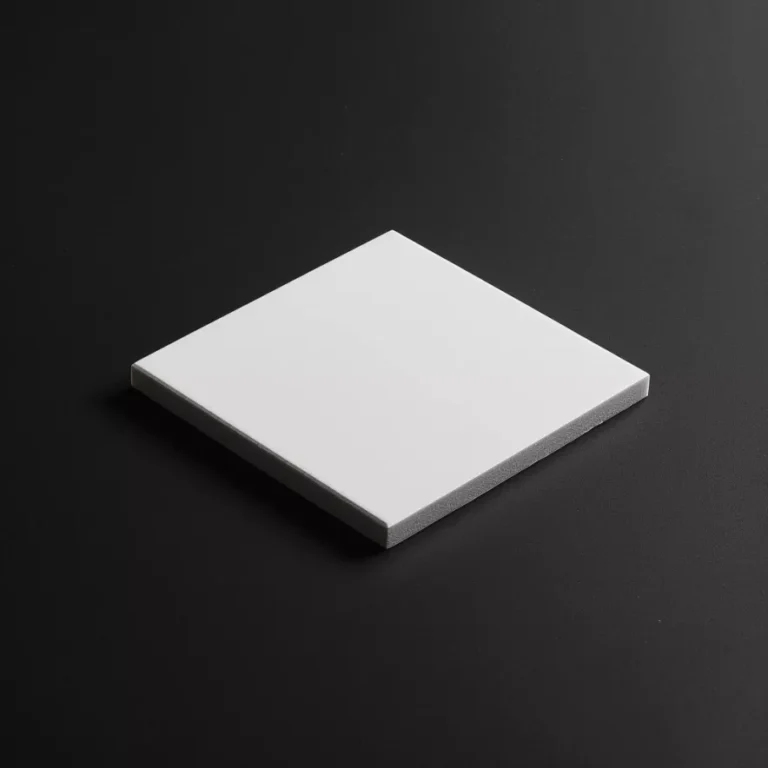
ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block supports demanding industrial systems where wear resistance, corrosion stability, and mechanical strength drive long service life. Engineers use Zirconia Ceramic Block for fluid metering components, oxygen sensing assemblies, and precision structural fixtures that operate under high load or temperature. It maintains reliable performance in chemical exposure and thermal cycling. Zirconia Ceramic Block is suited for manufacturers seeking stable quality and repeatable production supply.
Features of Zirconia Ceramic Block
- Flexural strength reaches up to 1,200 MPa, exceeding most technical ceramics used in pump and wear part assemblies.
- Fracture toughness ranges between 6–10 MPa·m¹⁄², enabling the block to resist edge chipping during repeated assembly or surface contact.
- Compression strength exceeds 2,000 MPa, supporting structural roles under mechanical or fluid pressure.
- Working temperature for PSZ reaches 1,400 °C, enabling safe use in combustion sensors and refractory fixtures.
- Thermal conductivity remains low at 2–3 W/m·K, reducing heat leakage in process environments.
- Resists degradation in pH 1–14 media, making Zirconia Ceramic Block suitable for metering in acid/base chemical loops.
- Remains inert in contact with NaOH, HCl, and sulfur compounds, tested up to 96-hour submersion with no surface change.
- Non-porous structure with ≥99.9% theoretical density, minimizing infiltration or surface reactivity in liquid and gas handling systems.
- Volume resistivity exceeds 10⁸ Ω·cm, suitable for insulating fixtures in mixed conductive assemblies.
