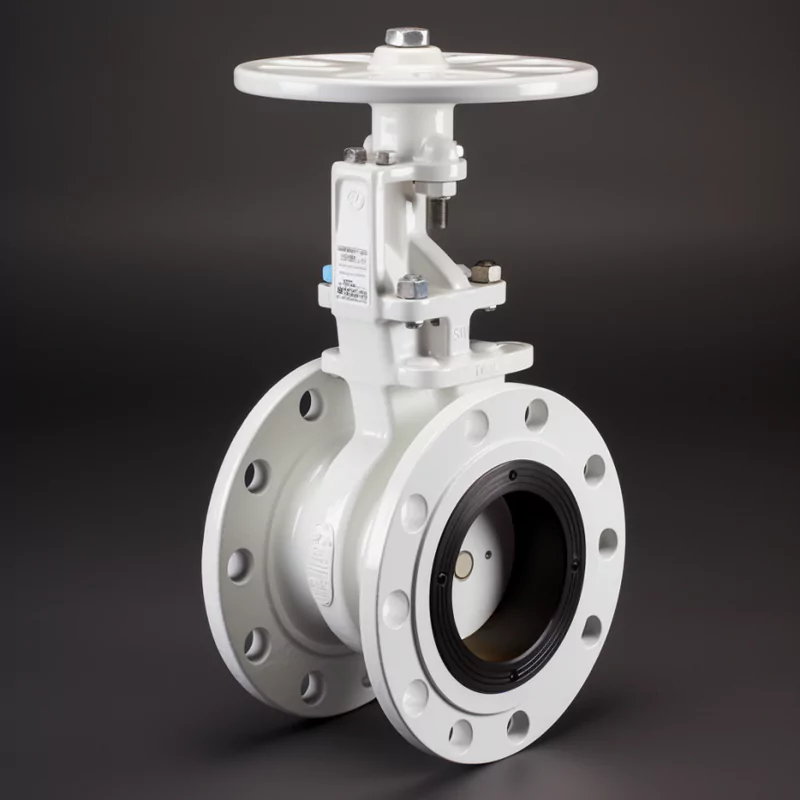
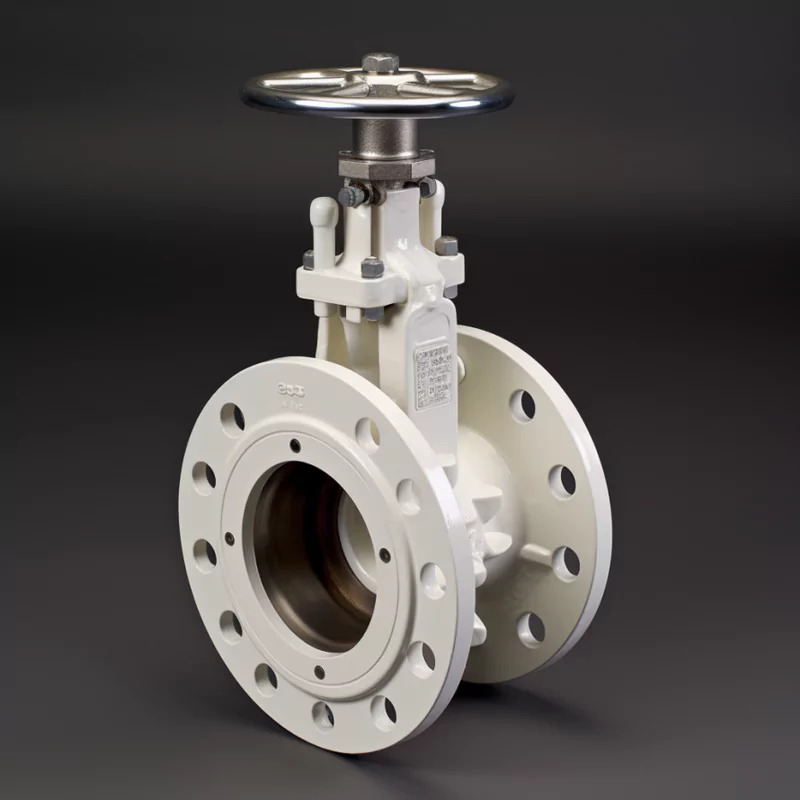
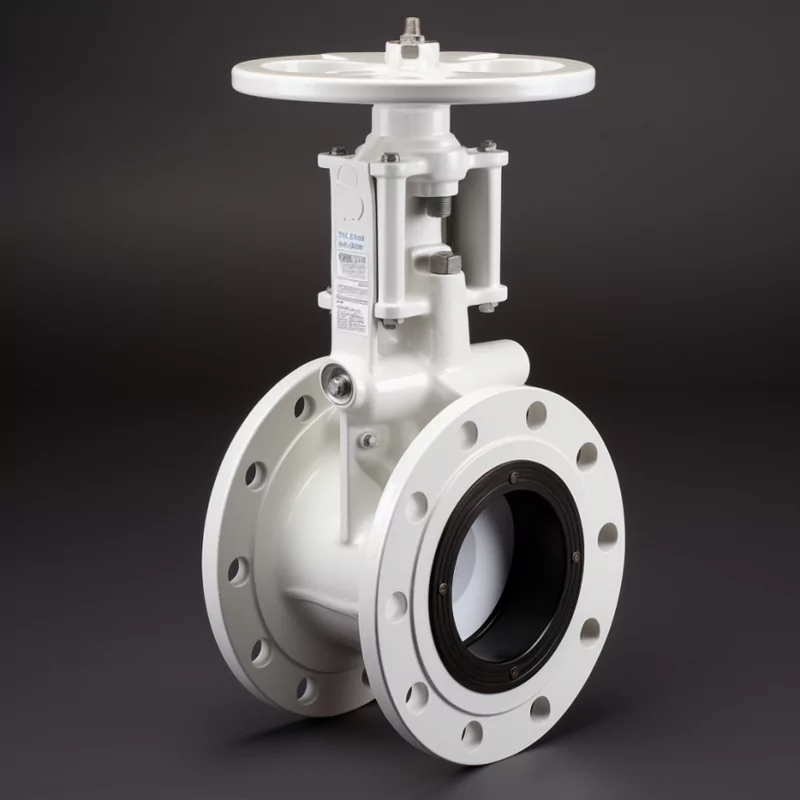
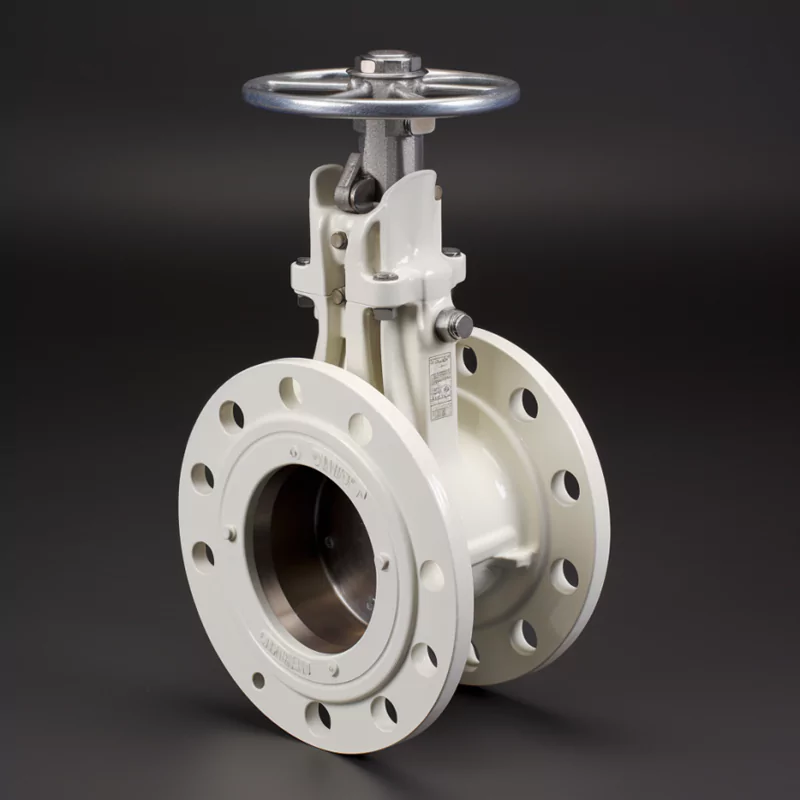
ADCERAX® Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve is designed for industries that face abrasive and corrosive media such as ash, slurry, and chemical solutions. Its zirconia ceramic discs provide high hardness and chemical stability, ensuring secure shut-off and extended service life. This valve is widely applied in power generation, mining, chemical processing, and water treatment systems where reliability and long-term performance are critical.
Features of Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
- The zirconia ceramic discs reach HRA 88 hardness, which is about 8 times higher than standard carbon steel, ensuring superior resistance to abrasive particle erosion.
- Independent tests show valves with zirconia sealing surfaces last 3–5 times longer than conventional metal gate valves in slurry transport systems.
