Ceramics Across EV System Requirements
EV Industrial Ceramics are used in electric vehicle systems where insulation stability, structural strength, and thermal control must remain consistent under continuous electrical load.
As operating voltage increases and component spacing becomes tighter, electric vehicle ceramic components are widely applied in power electronics assemblies, high-voltage interfaces, and thermal transfer paths where metals and polymers lose reliability.
Material systems such as alumina, ZTA, boron nitride, and aluminum nitride are selected to provide electrical isolation, mechanical support, and controlled heat flow across different EV applications.
In electric vehicles, engineering ceramics for EV systems function as load-bearing and insulating components rather than secondary or auxiliary materials.
resists leakage at elevated voltage levels
remains stable against coolant and vapor contact
Supports insulation or controlled heating functions
supports load without deformation or creep
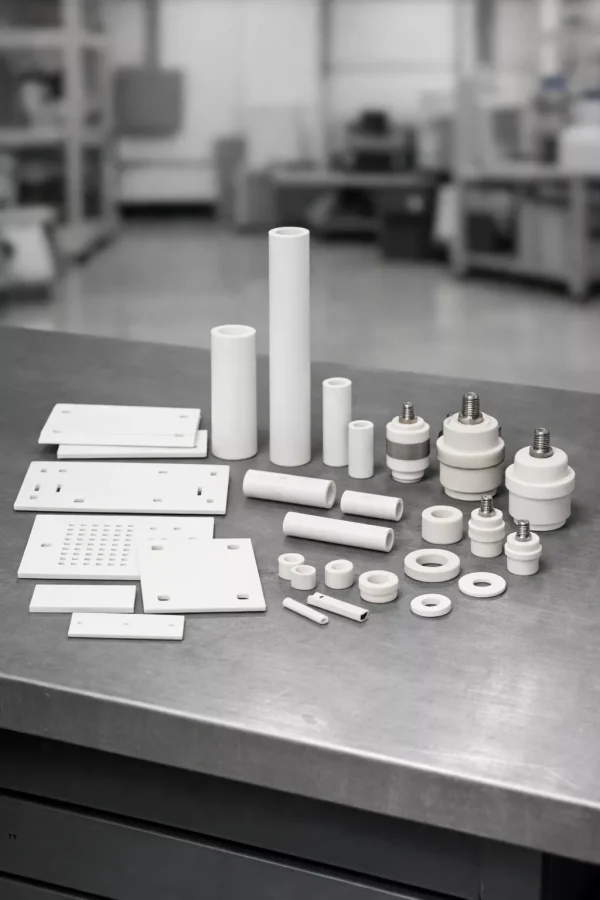

ADCERAX® Material Properties Supporting EV Ceramic Performance
Material behavior in EV Industrial Ceramics determines whether insulation, load support, and heat control remain stable throughout long operating cycles in electric vehicle systems.
Thermal Properties
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Max Continuous Service Temp (°C) | Thermal Expansion (10⁻⁶/K) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (96–99.5%) | 24–30 | 1600 | 7.5–8.0 | Measured at 25–1000 °C, air |
| ZTA Ceramic | 18–22 | 1500 | 7.8–8.2 | Measured at 25–1000 °C, air |
| Boron Nitride (Hexagonal) | 25–60 (anisotropic) | 900 | 1.0–2.0 | Basal plane, inert atmosphere |
| Aluminum Nitride | 160–180 | 1400 | 4.5–5.3 | Measured at 25 °C, air |
Electrical Properties
| Material | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 12–15 | ≥10¹⁴ | 9.5–10.0 | 25 °C, dry condition |
| ZTA Ceramic | 10–13 | ≥10¹³ | 10.0–10.5 | 25 °C, dry condition |
| Boron Nitride | 3–4 | ≥10¹² | 3.5–4.0 | 25 °C, dry condition |
| Aluminum Nitride | 10–15 | ≥10¹³ | 8.5–9.0 | 25 °C, dry condition |
Chemical Stability
| Material | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Oxidation Behavior | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Stable in most acids | Stable except strong alkali | Stable up to 1000 °C | Immersion tests, 25 °C |
| ZTA Ceramic | Stable in weak acids | Limited resistance | Stable up to 900 °C | Immersion tests, 25 °C |
| Boron Nitride | Inert to most chemicals | Reacts with strong alkali | Oxidizes above 850 °C | Static exposure tests |
| Aluminum Nitride | Hydrolysis sensitive | Limited alkali resistance | Oxidizes above 700 °C | Controlled humidity tests |
Mechanical Properties
| Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 300–380 | 3.5–4.0 | 320–380 | 3-point bending, RT |
| ZTA Ceramic | 600–800 | 5.5–7.0 | 300–330 | 3-point bending, RT |
| Boron Nitride | 30–50 | 2.0–2.5 | 30–40 | Machined specimen, RT |
| Aluminum Nitride | 320–360 | 3.0–3.5 | 310–330 | 3-point bending, RT |
Application Areas of EV Industrial Ceramics
In electric vehicle systems, EV industrial ceramics are applied according to how different materials address insulation performance, structural loading, and thermal control requirements within specific operating environments.
High Voltage Switching Assemblies
Alumina-based ceramic structures are widely used in EV high voltage switching systems where insulation stability and dimensional control directly affect electrical safety.
- Alumina ceramic maintains insulation integrity under repeated high-voltage switching cycles in relay assemblies.
- Metallized interfaces enable stable ceramic-to-metal sealing within compact high voltage enclosures.
- Dimensional stability supports consistent contact alignment during long-term EV operation.
Provides insulation stability for compact EV high voltage relay assemblies
Structural Support Interfaces
Zirconia Toughened Alumina materials are selected for EV components exposed to mechanical load and thermal fluctuation within constrained system layouts.
- ZTA ceramic substrate supports mechanical loading in EV assemblies requiring fracture resistance.
- Improved toughness reduces cracking risk under vibration and thermal cycling conditions.
- Structural consistency maintains alignment accuracy in power and control modules.
Supports load-bearing structures in EV power and control assemblies
Thermal Isolation Components
Boron nitride materials are applied in EV systems where controlled heat flow and electrical isolation must coexist in confined thermal environments.
- Boron nitride tube guides heat away from sensitive EV components without electrical conduction.
- Thermal stability maintains predictable performance under continuous temperature gradients.
- Chemical inertness supports long-term use near coolants and vapor exposure zones.
Manages localized heat while maintaining insulation in EV systems
Power Module Heat Dissipation
Aluminum nitride substrates are specified in EV power electronics where heat dissipation efficiency directly influences module reliability.
- Aluminum nitride ceramic enables rapid heat transfer away from high-density power devices.
- Copper bonded layers support electrical connection and thermal spreading within compact modules.
- Thermal consistency improves service life across repeated power cycling conditions.
Enhances heat dissipation in EV power electronic modules
EV Ceramic Selection Aligned With System Requirements
EV Industrial Ceramics are specified according to insulation limits, mechanical loading, and thermal behavior within electric vehicle systems.
Engineering evaluation at the material and geometry level helps reduce qualification risk across power electronics and high-voltage assemblies.
ADCERAX® Industrial Ceramic Categories for EV Applications
Material selection in EV Industrial Ceramics is guided by insulation demands, structural loading conditions, and thermal management requirements across different electric vehicle systems.

