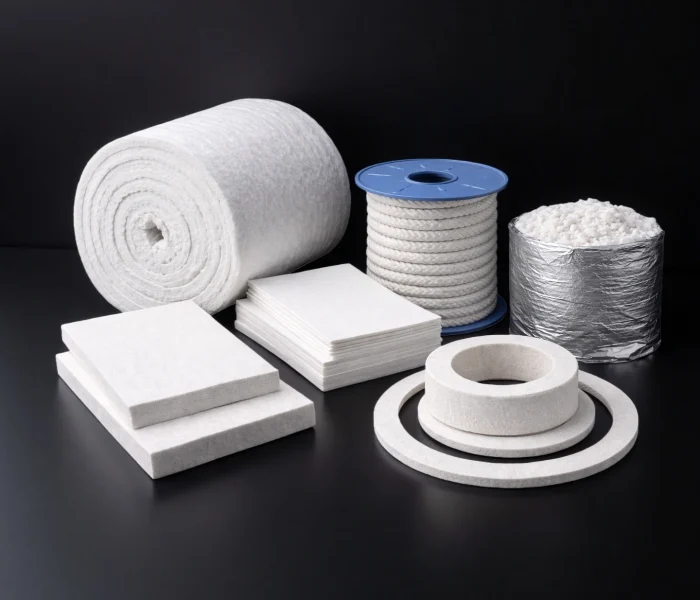
Ceramic Fiber Insulation Blanket, Board, Paper, Cloth & Modules
ADCERAX manufactures ceramic fiber insulation—blanket, board, paper, cloth, modules, rope, and gaskets. Designed to control heat loss and protect equipment in laboratory and industrial high-temperature service, especially where conventional materials age or fail. Common uses include furnaces, thermal analysis rigs, and hot-zone shielding to help reduce surface temperature and improve heating efficiency.
Quick quoting, customization support, and stable export supply simplify procurement.
What is Ceramic Fiber?
🧪 Ceramic fiber is a class of high-temperature inorganic fibers used primarily for thermal insulation. It is typically produced by melting mineral-based raw materials and forming them into fine fibers, which are then processed into different insulation formats.
📌 In engineering terms, ceramic fiber is valued because it combines low thermal mass (heats up/cools down quickly) with low thermal conductivity, making it useful for hot equipment where heat loss control and temperature uniformity matter.
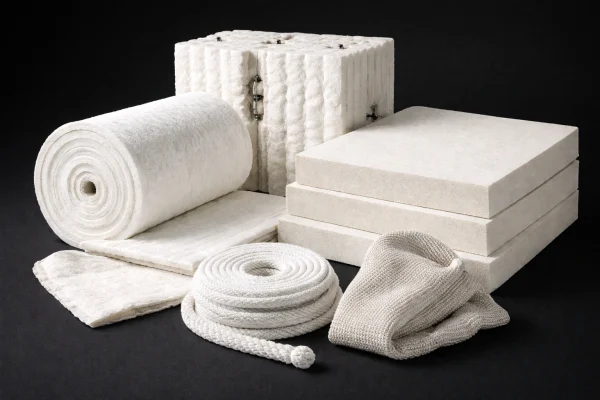

Ceramic Fiber Properties
High-temperature ceramic fiber insulation delivers low heat loss, fast heat-up, and stable thermal performance. Low thermal conductivity and strong thermal shock tolerance help protect linings and reduce shell temperature in furnaces, kilns, and heat-treatment equipment.
Aluminum Silicate Ceramic Fiber (RCF / Standard Ceramic Fiber)
Typical uses: general furnace/kiln insulation, heat-treating equipment, kiln cars, and backup insulation layers
- Temperature rating (continuous): 1260°C / 1430°C (by grade)
- Maximum exposure: available on request
- Density options: 64 / 96 / 128 kg/m³ (by product form)
- Thermal conductivity: reported at 400 / 600 / 800 / 1000°C (provide table or curve)
- Emissivity: available on request
- Melting point: reference only (available on request)
Alumina Ceramic Fiber ( Polycrystalline Alumina Fiber)
Typical uses: ultra-high-temperature zones, hot-face linings, furnaces requiring long service life, low shrinkage, and chemical stability
- Temperature rating (continuous): 1600°C / 1700°C (by grade)
- Al₂O₃ purity: ≥95% (typical high-purity grades)
- Bulk density options: 96 / 128 kg/m³ (by product form)
- Thermal conductivity (W/m·K): at 400 / 600 / 800 / 1000°C (publish the curve/table)
- Permanent linear change (PLC): % at 1400°C / 1600°C (by grade, publish test value)
- Fiber diameter: 2–4 μm (typical range)
Zirconia Ceramic Fiber
Typical uses: ultra-high-temperature zones, hot-face linings, furnaces needing low shrinkage, and thermal equipment requiring long service life.
- Temperature rating (continuous): 2000°C / 2200°C (by grade)
- ZrO₂ purity: ≥94% (typical stabilized grades)
- Bulk density options: 96 / 128 kg/m³ (by product form)
- Thermal conductivity (W/m·K): at 400 / 600 / 800 / 1000°C (publish the curve/table)
- Permanent linear change (PLC): % at 1600°C / 1800°C (by grade, publish test value)
- Fiber diameter: 2–5 μm (typical range)
Refractory Ceramic Fiber Products & Shapes
Ceramic fiber products are supplied as blankets, boards, modules, paper, cloth, rope, plugs, and formed parts for insulation, sealing, and lining. These shapes help reduce heat loss, protect refractory structures, and speed installation in furnaces, kilns, and thermal equipment.

alumina oxide ceramic fiber
Alumina ceramic fiber for cleaner hot-face insulation, often chosen to extend service intervals and keep process stability.

zirconia ceramic fiber
Zirconia ceramic fiber for extreme-heat zones, preferred when standard fibers age too fast under severe thermal cycling.
aluminum silicate ceramic fiber
Aluminum silicate ceramic fiber for cost-effective furnace insulation, easy to form and cover large areas with stable lining support.