Technical Properties for Zirconia Ceramic Block
Zirconia Ceramic Block is designed for performance stability under high stress, temperature fluctuation, and corrosive exposure. Its material properties support structural reliability, dimensional integrity, and electrochemical compatibility across a wide range of critical applications.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Type |
Yttria-Stabilized / Partially Stabilized Zirconia |
| Density |
≥ 6.0 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength |
Up to 1,200 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
> 2,000 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness |
6–10 MPa·m¹⁄² |
| Vickers Hardness |
12.5–13.0 GPa |
| Elastic Modulus |
200–220 GPa |
| Thermal Conductivity |
2–3 W/m·K |
| Maximum Operating Temperature |
1,400 °C (PSZ) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
10–11 ×10⁻⁶/K |
| Volume Resistivity |
> 10⁸ Ω·cm @ 25 °C |
| Dielectric Strength |
10–15 kV/mm |
| Grain Size |
≤ 0.5 μm |
| Apparent Porosity |
< 0.1% |
| Surface Finish (Lapped) |
Ra ≤ 0.2 μm |
Specifications of Zirconia Ceramic Block
|
Zirconia Ceramic Block |
|
Item No. |
Length(mm) |
Width(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
Purity(%) |
|
AT-ZB-0001 |
35 |
20 |
3 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0002 |
48 |
24 |
3.5 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0003 |
52 |
30 |
5 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0004 |
57 |
25 |
12 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0005 |
60 |
21 |
15 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0006 |
63 |
40 |
8 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0007 |
70 |
36 |
8 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0008 |
75 |
45 |
5 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0009 |
80 |
22 |
4 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0010 |
85 |
46 |
5 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0011 |
92 |
50 |
7 |
95 |
|
AT-ZB-0012 |
100 |
43 |
10 |
95 |
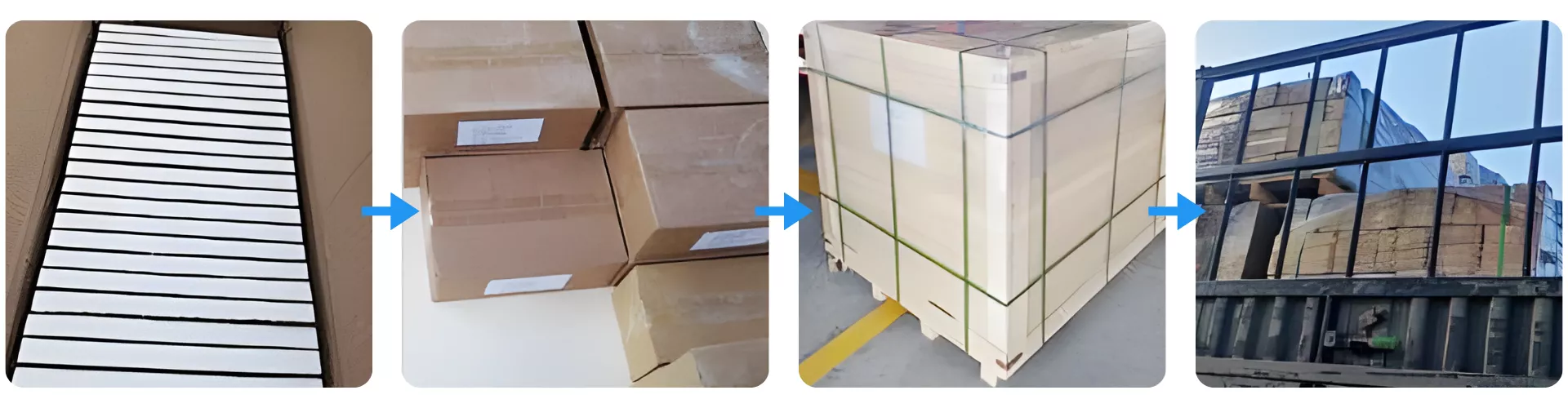
Packaging of Zirconia Ceramic Block
Zirconia Ceramic Block is individually arranged in protective foam slots to prevent surface contact or chipping. Units are then boxed with labeled cartons and stacked onto reinforced export-grade wooden pallets. Final packaging is shrink-wrapped and container-loaded to ensure impact resistance during international transit.

Solving Performance-Critical Challenges Across Precision Industries with ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block
ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block enables advanced engineering performance across multiple high-stress, high-precision sectors. Its combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and chemical inertness makes it a preferred solution where conventional materials fall short under thermal, mechanical, or chemical extremes.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Block in Ultrafine Grinding Equipment
✅Key Advantages
1. Edge Stability Under High RPM
Maintains edge geometry for >12 days continuous grinding at 30,000 rpm. Reduces dimensional drift in sub‑micron powder processing lines.
2. High Wear Factor Efficiency
Hardness ≥12.5 GPa lowers abrasive loss rate by >40% compared with carbide tools in pigment grinding.
