ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate is engineered specifically for industrial environments where uniform load distribution, full-surface coverage, and modular installation determine operational stability. Its square geometry enables predictable thermal behavior, consistent support of rectangular furnace chambers, reactor trays, and wear-protection linings—applications where circular or irregular shapes cannot achieve seamless edge alignment or efficient spatial utilization. Through this geometry-driven advantage, the plate provides higher structural reliability, improved stacking logic, and enhanced process consistency in high-temperature, corrosive, and abrasion-intensive systems.
Geometry-Driven Performance Advantages of Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate
-
Uniform Load Distribution Enabled by the Square Architecture
The square layout increases usable surface area by up to 27% compared with circular plates of equivalent span, allowing more stable material loading during high-temperature cycles. This expanded area enhances heat balance uniformity and reduces peripheral stress gradients.
-
Superior Wear Resistance and Edge Integrity for Modular Tiling Systems
Zirconia’s Vickers hardness reaches >1200 HV, and the square edges provide straight-line alignment absent in circular plates. This alignment enables tile-to-tile assemblies with < 1 mm installation gap, reducing abrasion concentration at transition points.
-
High Chemical Stability Across Square-Pattern Reactor Lining Designs
Corrosion tests show < 0.02 mg/cm² mass loss in strong acid environments, enabling long-term lining installation inside rectangular chemical reactors. Square plates eliminate the coverage gaps circular plates leave at corners.
-
Precision Insulation and Dielectric Reliability in Rectangular Electrochemical Devices
The material delivers dielectric strength exceeding 12 kV/mm, and the planar square layout ensures homogeneous electrical isolation across electrode arrays. Circular parts create uneven edge spacing that disrupts field uniformity.
-
Enhanced Thermal Flatness Retention Under Extreme Conditions
Stabilized zirconia exhibits a low thermal expansion coefficient of ~10.5 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹, and when distributed across a square shape, thermal gradients remain symmetrical. This symmetry prevents warpage that frequently occurs in round plates due to radial heat imbalance.
Technical Properties for Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate exhibits stable mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical characteristics derived from its fully dense yttria-stabilized zirconia microstructure, providing consistent performance across high-temperature, corrosive, and wear-intensive industrial environments.
| Property |
Specification |
| Density |
>5.9 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength |
900–1200 MPa |
| Compressive Strength |
>2000 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness (KIC) |
7–10 MPa·m¹ᐟ² |
| Vickers Hardness |
>1200 HV |
| Thermal Conductivity |
2–3 W/m·K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
10–11 ×10⁻⁶ /K |
| Maximum Service Temperature |
up to 1500°C |
| Thermal Shock Resistance |
>200°C/s |
| Dielectric Strength |
>12 kV/mm |
| Volume Resistivity |
>10¹² Ω·cm at 500°C |
| Chemical Stability |
<0.02 mg/cm² mass loss in acids |
| Porosity |
<0.1% fully dense structure |
| Water Absorption |
0% |
| Surface Roughness (as-fired) |
Ra 0.8–1.2 μm |
| Surface Roughness (polished) |
Ra <0.05 μm |
Specifications of Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate
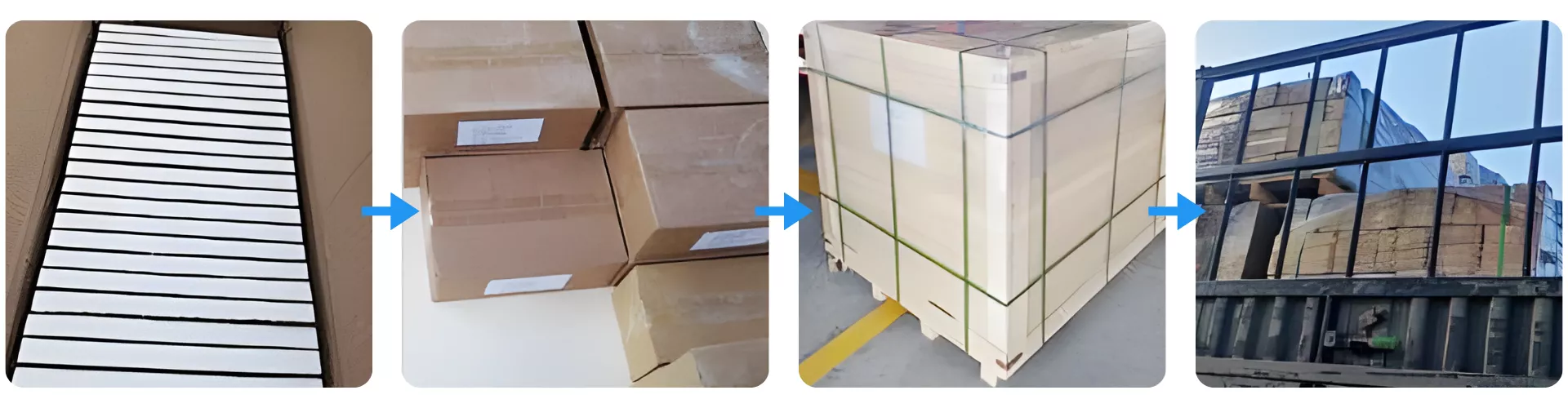
Packaging and Shipment Protection for Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate
Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate is packed through a multi-layer protection workflow to ensure safe arrival under long-distance international transport. Each plate is individually separated, boxed in reinforced cartons, and consolidated into wooden crates with full-surface strapping for vibration control. Final palletized units are securely loaded into containers to prevent movement and protect the ceramic plates from impact, moisture, and stacking pressure during shipment.

ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate Solving Real-World Industrial Application Challenges
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate from ADCERAX® is designed to address specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical challenges in high-temperature process equipment, electrochemical cells, and heavy-duty wear systems where stable planar support and modular coverage are essential. By combining a dense yttria-stabilized zirconia body with a square, tile-ready geometry, it supports long-term reliability in continuous operations where downtime, contamination risk, and uneven thermal loading are key concerns.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate in Chlor-Alkali and Chemical Electrolysis Cells
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Support in Alkaline Brine Cells
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate maintains dimensional stability with thickness variation typically below 0.03 mm after long-term exposure in hot brine environments. This flatness helps keep membrane compression uniform across the cell area, reducing localized mechanical stress by more than 20% compared with conventional metal frames.
2. Reduced Corrosion and Contamination Risk
Mass loss of stabilized zirconia measured in aggressive alkaline and chloride media can be below 0.02 mg/cm² over extended test campaigns. This low dissolution rate minimizes contamination of the electrolyte and supports stable electrochemical performance over thousands of operating hours.
3. Improved Current Distribution Across Rectangular Cells
By providing a consistent planar contact surface, the plate limits geometric distortion that would otherwise cause current hot spots, helping to keep current density variation within ±5% across the active membrane area. More uniform current distribution has been associated with membrane lifetime extensions in the range of 30–40% in properly controlled cells.
✅ ️Problem Solved
In one chlor-alkali plant case, internal metal support structures experienced visible distortion and pitting after less than two years in service, leading to recurring membrane failures and unplanned shutdowns several times per year. Membrane damage analysis showed stress concentration and over-compression at edge zones where frames had warped under thermal and chemical load. After replacing these supports with ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plates in key electrolysis units, the operator reported a reduction in membrane replacement frequency by approximately 35% over the next operating period. Cell availability improved as unplanned stoppages related to internal support deformation dropped by more than 25%, and maintenance inspections confirmed that plate flatness remained within tight limits despite continuous operation in hot alkaline brine.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate as Wear Tiles in Mining and Bulk Material Transfer Systems
✅Key Advantages
1. High Hardness with Tile-Based Impact Distribution
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate offers Vickers hardness values above 1200 HV, significantly higher than typical martensitic steels. Combined with the square tile format, this hardness allows each plate to dissipate impact energy over its full area, reducing local wear depth by 40–60% compared with monolithic liners in identical conditions.
2. Tight Tiling with Minimal Flow Disturbance
Square geometry allows installation with tile-to-tile gaps often below 1 mm, creating a nearly continuous wear surface in rectangular chutes and hoppers. This close fit maintains smooth bulk material flow and has been shown to cut blockage events in critical transfer points by approximately 30% where correct installation practice is followed.
3.Local Replacement Strategy for High-Impact Zones
By designing the liner as an array of square tiles, only the most heavily impacted zones must be replaced, rather than full liner panels. Field data from retrofit projects indicate that partial tile replacement strategies can reduce liner material consumption by 25–40% over a typical maintenance cycle while maintaining target uptime levels.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A mining operation handling abrasive ore fines experienced rapid wear in the lower impact zones of transfer chutes, with conventional steel liners requiring replacement on intervals shorter than six months. Inspections showed deep grooves and step-like wear patterns that disrupted flow and increased blockage risk, forcing extended shutdowns even when only limited regions were severely damaged. After installing ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plates as modular wear tiles across the impact area, the site reported that maximum wear depth in critical zones after one operating cycle was reduced by more than 50% compared with the previous liner material. Maintenance teams were able to change only the most exposed tiles, cutting total liner replacement volume by roughly 30% and reducing chute-related stoppages across the following year.
-
Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate in SOFC Stack Components and High-Temperature Insulation Boards
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Geometry Under Thermal Cycling
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate maintains structural integrity through repeated cycling between ambient conditions and temperatures in the 600–900°C range, with warpage kept below 0.05 mm in controlled tests. This stability significantly reduces misalignment between stack layers that can otherwise accumulate over hundreds or thousands of cycles.