ceramic fiber blanket
Ceramic fiber blanket wraps complex shapes fast, making it ideal for quick furnace repairs, expansion joints, and removable insulation layers.

ceramic fiber board
Ceramic fiber board provides a rigid, clean-cut surface for baffles, burner blocks, kiln furniture backing, and flat insulation where blankets sag.
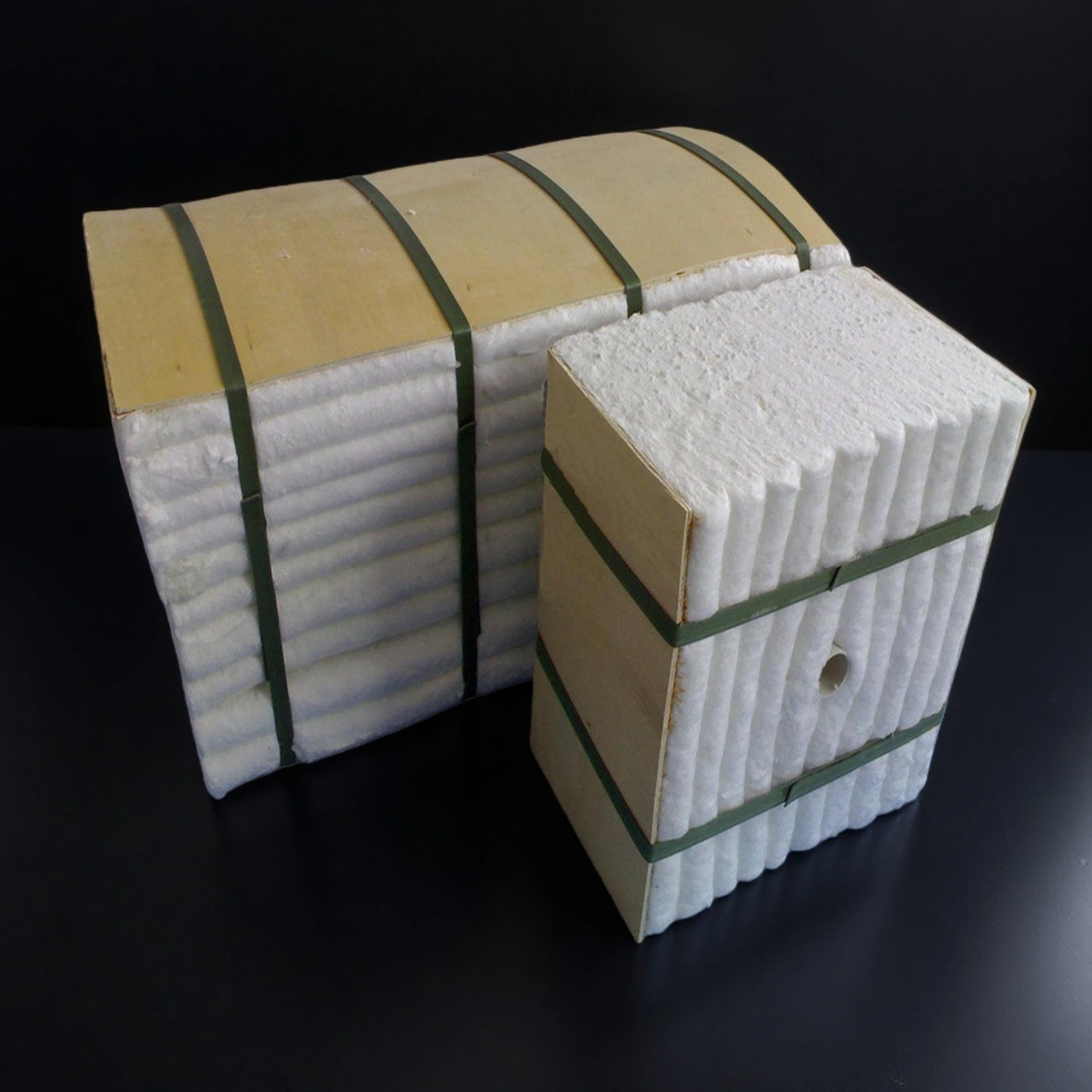
ceramic fiber modules
Ceramic fiber modules hold thickness and recovery, speeding lining installation while keeping a consistent hot-face across walls and roofs.

ceramic Fiber Cloth
Ceramic fiber felt adds flexible heat shielding with stitchable handling for curtains, and removable covers around equipment.

ceramic fiber rope
Ceramic fiber rope seals gaps as a compressible gasket, fitting door perimeters, ports, and flanges where you need resilience, not a rigid part.