- In coal-fired power plants, ceramic disc valves reduce unplanned shutdowns by up to 40%, directly lowering maintenance and replacement costs.
- The double disc structure provides bi-directional sealing, achieving leakage rates below Class V (FCI 70-2 standard) in both high- and low-pressure lines.
- Field performance data indicate ceramic-to-ceramic sealing can sustain over 100,000 open/close cycles without measurable degradation.
- When used in chemical pipelines, zirconia ceramic valves maintain zero visible leakage even after 12 months of continuous operation.
- Zirconia ceramics demonstrate corrosion resistance up to pH 2–12, outperforming stainless steel in acidic and alkaline environments.
- In pulp and paper processing, valve lifespan extends by 30–50% compared to alloy-based alternatives due to chemical inertness.
- Data from wastewater plants show zirconia ceramic valves maintain structural integrity after exposure to 200°C temperatures and abrasive slurry for over 18 months of service.
Technical Properties for Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
The Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve is engineered with advanced zirconia ceramic materials and metal housings to deliver high hardness, chemical stability, and long service life.
| Property |
Pure Zirconia (Monoclinic) - Unstabilized |
Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) |
Magnesia-stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ) |
| Typical Purity |
High-purity raw material, but unstabilized for the final product |
High purity |
High purity |
| Crystal Phases (at RT) |
Monoclinic (stable up to ~1170°C); Tetragonal and Cubic at higher temperatures. |
Primarily, Metastable Tetragonal can have a Cubic phase. |
Partially stabilized with tetragonal precipitates in a cubic matrix. |
| Density (g/cm³) |
5.65–6.05 |
5.85-6.1 |
~5.7 |
| Melting Point (°C) |
~2700-2715 |
Very High (similar to pure zirconia, but phase stability is key) |
Very High |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Low (approx. 2-3) |
Low (approx. 2.5-3) |
Low (approx. 3) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10⁻⁶/K) |
~10 |
9.5-10 |
10 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) |
Poor (due to phase transformation and brittleness) |
Up to 1000, 710-900 |
500 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) |
Not typically used structurally |
~2000 |
~2500 |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa·m^0.5) |
Low (inherently brittle) |
Up to 10 (exceptionally high for ceramics due to transformation toughening), 8-9 |
6 |
