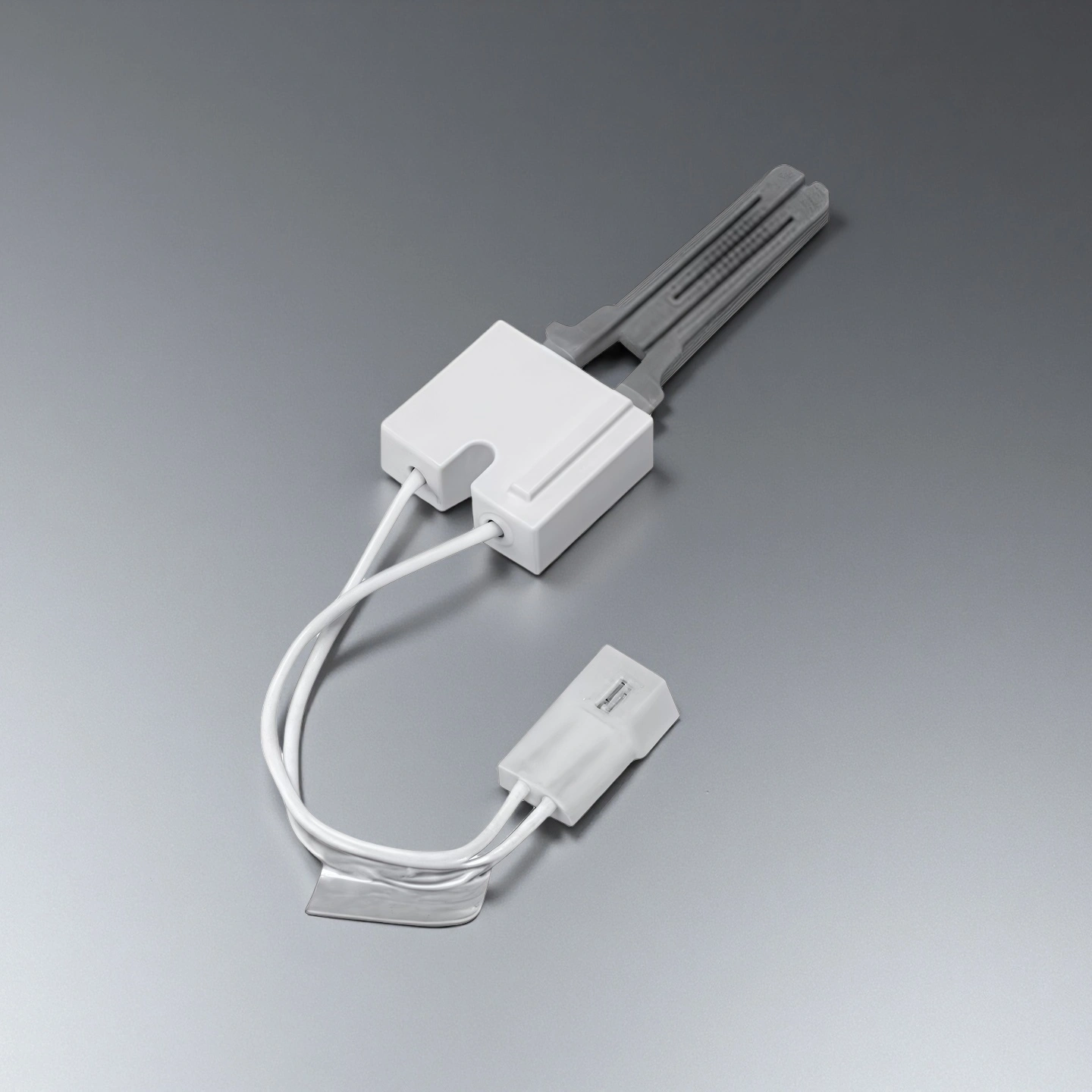
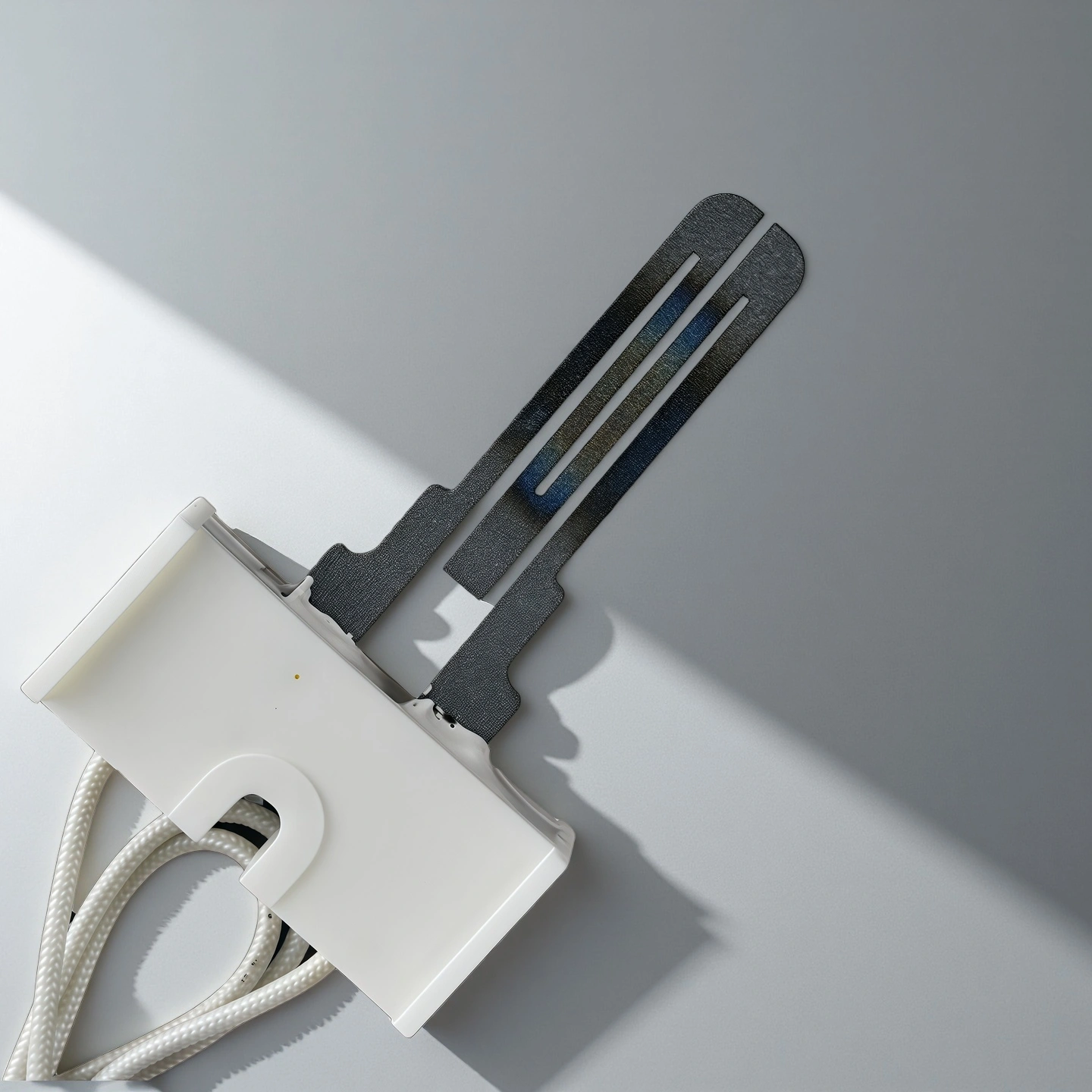
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter is engineered for combustion systems where ignition stability directly affects process continuity, equipment safety, and thermal efficiency. Its fine-grained silicon carbide structure delivers consistent temperature rise under rapid cycling, supporting gas furnaces and industrial heating equipment that operate with stringent reliability requirements. Designed for engineered burner assemblies and high-temperature kiln environments, the igniter maintains stable ignition behavior under heavy thermal loads and reactive gas exposure, enabling long-term operation in applications where durability, thermal endurance, and structural stability are essential.
Engineering Performance Features of the ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter
-
Fine-Grain Microstructure Control
The igniter maintains dimensional stability under thermal loads due to a fine-grain structure with grain size <10 µm, ensuring consistent heating behavior in combustion chambers.
Its microstructure reduces crack propagation rates by over 40% compared to coarse-grain ceramics in accelerated cycling tests.
-
High Elastic Modulus for Mechanical Rigidity
With an elastic modulus exceeding 380 GPa, the igniter retains stiffness under blower-induced vibration common in industrial heating units.
Mechanical deflection is reduced by over 30% compared with oxide-based ceramics in vibration benchmarks.
-
Rapid Heating Response Under Load
The heating zone reaches ignition temperature in 2–4 seconds under rated voltage, enabling efficient burner startup.
