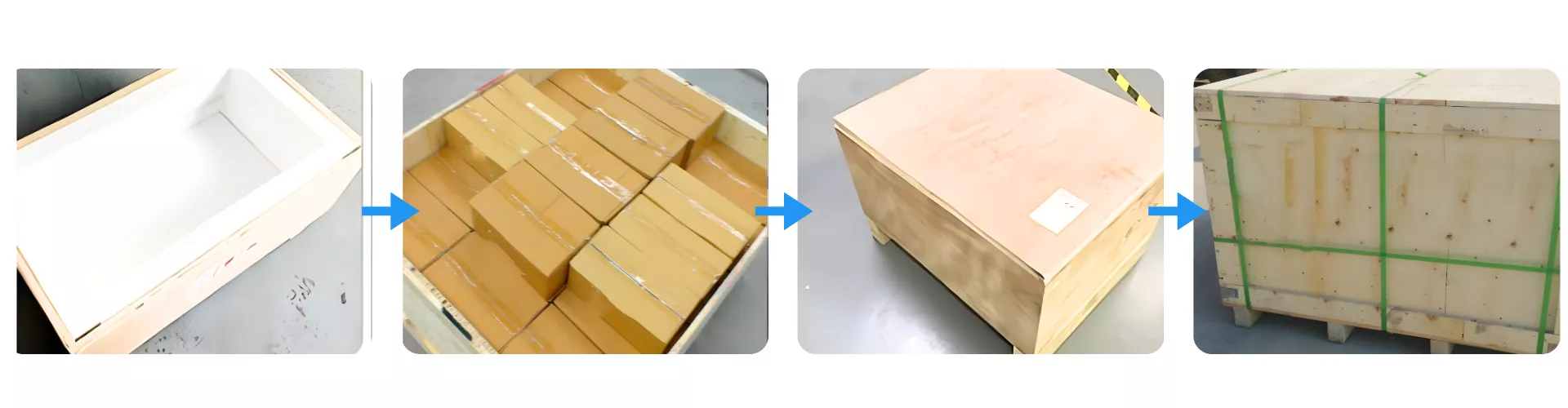
Packaging for Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring
Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring is securely packed using multilayer protection including shock-absorbing foam, sealed carton boxes, and reinforced plywood crates. Each unit is individually boxed to prevent mechanical impact during transit. Final export packaging complies with international pallet standards for sea and air freight.

ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring Resolves High-Load, High-Corrosion, and Thermal Shock Challenges in Critical Equipment Interfaces
ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring developed by ADCERAX® plays a pivotal role in enabling long-life sealing, support, and insulation functions across harsh industrial zones where traditional materials suffer rapid degradation under chemical and thermal fatigue.
-
Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring in Slag-Contact Interfaces of Continuous Casting Rollers
✅Key Advantages
1. High-Cycle Thermal Shock Durability
The MSZ ring tolerates temperature swings of 900–1000°C → cooling water without microcracking for >150 cycles, far exceeding alloy rings that crack within 30–50 cycles. This stability resists quench-induced fatigue at the roller interface.
2. Anti-Slag Infiltration Surface
With open porosity below 0.2%, molten slag and scale particles cannot penetrate the ring surface. This prevents dimensional swelling and erosion that typically alter roller alignment after weeks of service.
3. Abrasion Resistance Under Scale Loading
The Vickers hardness of ≥1200 HV withstands abrasive steel scale impact during each casting pass. This reduces wear scars and maintains a constant contact geometry critical for stable strand guidance.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A European steel plant reported premature failure of alloy roller rings, which developed microcracks and 0.3–0.5 mm dimensional loss after 6–8 weeks under slag splash and rapid quenching. After replacing these components with ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Rings, the service life extended to over 20 weeks with no recorded cracking or loss of roundness. This reduced unplanned stoppages by 40% and stabilized casting throughput by ensuring consistent roller alignment under continuous hot–cold cycling.
-
Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring in Metering Pump Sleeves for Chlor-Alkali Transfer Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. Zero Pitting in Chloride-Rich Media
MSZ material exhibits <0.02% mass loss after 72‑hour exposure to HCl and NaClO, while stainless alloys show visible pitting within similar timeframes. This ensures long-term sealing integrity in high-oxidizer environments.
2. Dimensional Stability in Low-pH Operation
Even after continuous immersion in pH 1–2 solutions, MSZ rings maintain dimensional drift below 0.5%, preventing variations in dosing accuracy. Metallic sleeves typically deform or erode, causing volumetric error over time.