ceramic fiber paper
Ceramic fiber paper seals tight as a thin, clean-cut barrier—ideal for gasketing, wrap layers, and thermal breaks where space is limited.
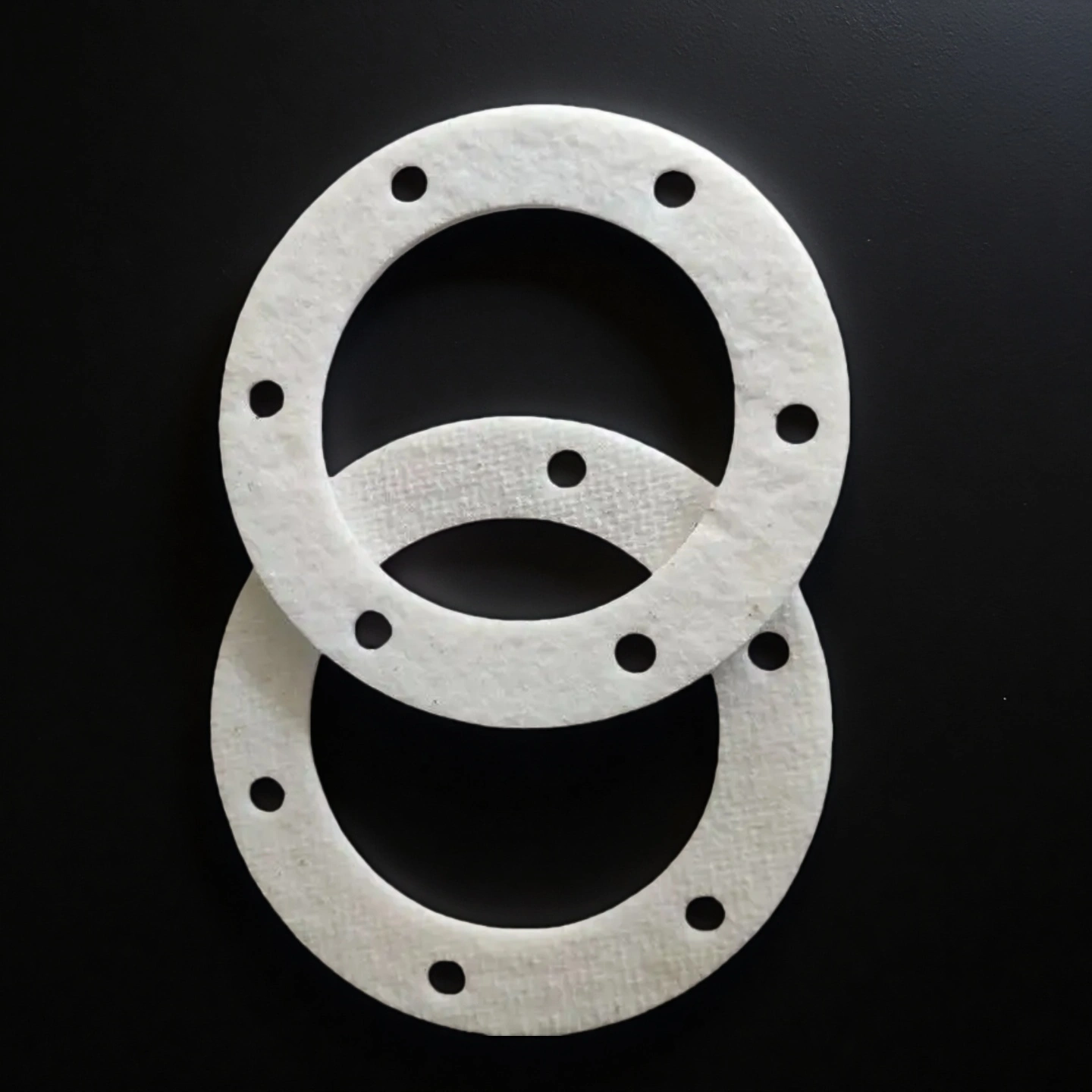

ceramic fiber gasket
Ceramic fiber gasket holds a stable seal at heat, reducing leak paths and flange drift in furnace doors, ducts, and hot joint interfaces.
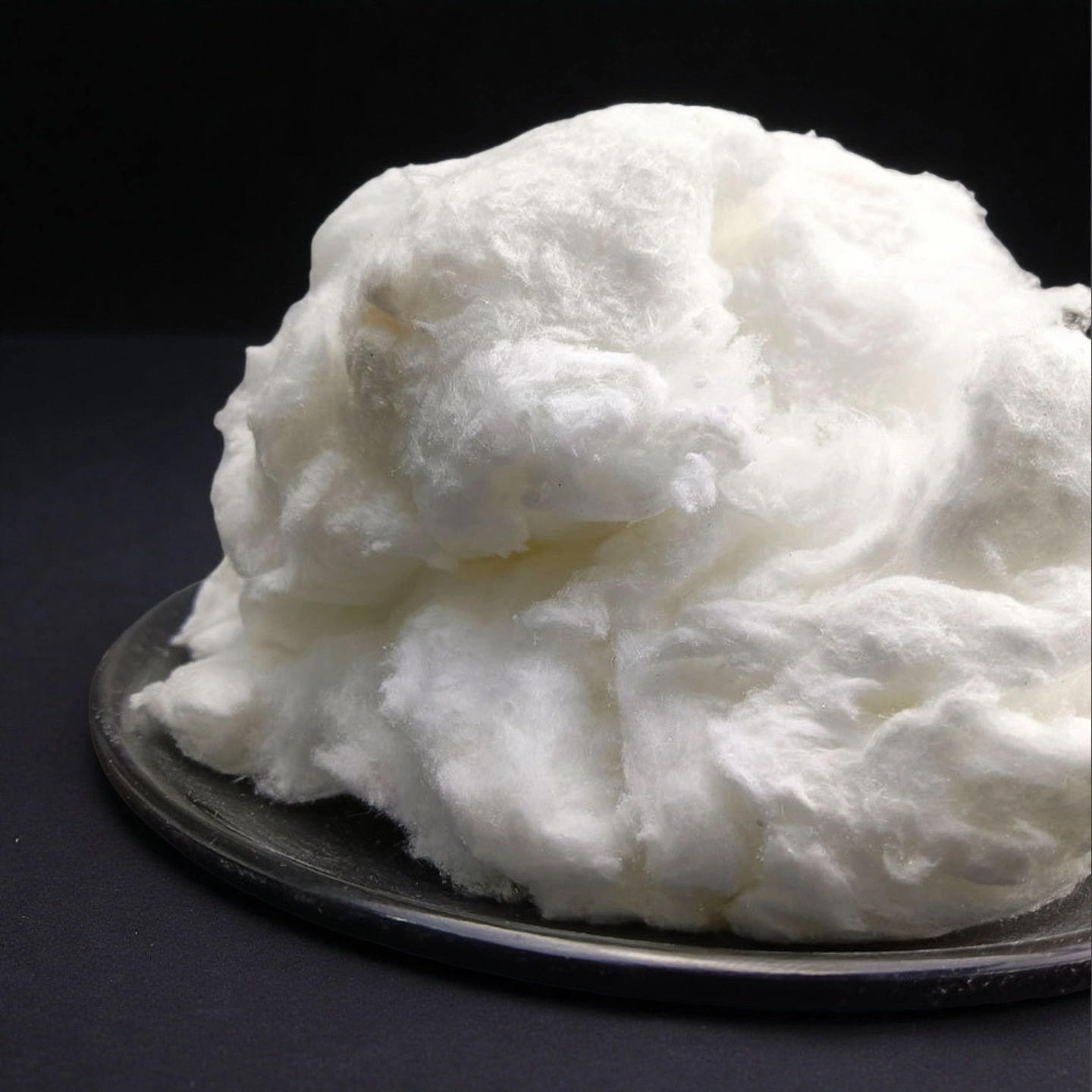