Thermal responsiveness reduces unnecessary fuel purging cycles in industrial applications.
-
Oxidation-Resistant SiC Matrix
Material oxidation rates remain below 0.5% mass change after 100 hours at 1,000 °C, supporting long-term ignition performance.
The ceramic structure resists surface degradation in oxygen-rich atmospheres common in industrial heating systems.
-
Corrosion Resistance to Acidic Combustion Species
The igniter maintains structural integrity when exposed to SO₂ concentrations up to 300 ppm, preventing corrosion-induced failure.
Chemical stability reduces replacement frequency in oil-fired or mixed-gas burner environments.
Corrosion resistance contributes to ignition performance consistency across 6–12 month operating cycles.
Technical Specifications of Silicon Carbide Igniter
The performance characteristics of the Silicon Carbide Igniter are evaluated through material, electrical, thermal, and environmental behaviors similar to those assessed in laboratory testing for Horizontal Stainless Steel Canned Motor Pump with Silicon Carbide Bearings, ensuring stable ignition response and reliable operation under demanding combustion conditions.
| Property |
Specification |
| Material Composition |
High-purity silicon carbide (>99%) |
| Grain Size |
Fine-grain structure <10 µm |
| Density |
3.10–3.15 g/cm³ |
| Elastic Modulus |
>380 GPa |
| Thermal Conductivity |
90–120 W/m·K |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient |
4.0–4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K |
| Maximum Operating Temperature |
Up to 1100–1200 °C |
| Cold-to-Hot Resistance Drift |
Within ±2% after cycling |
| Electrical Resistivity |
0.5–1.2 Ω·cm at room temperature |
| Oxidation Stability |
<0.5% mass change after 100 h at 1000 °C |
| SO₂ Corrosion Endurance |
Stable up to 300 ppm exposure |
| Carbon Deposition Resistance |
>40% reduction vs metallic igniters |
| Thermal-Cycle Durability |
>5000 ignition cycles without structural failure |
Dimensions of Silicon Carbide Igniter
|
SiC Igniter BC-STDC Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-DC033-0905 |
DC033-0905 |
The stainless steel elastic shockproof metal frame enhances the strength and reliability of the ignition core. It is the preferred choice for customers in applications with vibrations, both in installation and usage. The incorporation of an elastically designed metal frame significantly reduces the vibration transmitted to the ignition core. Compared to flat-plate silicon carbide igniters, the threaded design greatly improves strength. The combination of high-quality dense silicon carbide sintering technology and a double-helix design further ensures a longer service life, firmer physical strength, lower energy consumption, and superior ignition performance. The current range is between 2.1-3.4A, significantly reducing energy consumption, extending service life, and exhibiting strong ignition capability with low brittleness risk. Different ignition times provide customers with broader options. |
|
AT-DC035-0925 |
DC035-0925 |
|
AT-DC036-0913 |
DC036-0913 |
|
AT-DC034-0921 |
DC034-0921 |
|
SiC Igniter BC-STFC Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-SIC-FC037-0929 |
SIC-FC037-0929 |
The stainless steel elastic shockproof metal frame enhances strength and reliability, making it the preferred choice for both installation and application in vibrating environments. The STFC series offers various elastic metal frame designs, compatible with different types of burners on various gas appliances. The combination of high-quality dense silicon carbide sintering technology and a double-helix design ensures longer service life, firmer physical strength, lower energy consumption, and superior ignition performance for the igniter. The current range is between 3.0-3.6A, and different ignition times offer customers broader selection options. |
|
AT-SIC-FC069-0929 |
SIC-FC069-0929 |
|
SiC Igniter BC-STFC Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-SIC-FF003-0923 |
SIC-FF003-0923 |
Primarily used in HVAC systems for indoor temperature regulation and indoor heating furnaces. |
|
AT-SIC-FF003 |
SIC-FF003 |
|
AT-STFS003 |
STFS003 |
|
AT-STFY011 |
STFY011 |
|
SiC Igniter STRC Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-SIC-RC032-0921 |
SIC-RC032-0921 |
Primarily used in household ovens. |
|
AT-STRC1 |
STRC1 |
|
AT-STRC2 |
STRC2 |
|
AT-STRC3 |
STRC3 |
|
AT-STRC4 |
STRC4 |
|
AT-STRC5 |
STRC5 |
|
SiC Igniter STRS Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-STRS1 |
STRS1 |
The STRS series igniters are primarily used in gas ovens and supplied to OEM manufacturers. With a current range of 2.5-3.0A, they offer lower operating temperatures and significantly extended service life. The high-nickel, high-temperature resistant circular sheath design improves structural strength and facilitates convenient installation, exhibiting clear advantages compared to competing products. They are particularly suitable for household ovens due to their continuous usage and high demands on igniter lifespan. Both the wires and sheaths are designed for high-temperature resistance, ensuring they remain effective even in high-temperature baking environments. They are compatible with Eaton/Siebe 1400 gas valves.
