High Quality Industrial Ceramic Plates for Wear, Heat & Corrosion— Custom to Your Drawing
ADCERAX is an industrial ceramic plate manufacturer, supplying wear plates, liner plates,industrial refractory ceramic plate, furnace support plates, insulation plates, and corrosion-resistant ceramic barrier plates for harsh industrial service. Designed to stay stable under abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure, these plates help reduce chipping, cracking, warpage, and unplanned replacements.
Material selection can be matched to your duty—alumina, silicon carbide, or zirconia—with machinable or porous options when your design needs easier shaping or controlled permeability.
What is Industrial Ceramic Plate?
Industrial ceramic plate is a flat technical-ceramic component used as a functional surface in industrial equipment. Unlike decorative ceramics, it is specified by material system, thickness, flatness, edge condition, and service environment (wear, temperature, or chemical exposure).
In practice, it may serve as a wear-facing liner, a hot-face support surface, an electrical/thermal barrier, or a chemically inert contact plate, depending on the process requirements.
Industrial Ceramic Plate Material Properties
Industrial ceramic plates provide stable performance where metals or polymers wear, deform, or contaminate.Their material properties help engineers manage heat, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure, making it easier to select the right ceramic plate for specific operating conditions.
Mechanical Properties of Ceramic Plate Materials
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Hardness | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99–99.99%) | 3.88 – 3.98 | 312 – 320 | 13.5 – 30 GPa | 3.5 – 4.5 | 370 – 390 | 2000 – 3000 |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | 5.65 | 900 | 12 GPa (Vickers) | 8 | 210 | 2000 – 2500 |
| Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) | 2.15 – 2.19 | 173 (A-direction) | HV0.5 ≈ 651 | 2.0 – 3.0 | 30 – 40 | 154 (A-direction) |
| Hot Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN) | 1.96 – 2.0 | 310 | HV0.5 ≈ 62 | 2.5 – 3.5 | 20 – 30 | 120 |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RB-SiC) | 3.02 | 250 (20 °C) / 280 (1200 °C) | 2600 – 2800 kg/mm² | 3.0 – 4.0 | 330 | 1000 – 2200 |
| Sintered SiC (SSiC) | 3.10 | 380 (20 °C) / 400 (1200 °C) | 2600 – 2800 kg/mm² | 3.5 – 4.5 | 420 | 1000 – 2200 |
Thermal Properties of Ceramic Plate Materials
| Material | Maximum Working / Operating Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (×10⁻⁶/K) | Thermal Shock Resistance ΔT (°C) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99–99.99%) | ≤1700 – 1800 (no load) | 30 – 42 | 8.2 – 8.4 | 200 – 228 | ≈2050 |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | 1500 (continuous use) | 2.2 (at 1000 °C) | 10.3 (25–1000 °C) | ≈2715 | |
| Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) | 1000 (air) / 2300 (vacuum) | 60 (A-direction) | 0.6 | ≈3000 (sublimation) | |
| Hot Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN) | 900 (air) / 1850 (vacuum) | 55 | 1.8 | ≈3000 (sublimation) | |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RB-SiC) | ≤1380 | 45 | 4.1 – 4.5 | ≈2700 | |
| Sintered SiC (SSiC) | ≤1600 | 74 | 4.1 – 4.5 | ≈2700 |
Electrical Properties of Ceramic Plate Materials
| Material | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Relative Dielectric Constant (εr) | Electrical Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99–99.99%) | 10¹³ – 10¹⁵ | 10 – 15 | 9.0 – 9.8 | Stable electrical insulator, widely used for high-voltage and RF components |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | 10⁹ – 10¹¹ | 8 – 12 | 20 – 30 | Lower resistivity than alumina, suitable for insulated structural parts |
| Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) | ~2 × 10¹⁴ | ~55 | 3.5 – 4.0 | Excellent high-temperature electrical insulation, highly anisotropic |
| Hot Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN) | ~1.2 × 10¹⁴ | ~76 | 3.8 – 4.5 | High dielectric strength, machinable electrical insulator |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RB-SiC) | 10⁵ – 10⁷ | 2 – 4 | 9 – 10 | Semiconductive, not suitable for insulation |
| Sintered SiC (SSiC) | 10³ – 10⁵ | 2 – 4 | 9 – 10 | Strongly semiconductive, used where conductivity is acceptable |
Chemical Properties of Ceramic Plate Materials
| Material | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Oxidation Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Chemical Stability Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99–99.99%) | Excellent (except HF, hot H₃PO₄) | Good to Very Good | Excellent up to high temperatures | Excellent in most inorganic chemicals | Chemically inert in most industrial acids and solvents |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Excellent (except HF) | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Highly stable in aggressive chemical environments |
| Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) | Excellent (except molten alkali, HF) | Poor to Fair (molten alkali attack) | Fair (oxidizes above ~900 °C in air) | Excellent in non-oxidizing environments | Extremely pure and inert, but sensitive to oxidation |
| Hot Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN) | Excellent (except molten alkali, HF) | Poor to Fair | Fair (oxidizes above ~850–900 °C in air) | Excellent in vacuum or inert atmospheres | Chemically stable, machinable insulator |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RB-SiC) | Excellent (except HF, molten alkali) | Very Good | Good (surface oxidation above ~1000 °C) | Excellent | Resistant to most acids and corrosive media |
| Sintered SiC (SSiC) | Excellent (except HF, molten alkali) | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | One of the most chemically resistant structural ceramics |
Industrial Ceramic Plate Products & Types
Built for harsh industrial service, these ceramic plates resist abrasion, thermal shock, and chemical attack—so lining and barrier surfaces last longer with fewer changeouts. Standard sizes are available, and custom machining supports fit-critical designs.
alumina ceramic plate
Alumina (Al2o3) plates for wear liners and insulation barriers—stable fit, fewer chip-outs, easier replacements.
zirconia ceramic plate
Zirconia (Zro2) plate for impact-prone duty—reduces edge chipping and cracking in frequent changeout zones.
silicon carbide plate
Silicon carbide ceramic plate for heat + wear—slows fast erosion and extends liner life at harsh zones.