ceramic fiber cotton
Ceramic fiber cotton packs easily into gaps and irregular cavities, improving coverage in expansion joints, repairs, and insulation fill work.
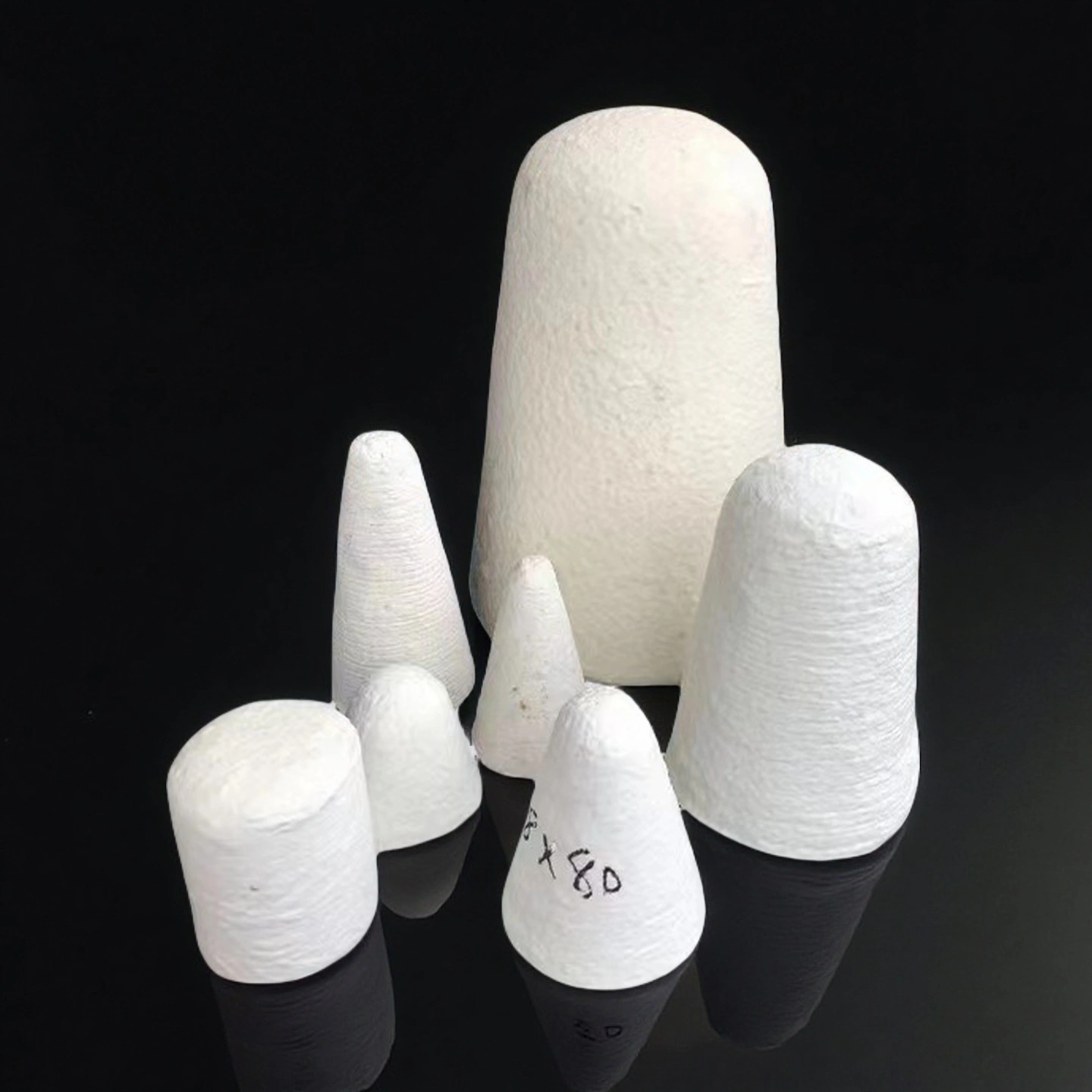