AT-STRS2 STRS2
AT-STRS3 STRS3 |
|
AT-STRS2 |
STRS2 |
|
AT-STRS3 |
STRS3 |
|
SiC Igniter STRS Series |
|
Item no. |
Model no. |
Remark |
|
AT-STRS1 |
STRS1 |
The STRS series igniters are primarily used in gas ovens and supplied to OEM manufacturers. With a current range of 2.5-3.0A, they offer lower operating temperatures and significantly extended service life. The high-nickel, high-temperature resistant circular sheath design improves structural strength and facilitates convenient installation, exhibiting clear advantages compared to competing products. They are particularly suitable for household ovens due to their continuous usage and high demands on igniter lifespan. Both the wires and sheaths are designed for high-temperature resistance, ensuring they remain effective even in high-temperature baking environments. They are compatible with Eaton/Siebe 1400 gas valves.
AT-STRS2 STRS2
AT-STRS3 STRS3 |
|
AT-STRS2 |
STRS2 |
|
AT-STRS3 |
STRS3 |
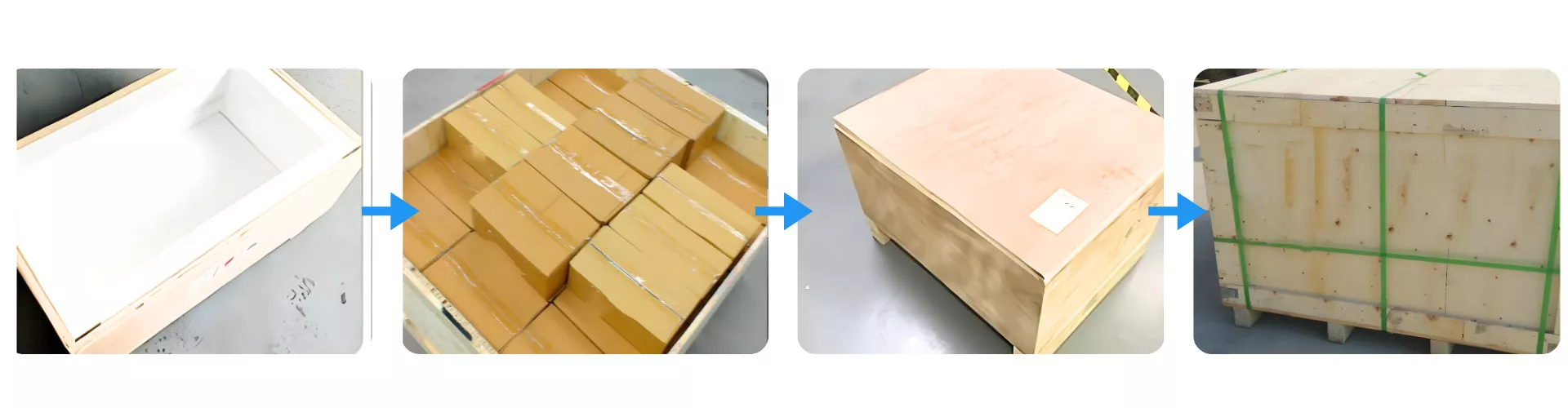
Packaging Method for ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter
Silicon Carbide Igniter is protected through a multi-layer packaging process designed to prevent shock, moisture exposure, and surface abrasion during global transit. Each unit is first boxed and then placed into reinforced cartons that are tightly arranged within a foam-lined wooden crate. The sealed crate is secured with external strapping to maintain structural integrity from factory dispatch to end-user installation.

ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter Resolves Critical Challenges in Industrial Combustion Applications
The Silicon Carbide Igniter plays a decisive role in combustion systems where ignition reliability, thermal endurance, and long operational life determine the stability and efficiency of high-demand industrial equipment. Across furnace manufacturing, engineered burner systems, and thermal-processing kilns, harsh operating environments create persistent ignition challenges that require a discharge element with predictable thermal behavior and strong resistance to degradation.