aluminum nitride ceramic plate
AlN ceramic plates for heater and power-module builds—fast heat spread and stable insulation in compact layouts.

ZTA ceramic plate
ZTA ceramic plate for transfer points—cuts premature wear and liner failure where abrasion spikes.

Boron Carbide ceramic plate
BC ceramic plate for extreme wear liners—used where abrasion eats through metal too quickly.
Boron Nitride Ceramic Plate
Boron nitride ceramic plate for non-stick hot-face fixtures—clean release in high-heat handling and forming steps.

Magnesia Ceramia Plate
Magnesia ceramic plate for hot-face contact—keeps stable support surfaces in dry high-heat service.

Machinable Glass Ceramic Plate
Machinable glass ceramic plate for quick prototypes and fixture plates—easy machining without long lead-time tooling.

Machined Lanthanum Hexaboride Plate
LaB6 plate for high-temperature electron-emission parts—stable geometry for precision vacuum duty.

ceramic heater plate
Ceramic heater plates deliver stable, even heating for compact equipment, helping reduce hot spots and control temperature drift.

ceramic liner plates
Ceramic liner plates protect chutes, hoppers, and transfer points from rapid abrasion, extending service life with fewer changeouts.

Ceramic Wear Plates
Ceramic wear plates take the impact in high-wear zones, helping prevent scoring, thinning, and premature failures on metal surfaces.

porous ceramic Plate
Porous ceramic plates deliver controlled permeability across a wide face, helping distribute vacuum or airflow evenly and reduce channeling.
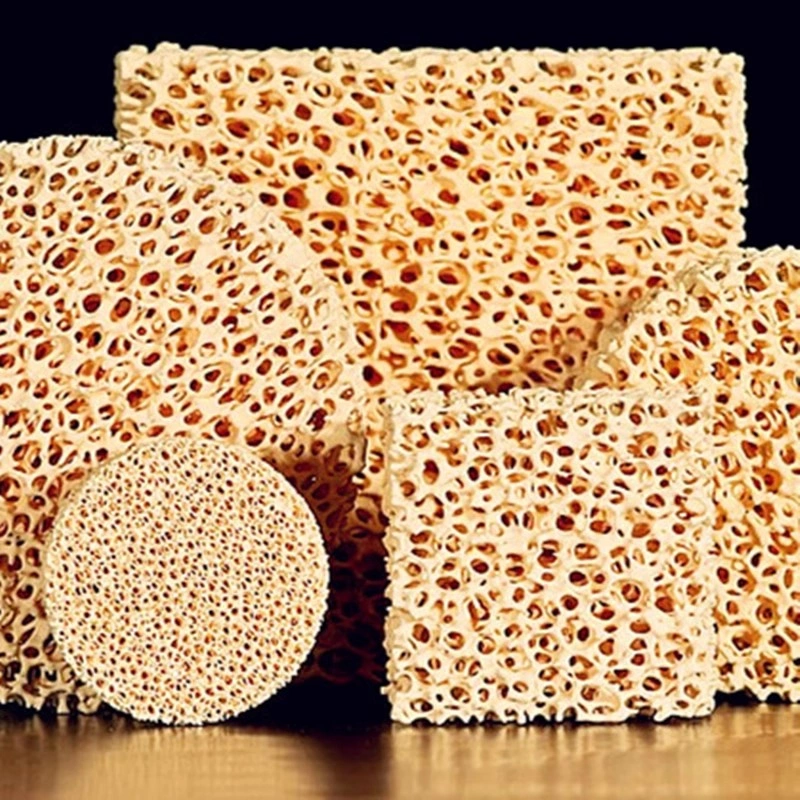