ceramic fiber plug
Ceramic fiber plug creates quick, removable insulation closures for ports and openings—helping cut shell hot spots during maintenance.
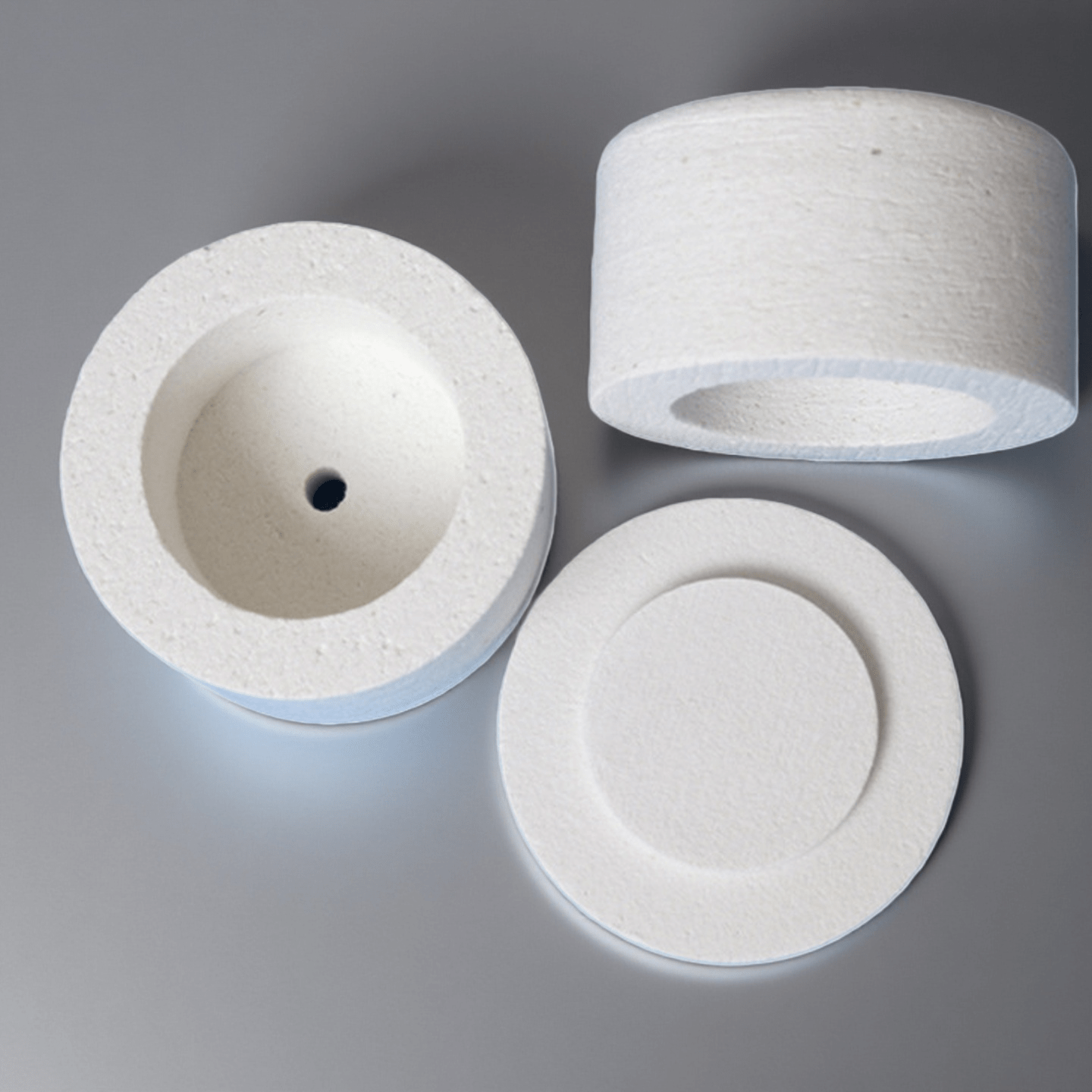

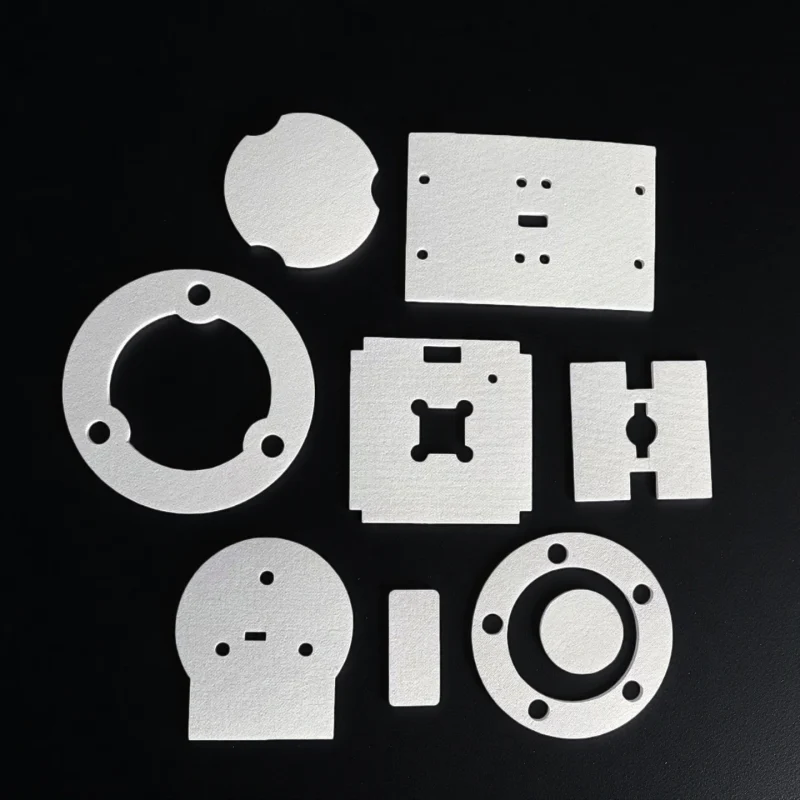
Ceramic Fiber Parts
Ceramic fiber parts provide shaped, fit-ready insulation pieces that simplify assembly and keep hot-zone geometry consistent in repeat builds.
Ceramic Fiber Insulation — Cut Heat Loss, Protect Linings, and Keep Furnace Shell Temperatures Under Control.
ADCERAX supplies ceramic fiber materials for laboratory and industrial thermal insulation, supporting standard forms and application-specific customization.
Ceramic Fiber Uses
Ceramic fiber applications focus on cutting heat loss, stabilizing lining performance, and protecting steel shells in high-temperature equipment. Select the product form by temperature class, mechanical abuse level, and installation method to reduce unplanned relines.
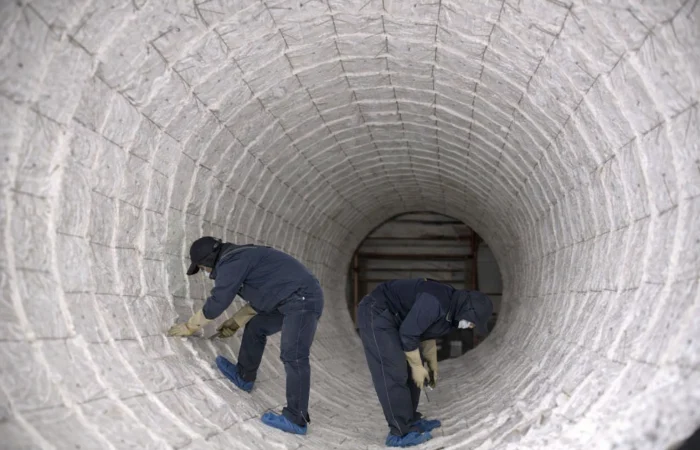