Aluminum Oxide
Alumina-based components are commonly used where electrical insulation and dimensional stability are required in EV assemblies.
- High voltage insulation reliability
- Metallization compatibility stability
- Consistent dimensional tolerance

ZTA
Zirconia Toughened Alumina materials are specified for EV components exposed to mechanical load and thermal variation.
- Improved fracture resistance
- Structural load stability
- Thermal shock tolerance

Boron Nitride
Boron nitride components are selected for EV environments requiring thermal control combined with electrical isolation.
- Controlled heat transfer paths
- Electrical insulation performance
- Chemical stability in service
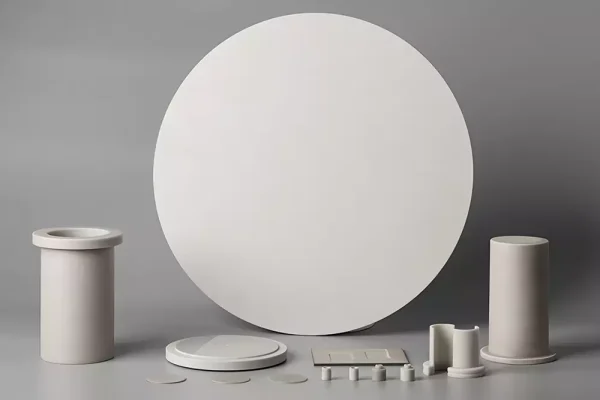

Aluminum Nitride
Aluminum nitride substrates are applied in EV power electronics where heat dissipation and insulation must coexist.
- High thermal conductivity
- Electrical insulation integrity
- Power module integration
Integrated Manufacturing Services for EV Ceramic Components
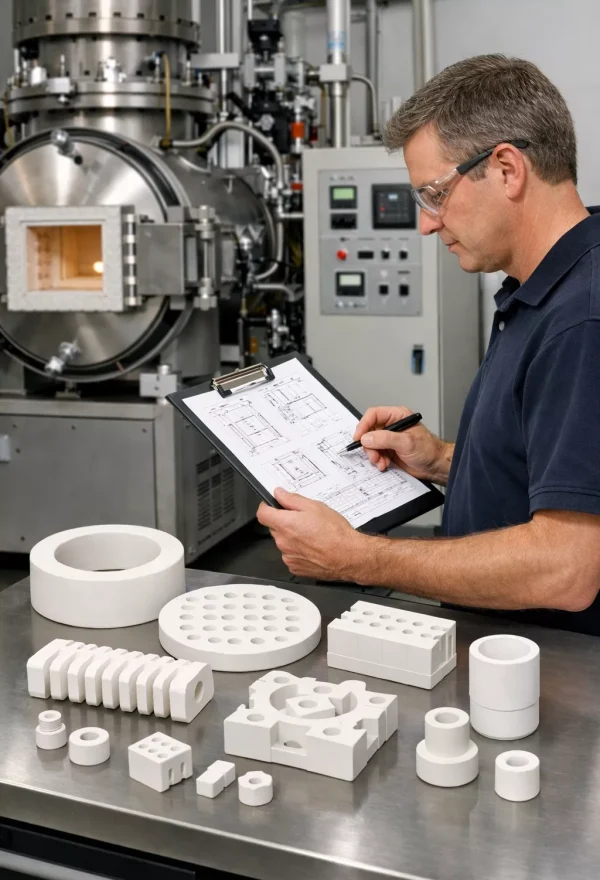