| Hardness (Vickers, HV1) |
Moderate |
11-13 GPa, 1100-1220 kg/mm² |
1100 kg/mm² |
| Chemical Inertness |
Excellent in acids and alkalis |
Excellent |
Excellent |
| Biocompatibility |
Generally good, but stabilized forms are preferred for medical use |
Excellent, widely used in dental and medical implants |
Good |
| Typical Applications |
Refractories (at high temperatures) |
Structural ceramics, dental implants, oxygen sensors, cutting tools, thermal barrier coatings |
Refractories, structural components requiring specific thermal properties |
Specifications of Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
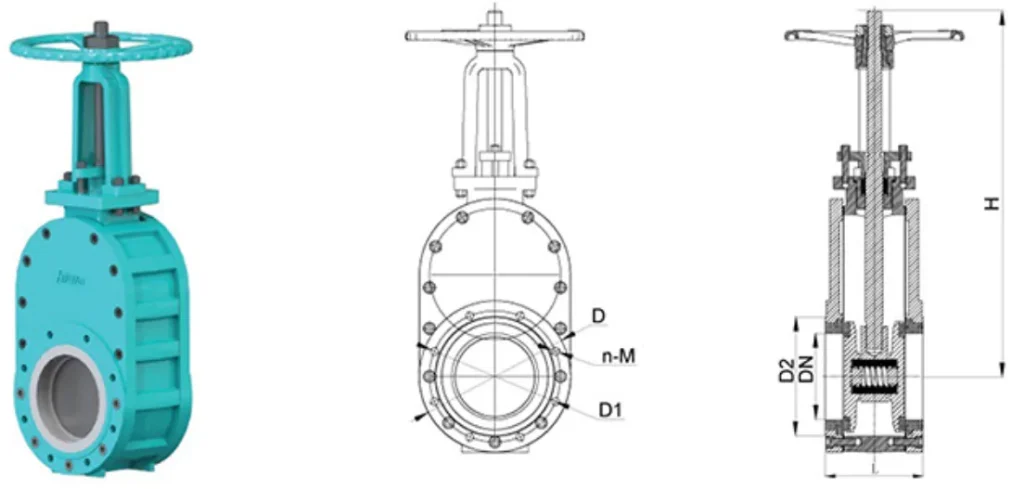
|
Model |
inch |
DN(mm) |
L |
D |
D1 |
D2 |
n-M |
H |
Notes |
|
AT-ZV2-S001 |
2" |
50 |
90 |
160 |
125 |
99 |
4-M16 |
380 |
Nominal Diameter: DN50–DN250;
Working Pressure: 1.0 MPa–1.6 MPa;
Operating Temperature: -20°C to 180°C;
Connection Types: Flanged, Wafer;
Actuation Methods: Manual. |
|
AT-ZV2-S002 |
2 1/2" |
65 |
125 |
185 |
145 |
118 |
4-M16 |
485 |
|
AT-ZV2-S003 |
3" |
80 |
140 |
200 |
160 |
132 |
8-M16 |
490 |
|
AT-ZV2-S004 |
4" |
100 |
170 |
220 |
180 |
156 |
8-M16 |
585 |
|
AT-ZV2-S005 |
5" |
125 |
185 |
250 |
210 |
184 |
8-M16 |
630 |
|
AT-ZV2-S006 |
6" |
150 |
200 |
280 |
240 |
211 |
8(12)-M20 |
750 |
|
AT-ZV2-S007 |
8" |
200 |
220 |
340 |
295 |
266 |
8(12)-M20 |
830 |
|
AT-ZV2-S008 |
10" |
250 |
220 |
395 |
350 |
320 |
12-M20 |
985 |
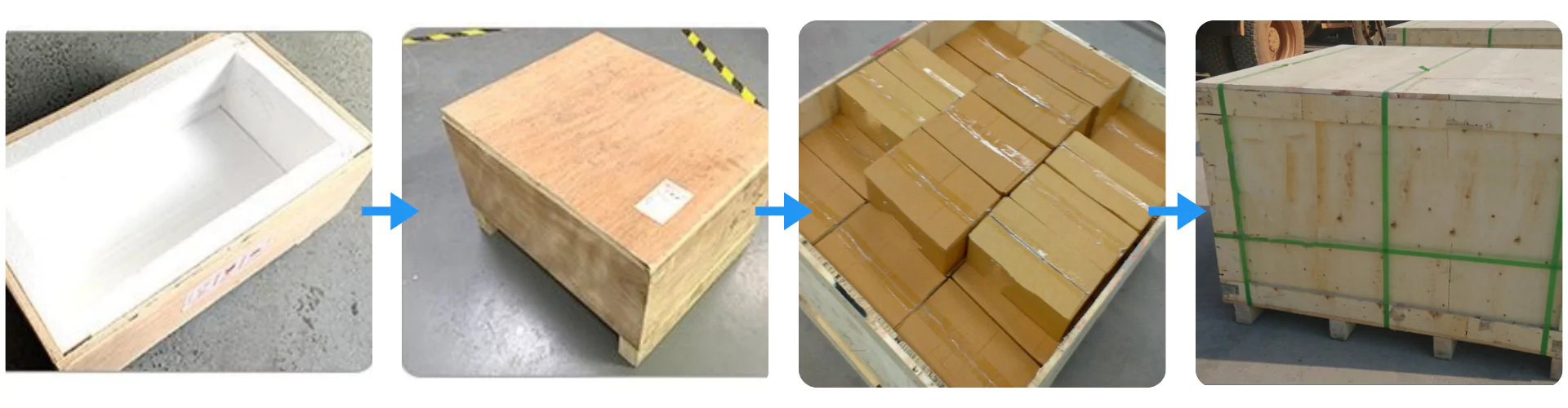
Packaging of Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
Each Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve is first protected with foam-lined wooden boxes to prevent impact during transit. Valves are then packed into reinforced cartons and secured inside export-grade wooden crates for bulk shipment. This ensures them arrives intact, safe, and ready for installation.

Solving Application Challenges with ADCERAX® Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
The Manual ZrO2 Double Disc Gate Valve addresses the critical challenges of industries handling abrasive, corrosive, or high-temperature media. By combining zirconia ceramic hardness with bi-directional sealing and chemical inertness, it provides measurable solutions in specialized industrial environments.
-
Dry Ash Hopper Discharge
✅Key Advantages
1. Bi-Directional Class V Sealing — Verified both flow directions to FCI 70-2 Class V at line classes PN10–PN16; prevents reverse leakage during hopper pressure equalization.
2. High-Temperature Abrasion Endurance — Zirconia discs at HRA ≥ 88 maintain sealing for >100,000 cycles in fly-ash service at 200–350 °C.