3. No Polymer-Type Swelling or Softening
Unlike PTFE or elastomeric components that expand by 2–5%, MSZ maintains a rigid crystalline phase regardless of chemical exposure. This prevents clearance loss and the resulting leakage or shaft scoring inside the metering pump.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A chemical processing facility operating sodium hypochlorite dosing pumps reported seal failures every 10–12 weeks due to pitting corrosion on Hastelloy sleeves and swelling of polymer components. Introducing ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Rings extended sleeve life to over 12 months with zero observed dimensional drift or leakage events. This improvement cut pump recalibration frequency by 75%, stabilized dosing precision, and reduced maintenance downtime across the continuous chlor-alkali process line.
-
Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring in High-Speed Grinding Spindles for Tool Manufacturing
✅Key Advantages
1. Low Thermal Conductivity for Heat Isolation
The MSZ ring’s thermal conductivity of 2.0–2.5 W/m·K minimizes heat transfer from friction points into the spindle bearing zone. This reduces thermal drift that typically causes alignment shifts at speeds over 10,000 RPM.
2. Non-Magnetic, Encoder-Safe Material
With magnetic permeability ≈ 0, MSZ rings eliminate magnetic interference affecting spindle encoders. This prevents signal noise observed when steel rings cause encoder jitter or fluctuation during high-RPM rotation.
3. Wear Stability Under High Surface Velocity
Hardness ≥ 1200 HV resists wear marks and micro-chatter initiation. Where alumina rings degrade under high-frequency vibration, MSZ maintains consistent surface integrity—supporting precise tool concentricity.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A precision tool manufacturer experienced thermal creep and encoder noise in high-speed grinding spindles running at 10,000–15,000 RPM, caused by alumina ring wear and steel ring magnetic interference. After switching to ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Rings, spindle displacement dropped by 35%, encoder jitter was eliminated, and grinding accuracy remained within tolerance over 40% longer operating cycles. This reduced recalibration intervals and enhanced tool dimensional consistency during continuous production.
How to Maximize the Performance of ADCERAX® Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring Across Industrial Use Cycles
The proper handling, integration, and maintenance of Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia MSZ Ceramic Ring in your system is essential to ensure its full material advantages under high temperature, chemical, and load cycling conditions. This guide outlines best practices to help users extend service life and reduce the risk of premature failure across metallurgical, chemical, and mechanical applications.
-
Storage and Pre-Installation Handling
1. Store in a stable temperature environment
Fluctuations beyond ±10°C/day can create micro-stress in dense ceramics. Keep rings away from direct sunlight, heaters, and high-humidity zones.
2. Use original packaging for interim storage
The multilayer foam-carton-wood structure minimizes vibration risk. Partial unboxing without re-protection may cause edge chipping or hairline cracks.
3. Avoid direct contact with concrete or metal surfaces
Store only on clean plastic trays or anti-static mats. Contact with unclean surfaces can introduce micro-abrasives into mounting zones.
-
Installation Best Practices
1. Verify axial and radial alignment before pressing
Misalignment beyond 0.1 mm can create concentrated loads that exceed ceramic tolerances. Use alignment pins or jigs to control fit geometry.
2. Use elastic intermediary materials where applicable
In metal-ceramic interface zones, install PTFE or graphite washers to buffer differential thermal expansion. This avoids shear stress accumulation.
3. Tighten fixtures in a cross-pattern sequence
Uniform preload reduces ring distortion. Over-tightening localized fasteners may induce asymmetric stress and premature ring fatigue.
-
Operational Guidelines in Active System Conditions
1. Do not exceed continuous operating temperatures of 1000°C
Short-term spikes must remain under 1100°C, or long-term structural phase changes may occur. Use in combination with thermocouple monitoring.
2. Prevent rapid temperature drops >150°C/min
High thermal gradients increase fracture risk, especially in rings with asymmetrical geometry or tight insertion zones.
3. Avoid chemical exposure beyond compatibility range
While resistant to most industrial acids and bases, prolonged exposure to HF or fluorine-bearing gases should be avoided unless lab-qualified.
-
Inspection, Maintenance, and Replacement Recommendations
1. Conduct quarterly surface wear and fracture inspections
Use 10× magnification to check for chipping, grain pull-out, or crack initiation. Early-stage wear signs can be invisible to the naked eye.
2. Track hours of exposure in cyclic thermal environments
For rings in quenching or alternating high-heat zones, record every 500-hour segment to anticipate material fatigue before visible degradation.
3. Replace rings after deformation exceeds 0.02 mm
Even if surface looks intact, diameter drift beyond this threshold may compromise sealing, insulation, or mechanical support function.