3. Consistent Surface Profile
Grain size ≤0.5 μm preserves flatness under cyclic load, stabilizing product particle distribution.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A precision grinding line experienced yield loss of 8–10% due to insert deformation every 72 hours at 30,000 rpm. Surface rounding caused aggressive particle size spread and frequent unplanned tool swaps (4–6 per week). After adopting ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block grinding inserts, tool change frequency dropped to once per 12 days, and particle variation stayed within ±3%, restoring continuous, stable production.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Block in Catalyst Carriers for Fine Chemical Reactors
✅Key Advantages
1. Zero Leaching in Acid/Base Media
Maintains structure under pH 1–14 exposure for >96 h without measurable mass change.
2. High‑Density Support Structure
Density ≥99.9% theoretical prevents contaminant adsorption and carries catalytic layers uniformly.
3. Thermal Shape Retention
Stable up to 1,400 °C in batch reactors, avoiding geometry shift under thermal cycling.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A continuous‑flow reactor used alumina carriers which suffered leaching, leading to 15% catalyst deactivation every 200 hours. This forced shutdowns and disposal of contaminated media. The plant replaced supports with ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block carriers and extended catalyst life cycles by 2.5×, while reducing waste generation and cleaning frequency by >35%.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Block in Lithium Battery Metering Pumps
✅Key Advantages
1. No Ion Migration into Electrolytes
Volume resistivity >10⁸ Ω·cm prevents charge drift and contamination in lithium salt solutions.
2. Surface Integrity for Precision Flow
Polished finish (Ra ≤0.2 μm) lowers particle retention and supports repeatable dosing curves.
3. High Pressure Reliability
Compressive strength >2,000 MPa holds stable displacement under cycling pressure in slurry feed lines.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In a lithium battery gigafactory, metal plungers caused conductivity drift of 12% due to micro‑pitting after 3 weeks in production. Dosing variability resulted in defective cells and increased electrolyte filtration workload. With ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Block plungers installed, drift decreased to <2% over 60 days, improving first‑pass yield and eliminating ion‑leaching risk.
User Guide for Safe Handling and Optimal Operation of Zirconia Ceramic Block
To maximize performance and minimize failure risks, users of Zirconia Ceramic Block must understand its material behavior, compatibility boundaries, and post-machining sensitivities. This guide offers structured best practices for installation, maintenance, storage, and interface design, tailored for industrial users working with fluidic, thermal, or abrasive applications.
-
Installation Guidelines for High-Stress Environments
1. Avoid mechanical overconstraint: Always allow for thermal expansion gaps during fixture design, especially for systems operating above 600 °C. This reduces stress concentration that can trigger edge fracture.
2. Use compliant seating or shimming: When assembling the Zirconia Ceramic Block into metal housings, apply intermediate elastomer layers or ceramic-compatible cushions to mitigate stress transients.
3. Avoid concentrated point loading: Ensure even distribution of applied torque or mechanical contact during installation. Use flat interfaces and matching surface geometry where possible.
-
Cleaning and Maintenance Instructions
1. Avoid high-velocity abrasive blasting: Clean using non-metallic brushes and neutral pH solvents. Harsh mechanical cleaning may micro-damage surface finish or weaken edge zones.
2. Flush systems with inert solvents before restart: After storage or downtime, use ethanol, DI water, or filtered air to remove trace residues. This protects both surface condition and downstream fluid integrity.
3. Inspect contact areas periodically: Every 6–12 months, check for microchipping, discoloration, or surface erosion using a magnifier or white light inspection.
-
Storage and Handling Recommendations
1. Store in dry, vibration-free environments: Keep Zirconia Ceramic Block units in sealed containers or cushioned trays, away from high humidity, shock, or UV exposure.
2. Handle only with nitrile-coated gloves: Avoid contamination from skin oils or abrasives that can affect critical surface finishes, particularly for polished or metering-use units.
3. Separate contact between finished surfaces: Never stack blocks with machined or polished faces touching directly. Use foam, film, or non-scratching separators.
-
Interface Design and Application Matching
1. Avoid mismatched thermal expansion interfaces: When joining with metals or other ceramics, match CTE within ±2 ×10⁻⁶/K to prevent cracking during heat cycling.
2. Minimize edge stress concentration zones: Chamfered or rounded edges should be incorporated into CAD design to at least 0.3 mm radius to mitigate tensile failure risk.
3. Confirm media compatibility in advance: Test exposure to acids, alkalis, or aggressive solvents before full-scale deployment. Zirconia is stable in most cases, but test validation is essential.