Ceramic Fiber in Industrial Applications
💠Where ceramic fibers are used:
Ceramic fiber is widely used in high-temperature industrial environments to reduce heat loss, protect refractory linings, and control shell temperature. Typical uses include furnace and kiln insulation systems, heat treatment lines, foundry equipment, and thermal processing units where fast heat-up, lightweight insulation, and energy efficiency are critical to uptime and operating cost.
💠Why choose ceramic fiber for industrial:
Ceramic fiber to cut heat loss, lower shell temperature, and speed heat-up with a lightweight lining—reducing energy cost and downtime.
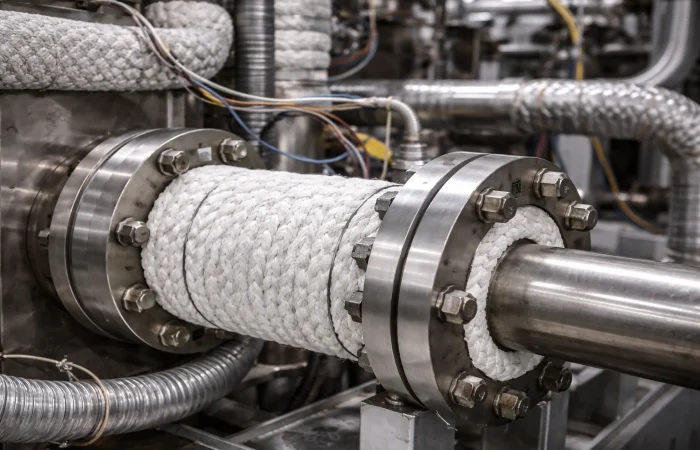
Ceramic Fiber in Mechanical Applications
💠Where ceramic fibers are used:
In mechanical and process systems, ceramic fiber supports thermal management and sealing in areas exposed to continuous or cyclic heat. It is commonly applied around hot ducts, expansion joints, access ports, covers, and moving interfaces—helping limit heat transfer, accommodate thermal movement, and reduce distortion or premature component wear.
💠Why choose ceramic fiber:
Ceramic fiber to handle thermal cycling and movement, seal hot interfaces, and limit heat transfer without adding heavy mass.
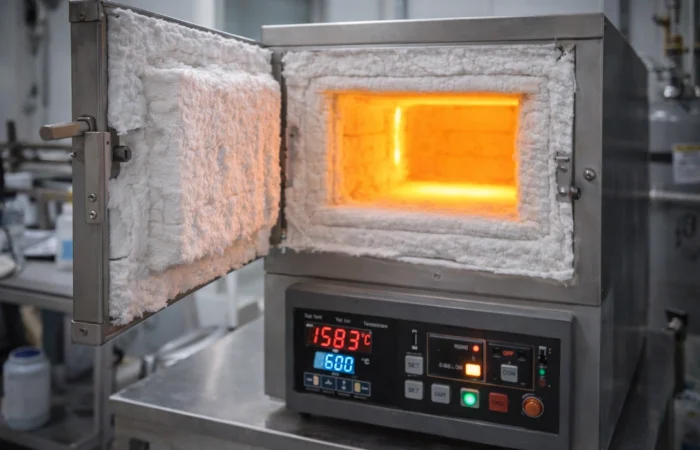

Ceramic Fiber for Laboratory Applications
💠Where ceramic fiber are used
In mechanical and process systems, ceramic fiber supports thermal management and sealing in areas exposed to continuous or cyclic heat. It is commonly applied around hot ducts, expansion joints, access ports, covers, and moving interfaces—helping limit heat transfer, accommodate thermal movement, and reduce distortion or premature component wear.
💠Why choose ceramic fiber for lab:
ceramic fiber to stabilize furnace temperature, protect the outer shell, and simplify clean maintenance for repeatable tests.
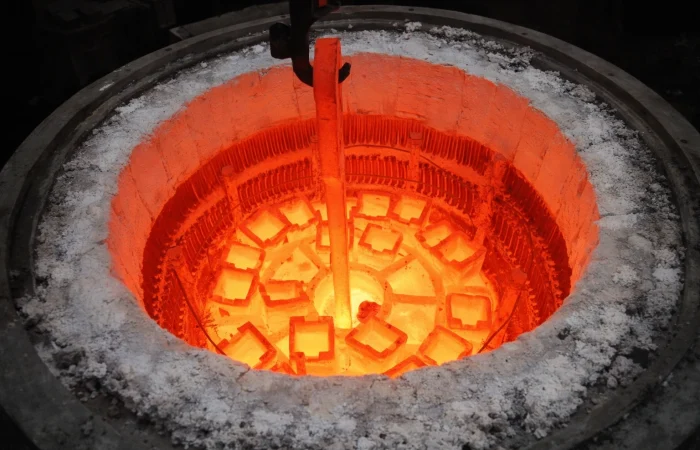