ADCERAX® provides integrated manufacturing support for EV ceramic components used in high-voltage switching, structural support, thermal isolation, and power module assemblies across electric vehicle systems.
For electric vehicle industrial ceramics, manufacturing capability directly determines whether material performance can be realized at component level.
End-to-end control across forming, machining, joining, and surface preparation enables ceramic components to meet electrical, thermal, and mechanical requirements defined at application level.
align ceramic grade with electrical and thermal requirements
achieve near-net shapes with controlled shrinkage behavior
hold critical dimensions within ±0.02–0.05 mm range
apply uniform Mo-Mn layers for ceramic-metal joining
support brazing or copper bonding for EV assemblies
deliver defined roughness for sealing or contact interfaces
ADCERAX® Advanced Processing of EV Industrial Ceramics
Dimensional Control Machining
Precision machining enables complex ceramic geometries to meet tight dimensional and surface requirements within EV assemblies.
multi-axis ceramic machining centers, ≤0.02 mm tolerance
diamond tooling optimized for brittle ceramic cutting
Ra 0.4–0.8 μm on functional interfaces
Ceramic-to-Metal Interface Formation
Metallization processing creates reliable ceramic-to-metal interfaces required in EV high-voltage and power electronics applications.
Mo–Mn metallization with controlled layer thickness
hydrogen or controlled atmosphere furnaces up to 1500 °C
shear strength typically ≥120 MPa after brazing
Ceramic Bonded Assembly Integration
Bonding integration connects ceramic components with metal or copper structures for electrical and thermal functionality.
vacuum brazing furnaces below 10⁻⁴ Pa
copper bonding on AlN substrates up to 300 μm
low interface resistance for heat transfer efficiency
Custom Engineering for EV Ceramic Components
Custom ceramic components for EV programs are defined by application-specific electrical, thermal, and mechanical constraints rather than standard part catalogs.
For EV Industrial Ceramics, effective customization requires early alignment on material selection, geometry tolerance, and interface conditions across high-voltage, structural, and power electronics systems.
Engineering discussions initiated at the drawing or application stage help ensure ceramic components are manufacturable and compatible with EV system requirements.
ADCERAX® EV Industrial Ceramics Addressing Engineering Constraints in EV Systems
Industrial ceramic components provide stable dielectric strength that is inherently insensitive to temperature and aging. In EV engineering systems, insulation failure often occurs under coupled thermal and electrical stress rather than voltage alone. Ceramic materials for EV high voltage systems maintain predictable insulation behavior across long operating cycles.
Alumina-based industrial ceramic components combine electrical insulation with mechanical rigidity and dimensional stability. Relay housings require fixed insulation spacing under heat and vibration, which polymers and metals cannot maintain consistently. Engineering ceramics for EV systems preserve geometry and insulation integrity throughout service life.
Industrial ceramics offer a unique balance between electrical insulation and controlled thermal conductivity. Power electronics require heat dissipation without creating conductive paths. Ceramic components for EV power electronics satisfy both constraints within compact assemblies.
Rising EV system voltages reduce insulation margins and increase electric field intensity. Industrial ceramic materials exhibit high dielectric strength independent of humidity or aging mechanisms. This property allows ceramic materials for EV high voltage systems to support higher voltage architectures safely.
Thermal cycling introduces internal stress due to material expansion mismatch. Engineering ceramics for EV systems resist microcrack initiation through stable crystal structures and controlled grain boundaries. This supports long-term reliability in dynamic EV operating conditions.
Many EV components require both insulation and mechanical attachment to metal structures. Industrial ceramic components support metallization and brazing to form stable ceramic-to-metal interfaces. These interfaces maintain electrical isolation while tolerating thermal and mechanical loads.
Certain engineering ceramics exhibit high flexural strength and fracture toughness. In EV systems, this allows ceramic components to carry mechanical loads while remaining electrically insulating. Such dual functionality reduces part count and assembly complexity.
Compact EV architectures demand thinner insulation and tighter spacing. Industrial ceramic components provide high dielectric strength even at reduced thickness. This enables higher integration density without compromising electrical safety.
Metals can soften, oxidize, or creep under heat and electrical fields. Industrial ceramic components retain mechanical and electrical properties under combined thermal, electrical, and mechanical stress. This behavior aligns with long-life requirements in EV engineering systems.
EV environments introduce vibration from road and drivetrain dynamics. Properly engineered industrial ceramic components resist fatigue and crack propagation. This ensures stable performance in mobile EV systems.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