3. Maintenance-Ready Manual Control — Handwheel rising-stem with dual cleaning/drain ports supports safe isolation and purging during planned outages.
✅ ️Problem Solved
At coal units handling dry fly ash, metal knife gates leaked under variable head, causing blockages and unplanned cleanups. After switching to ADCERAX® Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve (PN16, Class V), sites reported fewer reverse-flow events and longer service intervals, aligned with >100,000-cycle endurance and HRA ≥ 88 sealing faces. Plants documented outage work confined to planned windows as purging leveraged the dual side ports, and unplanned shutdowns fell up to 40% in the first season.
-
High-Density Slurry Recirculation Loops
✅Key Advantages
1. Dual-Direction Shut-Off in Slurry — Double-disc design sustains Class V sealing under recirculating loads at PN10–PN16, preventing back-mixing.
2. Extended Wear Life in Abrasives — Zirconia sealing faces (HRA ≥ 88) deliver >12 months typical service in dense mineral slurries versus metal gates.
3. Actuator-Free Reliability — Manual handwheel operation reduces actuator failure points; cycle life validated at >100,000 cycles in slurry duty.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A concentrator loop experiencing seal loss every 3–6 months on metal gates adopted ADCERAX® Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve. With bi-directional Class V shut-off and HRA ≥ 88 discs, mean time between interventions exceeded 12 months, and unexpected stoppages tied to valve leakage were eliminated across the review period. Manual local control simplified spares and reduced logistics burden at remote sites.
-
Neutralization Tank Outlet Control
✅Key Advantages
1. Corrosion Stability Across pH 2–12 — Zirconia ceramic sealing resists alternating acidic/alkaline streams, preserving surface integrity.
2. Reverse-Flow Isolation for Batches — Double-disc geometry maintains Class V shut-off in both directions, avoiding cross-contamination between cycles.
3. Manual Precision Metering — Rising-stem travel enables fine outlet control; installations have held zero visible leakage after 12 months of batch operation.
✅ ️Problem Solved
Facilities running alternating acid/alkali batches saw butterfly and ball valves corrode and leak during reverse isolation, destabilizing pH control. Replacing them with ADCERAX® Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve delivered pH-range (2–12) compatibility and bi-directional Class V sealing, keeping outlet pH within tight process bands and removing contamination events through consecutive campaigns. Maintenance records showed stable performance over 12 months without leakage rework.
User Guide for Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve
Proper operation of a Manual ZrO2 Double Disc Gate Valve requires careful handling, installation, and maintenance. This guide provides practical recommendations to help users maximize service life, ensure safe operation, and reduce unnecessary downtime.
-
Pre-Installation Checks
1. Visual inspection: Examine the valve body and ceramic discs for cracks or visible surface damage before installation. Three minutes of inspection can prevent unexpected leakage in service.
2. Component verification: Confirm flange size, pressure rating, and flow direction alignment with pipeline requirements. This ensures correct fitment and avoids system mismatch.
3. Cleanliness assurance: Flush pipeline to remove debris and foreign particles before mounting the valve. Residual solids can scratch ceramic discs and compromise sealing performance.
-
Installation Guidelines
1. Correct orientation: Position the Manual Zirconia Ceramic Double Disc Gate Valve according to flow direction arrows on the body. Wrong alignment can reduce sealing efficiency and shorten lifespan.
2. Secure tightening: Apply uniform torque to flange bolts during installation. Uneven tightening may distort sealing faces and cause leakage under pressure.
3. Shock prevention: Avoid hammering or direct impact on the valve body when positioning. Sudden shocks may fracture zirconia components due to their brittle nature.
-
Operational Recommendations
1. Gradual operation: Rotate the handwheel slowly during opening and closing cycles. Abrupt movement can stress the discs and accelerate wear.
2. Cycle frequency: Operate the valve at least once every four weeks in idle systems. Regular cycling prevents sticking and maintains smooth sealing contact.
3. Pressure monitoring: Always verify that line pressure stays within the rated limit. Exceeding PN16 or equivalent ANSI rating risks premature failure.
-
Maintenance and Storage
1. Routine inspection: Check for signs of leakage, torque resistance, or unusual vibration after every 500 operating cycles. Preventive maintenance reduces downtime costs.
2. Seal care: Replace sealing elements if leakage exceeds 1% of rated flow. Overused seals compromise Class V shut-off standards.
3. Storage conditions: Store the valve in a dry, vibration-free environment, ideally between 5–40°C. Proper storage maintains dimensional stability and ceramic integrity.