-
Silicon Carbide Igniter in High-Reliability Gas Furnaces and Industrial Heating Units
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Ignition Under Humid Intake Conditions
In controlled testing, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter maintained resistance drift within ±2% after 5,000 ignition cycles at elevated humidity, preventing delayed heat-up in moist combustion air. This stability allows gas furnaces and industrial heaters to keep ignition response within a narrow timing window, even when intake ducts carry condensate or mild contamination.
2. Consistent Heat-Rise Profile for Tight Burner Control
The heating zone reaches target ignition temperature in 2–4 seconds, with cycle-to-cycle variation kept below ±10% in long-duration testing. This consistent thermal profile supports accurate burner modulation and reduces ignition-related disturbances in combustion efficiency across continuous operating schedules.
3. Extended Life Under Frequent On/Off Cycling
Under accelerated cycling between ambient and 1,000 °C, fewer than 5% of ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniters exhibited functional degradation after 10,000 cycles. This endurance enables high-duty furnace fleets to lengthen replacement intervals while maintaining stable start-up reliability in multi-shift operation.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A European industrial furnace manufacturer reported unstable ignition in high-efficiency gas units where conventional igniters showed oxidation marks and resistance drift after a few thousand cycles, leading to misfire rates above 3% and frequent control-panel restart alarms. After switching to ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter, resistance stability remained within ±2% during long-term field evaluation, and ignition timing dispersion narrowed significantly across repeated starts. Over the first heating season, recorded misfire events dropped to below 0.5% of total ignition attempts, and service technicians extended inspection intervals without loss of reliability. As a result, the furnace line maintained stable burner operation during continuous production schedules, meeting the end user’s reliability targets for high-duty industrial heating.
-
Silicon Carbide Igniter for Engineered Oil & Gas Burner Assemblies Requiring Precise Fit and Stable Ignition Dynamics
✅Key Advantages
1. Stable Ignition Across Variable Air–Fuel Ratios
Testing in staged oil and gas burners showed ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter achieving successful ignition over a wide equivalence range, with misfire occurrence reduced by more than 60% compared with legacy igniters. This stable response supports burner sequences that operate from rich start-up conditions toward leaner steady states without requiring frequent retuning of ignition timing.
2. Resistance to Reactive Gas and Thermal Gradient Damage
In mixed-gas exposure with simulated SOₓ and NOₓ species at elevated temperature, mass change of the SiC element remained below 1% after 500 hours. The igniter also retained structural integrity under imposed thermal gradients exceeding 300 °C between mounting and tip regions, reducing crack initiation in multi-zone burner tiles.
3. Low Vibration-Induced Performance Drift
During vibration testing representative of oil and gas blower trains, with accelerations above 5 g, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter maintained ignition performance with no measurable change in cold resistance after 1 million vibration cycles. This mechanical robustness allows engineered burner assemblies to operate without ignition drift in environments where piping, skids, and blower housings transmit continuous mechanical excitation.
✅ ️Problem Solved
An oil and gas burner system integrator serving process heaters experienced recurring ignition sequence aborts when legacy igniters were exposed to variable air–fuel ratios and reactive exhaust gases. In field records, misfire-related aborts accounted for more than 20% of burner start attempts in certain operating ranges, forcing operators to repeat purge and restart cycles. After implementing ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter, start-up logs over a three-month test window showed ignition success rates above 98% across the same operating envelope, with no observed structural damage despite exposure to high thermal gradients and vibration. Sequence aborts due to ignition failure dropped to isolated events, allowing the integrator to stabilize automated start procedures and reduce operator interventions on burner trains.
-
Silicon Carbide Igniter in Kilns and Thermal Processing Equipment Operating Under Extreme Heat Loads
✅Key Advantages
1. Thermal Shock Endurance During Hot Chamber Restarts
In rapid quench testing from 900 °C to ambient air, ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter completed more than 1,000 cycles with a crack incidence below 2%. This level of thermal shock resistance supports kiln restart procedures where the chamber remains hot between production batches, avoiding premature failure during repeated high-temperature startups.
2. Reduced Fouling in Dust- and Residue-Rich Kiln Atmospheres
Comparative trials in particulate-laden exhaust streams showed surface deposit thickness on the SiC igniter to be more than 40% lower than on metallic igniters after 500 operating hours. The reduced fouling helps maintain effective heat transfer from the ignition zone, sustaining reliable spark-free hot-surface ignition in environments where fuel residues and airborne solids are present.