Ceramic Fiber in Steelmaking Applications
💠Where ceramic fiber are used
In steelmaking and metallurgy, ceramic fiber is commonly specified as backup insulation to cut shell temperature, reduce heat loss, and support faster heat-up and turnarounds. It is used in reheat/soaking furnaces, ladle and tundish covers, furnace doors and roof zones, off-gas duct outer insulation, and access ports/peepholes where lightweight insulation and quick maintenance matter.
💠Why choose ceramic fiber for steelmaking:
Ceramic fiber helps cut fuel loss, reduce shell hot spots, and speed relines. It’s commonly used as backup insulation behind hot-face refractories without adding heavy thickness.
ADCERAX: Ceramic Fiber Insulation Manufacturer in China
ADCERAX is a ceramic fiber supplier with factory-direct engineering support and controlled production for consistent thickness, density, and thermal performance. Fast spec review, flexible sampling, and batch inspection help reduce risk and keep repeat-order supply reliable.
Competitive pricing with strict quality control from raw material sourcing to final delivery
Professional team providing comprehensive technical support and collaborative design
Small batch orders to large-scale production with complex geometries and tight tolerances
24-hour response and 24-hour dispatch for standard items, 3-7 weeks for custom orders.
China Ceramic Fiber Factory & Exporter——ADCERAX
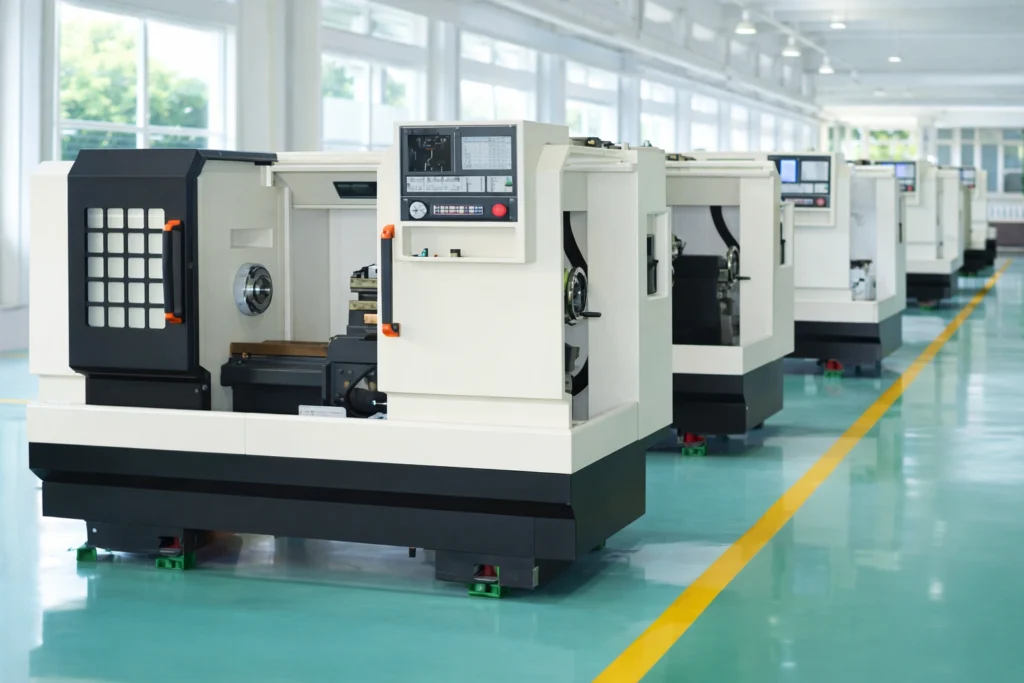