2. High Dielectric Strength at Elevated Temperature
Dielectric strength values above 12 kV/mm and volume resistivity exceeding 10¹² Ω·cm at 500°C provide robust electrical isolation between conductive stack components. This enables tighter electrode spacing and more compact stack layouts without compromising insulation safety margins.
3. Low Thermal Conductivity for Localized Insulation
Thermal conductivity in the range of 2–3 W/m·K supports effective thermal barriers around active zones within SOFC stacks and high-temperature power modules. By limiting heat leakage through support areas, the plate helps maintain more uniform internal temperature profiles and can improve thermal efficiency by several percentage points in optimized designs.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A manufacturer of high-temperature electrochemical power modules observed gradual seal degradation and frame distortion after extended operation, driven by thermal gradients acting on metal-based support structures. Over time, this led to increased leakage rates, alignment drift, and a noticeable decline in stack performance metrics during long-term testing campaigns. By integrating ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plates as insulating structural supports beneath and around rectangular stack assemblies, the engineering team recorded a measurable reduction in geometric drift, with post-test flatness remaining within 0.05 mm and leakage rates reduced by approximately 20% compared with the previous design. Long-duration trials demonstrated more stable output profiles and fewer seal-related failures, indicating improved stack durability under repeated thermal cycling.
ADCERAX® Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate User Guide for Safe and Stable Operation
The Zirconia Ceramic Square Plate from ADCERAX® should be installed, operated, and maintained according to structured guidelines so that its mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties are fully retained in demanding industrial environments. Clear handling, heating, cleaning, and storage practices help protect the plate from avoidable damage and ensure that its square geometry continues to deliver uniform support and coverage throughout the service life.
-
Handling and Installation
1. Careful manual handling
The plate should be lifted using both hands or suitable lifting tools to avoid bending stress on corners and edges. Sudden contact with hard metal fixtures or dropped tools should be avoided, because localized impact can initiate microcracks that are not visible at first inspection.
2. Edge and corner protection
During installation into furnace floors, reactor trays, or chutes, all contact points should be checked for sharp metal burrs or weld spatter. These should be removed or covered so that stress is distributed across a broad area, rather than concentrated at a single point.
3. Controlled mechanical clamping
When clamping or bolting around the plate, the contact pads should be broad and flat so that no single fastener introduces excessive point load. Torque should be increased gradually and symmetrically, allowing the plate to settle evenly into its support frame.
-
Operating Conditions and Thermal Management
1. Gradual heating and cooling
The system should be heated at a controlled rate so that thermal gradients remain as low as practical across the plate surface. Avoiding abrupt cold air or liquid impingement on a hot plate helps reduce thermal shock and extend service life.
2. Respecting maximum service temperature
Furnace and reactor setpoints should remain within the defined operating range so that zirconia phase stability and mechanical strength are preserved. Occasional overshoot events should be minimized, because repeated excursions may accumulate damage over many cycles.
3. Uniform support under load
Loads such as product stacks, catalyst beds, or bulk materials should be distributed as evenly as possible to maintain balanced contact pressure across the square surface. Concentrated weight at one corner or edge can amplify bending stress and lead to premature failure.
-
Cleaning, Inspection, and Condition Monitoring
1. Non-abrasive surface cleaning
For routine cleaning, a soft brush or cloth and mild, compatible cleaning agents should be used to remove deposits or residues. Steel wire brushes, grinding tools, or aggressive chemicals can scratch the surface and create stress raisers.
2. Regular visual and dimensional checks
The plate should be inspected at planned intervals for chipping, cracks, and unusual discoloration around high-stress areas. Any part that shows progressive damage should be replaced in a controlled shutdown, preventing unexpected failure during critical operation.
3. Monitoring contact interfaces
Mating metal frames, supports, and fasteners should be checked to confirm that no distortion or wear has changed contact geometry. Restoring flat contact surfaces helps maintain the designed load path through the square plate and avoids new stress concentrations.
-
Storage, Transport, and Replacement Strategy
1. Protected storage conditions
Plates should be stored in a dry, vibration-free, and dust-controlled area, separated by soft spacers or padding to prevent edge contact. Stacking height should be limited so that lower plates are not compressed beyond safe levels during long storage periods.
2. Secure packaging and transport
During internal handling or external shipment, plates should be placed in reinforced cartons or crates with stable support to avoid sliding and impact between units. Proper labeling of orientation and fragility helps operators maintain correct handling practices from warehouse to installation site.
3. Planned replacement and traceability
Each installation can benefit from a documented service history and identification marking that records operating hours and major events. This information supports predictive replacement before failure, especially in high-temperature or corrosive lines where unplanned downtime is costly.