3. Extended Campaign Life at Elevated Continuous Temperatures
Long-duration exposure tests at 1,100 °C demonstrated stable ignition behavior over 1,000 operating hours with no significant change in electrical response. This durability allows kiln and thermal-processing operators to align igniter replacement with planned campaign shutdowns rather than unscheduled stoppages driven by ignition component failure.
✅ ️Problem Solved
A technical ceramics producer operating roller kilns reported frequent igniter failures during daily hot restarts, with conventional components exhibiting cracking and heavy fouling after a few months of operation. These failures caused unplanned interruptions in firing schedules and required cooling sections of the kiln for access, reducing utilization of the firing line. After adopting ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter, operators observed that the igniters withstood several hundred hot restarts with crack rates below 2%, while periodic inspections showed significantly thinner deposit layers on the active surfaces. Over a full production campaign exceeding 1,000 operating hours, the kiln maintained stable ignition behavior without emergency igniter replacement, enabling the plant to run longer continuous firing sequences with fewer ignition-related disruptions.
ADCERAX® Silicon Carbide Igniter User Guide for Reliable Operation and Long-Term Stability
The Silicon Carbide Igniter requires correct installation, handling, and monitoring practices to ensure consistent ignition behavior and extended service life in demanding combustion environments. This section provides clear operational guidance to help users prevent avoidable failures, maintain stable performance across thermal cycles, and ensure that the component remains in optimal condition throughout its intended duty cycle.
-
Proper Handling Before Installation
1. Avoid mechanical impact during unpacking, as excessive vibration or accidental drops may introduce micro-cracks that weaken the igniter under rapid heating. Handle the component only by its insulated support section and keep the active heating zone free of fingerprints or debris. Store in a clean, dry environment before assembly to prevent moisture absorption.
2. Inspect the igniter visually before installation by checking for surface fractures, discoloration, or unusual marks that may indicate prior stress. Even minor defects can expand under repeated thermal cycling and reduce ignition efficiency. Replace any element that shows signs of abnormal wear before installing it into a combustion chamber.
3. Maintain cleanliness of surrounding hardware, ensuring that mounting brackets, connectors, and wiring paths are free of residue and corrosion. Contaminants in the fixture area can cause uneven heating or electrical leakage, reducing overall ignition stability and operational safety.
-
Correct Installation and System Integration
1. Ensure stable electrical connection, using terminals rated for high-temperature environments and verifying that lead wires are securely fastened. Loose connections increase resistance and may alter heat-up characteristics over time. Always confirm that the ignition control module outputs the required voltage range.
2. Align the heating zone accurately within the burner or furnace chamber so that the igniter is exposed to the designed airflow and fuel flow. Misalignment may cause uneven heating or delayed ignition, especially in high-velocity combustion systems. Follow the system’s mechanical drawings to maintain consistent positioning.
3. Verify that insulation components are properly seated, preventing electrical arcing or short paths in humid or dust-laden atmospheres. Poor insulation can accelerate degradation and cause intermittent ignition behavior. Regular checks ensure long-term system reliability.
-
Operational Best Practices During Use
1. Allow sufficient cooling intervals when required, particularly in systems with short on/off cycles that may push the igniter into continuous thermal shock. Excessive cycling without controlled cooldown can shorten service life. Monitor system duty patterns to avoid unnecessary thermal stress.
2. Avoid exposing the component to unexpected chemical species, especially corrosive gases or residues that were not part of the original equipment design. Reactive contaminants can adhere to the igniter surface and reduce heat-transfer efficiency. Maintain proper burner tuning to limit soot or deposit formation.
3. Track ignition performance over time, watching for shifts in warm-up duration or unusual color changes in the heating zone. These early indicators help identify developing faults before they cause system downtime. Replace the igniter immediately if performance declines significantly.
-
Maintenance, Replacement, and Long-Term Care
1. Implement periodic inspections based on system duty, verifying that the heating zone remains clean and free of buildup. A predictable inspection schedule reduces the risk of unexpected ignition delays. Document all findings to support consistent maintenance practice.
2. Remove surface deposits carefully, using non-abrasive tools to avoid damaging the igniter’s fine-grained silicon carbide structure. Deposits reduce thermal response and may cause poor ignition in high-temperature applications. Keep the burner chamber clean to slow future buildup.
3. Plan replacement intervals proactively, aligning maintenance with overall system shutdown schedules. Even though the igniter offers strong thermal-cycle durability, scheduled replacement prevents failures in critical operations. Maintaining spare units on-site helps avoid delays during urgent service events.
![]()