ADCERAX specializes in export-ready ceramic fiber insulation manufacturing in China, backed by 20+ years of advanced ceramics experience and proven process control. Our lineup covers ceramic fiber blankets, boards, paper, modules, cloth, rope, gasket, and ceramic fiber formed shapes for high-temperature insulation duty.
Standard sizes support fast replacement, and custom-to-spec builds are available for thickness, density, and format needs. With batch inspection, traceable records, and export-ready packing, ADCERAX helps buyers keep supply stable, reduce downtime risk, and maintain predictable maintenance cycles.
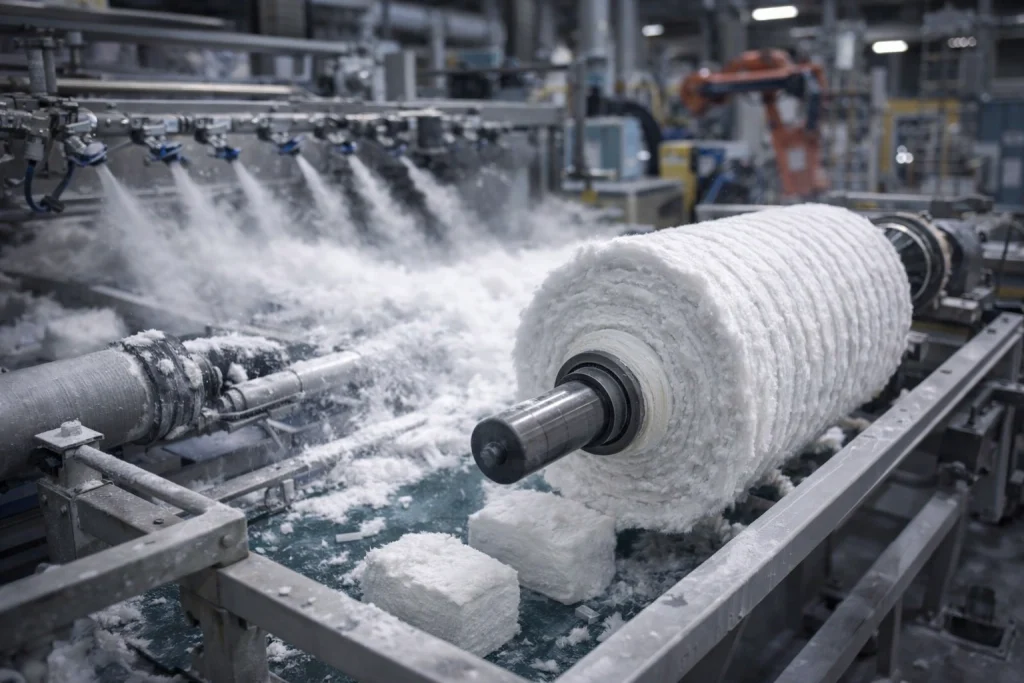
Ceramic Fiber Manufacturing Process
Controlled chemistry and shot content control to keep insulation performance consistent across lots.
Mechanical interlocking to build stronger, more uniform blanket integrity, thickness stability, and recoverability.
Controlled firing to reduce shrinkage risk and improve long-term, high-temperature dimensional stability.
High-temperature fiber formation to produce stable fiber diameter and uniform bulk structure.
Cutting, laminating, rigidizing, or molding into boards, modules, paper, rope/cloth, and ceramic fiber formed shapes.
Density/thickness checks, visual defect screening, and export-ready packing for clean delivery.
Custom Machined Ceramic Fiber
ADCERAX supports custom ceramic fiber insulation builds—cut-to-size blankets/boards/paper, and made-to-print ceramic fiber formed shapes for fit-critical furnace, kiln, and thermal equipment zones.
Each order is engineered to match temperature rating, thickness, density, and installation method, helping reduce gaps, control hot spots, and keep lining performance repeatable across batches.
Send your drawing/specs (ID/OD, thickness, density, temp class, quantity) to get a fast recommendation and a factory-direct quote.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ceramic Fiber
Use blanket for fast coverage on irregular surfaces, board for rigid flat insulation and baffles, and modules when you need fast installation and consistent hot-face thickness across large furnace walls/roofs.
In most applications, ceramic fiber is not electrically conductive. Standard ceramic fiber insulation is designed to be an electrical insulator, so it does not normally carry current.
Use sharp insulation knives or dedicated cutting tools, cut on a stable surface, and control dust. For boards, straight-edge scoring and controlled cuts help reduce edge damage.
- RCF (alumino-silicate) is commonly used for cost-effective high-temperature insulation.
- PCW polycrystalline alumina fiber is selected for higher temperature stability and lower shrinkage in severe duty.
Yes. Common custom work includes cut sheets, die-cut gaskets, slit rolls, shaped plugs, and made-to-print formed parts. Provide dimensions, density, temperature class, quantity, and drawing if available.
Send: product type, grade/temperature rating, density, thickness, size, quantity, and target application conditions (hot-face or backup, cycling, gas velocity, contact media). For shapes, include drawings and tolerances.
Ceramic fiber is not inherently dangerous, but it can be hazardous when airborne dust/fibers are inhaled—especially during cutting, tearing, removal, or cleanup.
Key risks
Respirable dust exposure (main concern)
Skin/eye irritation
Highest dust tasks: dry cutting, aggressive handling, compressed air, dry sweeping
How to reduce risk
Minimize dust: cut slowly, avoid shaking, keep scraps bagged
Clean correctly: HEPA vacuum or damp wipe; no compressed air
Use PPE: eye protection, gloves, suitable respirator for dusty work
Bottom line: Control dust and use basic PPE, and ceramic fiber is typically manageable for industrial insulation work.
Yes — but because ceramic fiber products vary widely by specification and format, ADCERAX need a few key details before giving an accurate quote.Like below:
- Product form (blanket, board, paper, cloth, rope, formed shape)
- Temperature class (e.g., 1260°C vs 1430°C vs 1600°C)
- Density (e.g., 64, 96, 128 kg/m³ or higher)
- Size / thickness
- Quantity
- Custom machining or cutting
- Delivery terms (FOB/CIF/DDP) and destination
Ceramic fiber is used in laboratories as high-temperature insulation and heat shielding to reduce heat loss, protect equipment, and stabilize hot zones during repeated heating cycles.
Typical laboratory uses include:
Muffle furnace insulation (door lining, chamber backup insulation) to reduce external surface temperature and improve heating efficiency.
Tube furnace hot-zone insulation to stabilize the hot zone and protect tube ends, fixtures, and nearby hardware.
DSC / TGA peripheral heat shielding to limit radiant heat and protect sensors, wiring, and instrument housings.
Lab hot plate thermal isolation to reduce heat transfer to benches, clamps, and adjacent components.
Crucible wrapping for high-temperature testing (fiber paper/blanket) to reduce heat loss and improve local temperature stability during ashing or calcination.
If you tell us your equipment type, temperature, and insulation form needed (blanket, board, paper, module, rope/gasket), we can recommend the most suitable ceramic fiber configuration for your setup.
Ceramic fiber is a lightweight insulation used to reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, while refractory brick is a dense hot-face lining used for durability and mechanical abuse.
Thermal response: Fiber heats/cools faster; brick stores more heat and responds slower.
Best use: Fiber for lab furnaces, tube furnaces, and heat shielding; brick for hot faces with impact, abrasion, or flame impingement.
Maintenance: Fiber is easier to cut and replace; brick needs heavier construction and longer repairs.
Many furnaces use brick (hot face) + ceramic fiber (backup insulation) for both protection and efficiency.
Yes. Ceramic fiber can be easily cut and shaped using simple hand tools or basic shop equipment. Blankets, paper, and cloth are typically cut with knives or shears, while boards can be sawed, drilled, or grooved for fit-critical insulation parts.
Because ceramic fiber is non-structural, machining is limited to sizing and shaping rather than precision tolerances, making it well suited for custom insulation and quick on-site adjustments.
Ceramic fiber insulation can last months to many years, depending on temperature, thermal cycling, airflow/abrasion, and atmosphere. In stable laboratory furnaces, it often provides multi-year service, while harsher industrial hot zones may need more frequent replacement.
Replace it when you see shrinkage, surface erosion, widening joints, or a noticeable rise in outer-surface temperature/energy use.
Ceramic fiber is for high-temperature insulation (furnaces, kilns, lab ovens). Fiberglass is for lower-temperature insulation (buildings, HVAC, appliances).
✅ Choose ceramic fiber when: you need higher temperature capability, low heat storage, and better shell-temperature control.
✅ Choose fiberglass when: temperatures are moderate and cost/easy handling matter most.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
info@adcerax.com
Telephone: +(86) 0731-74427743
WhatsApp: +(86) 19311583352
Within 24 hours
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.