ceramic filter plate
Ceramic filter plates enable stable solid–liquid separation with cleanable pores, supporting repeatable filtration and longer service intervals.
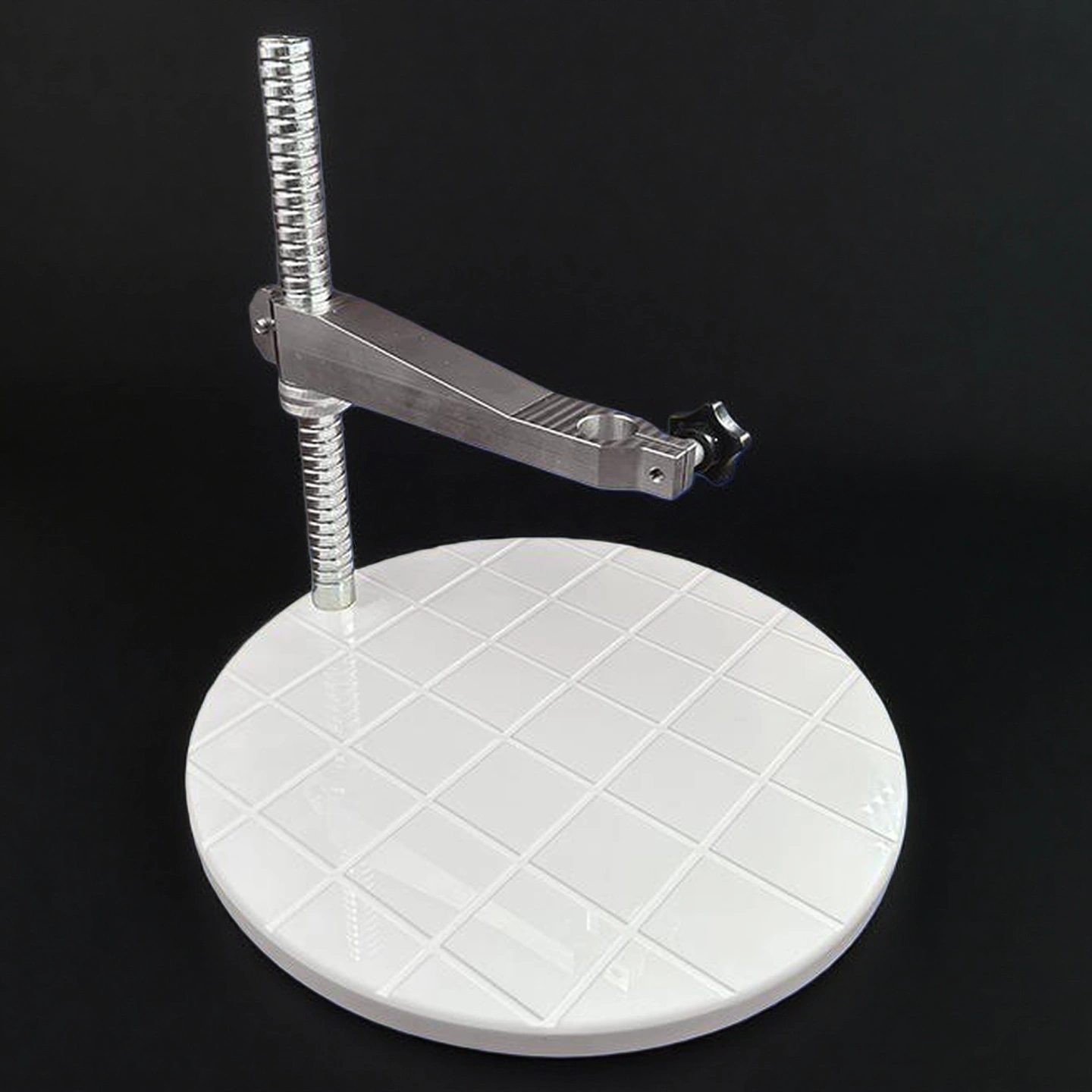

Ceramic Grinding Plate
Ceramic grinding plates provide a rigid, flat wear surface for lapping and grinding setups, helping keep contact uniform and reduce edge rounding.
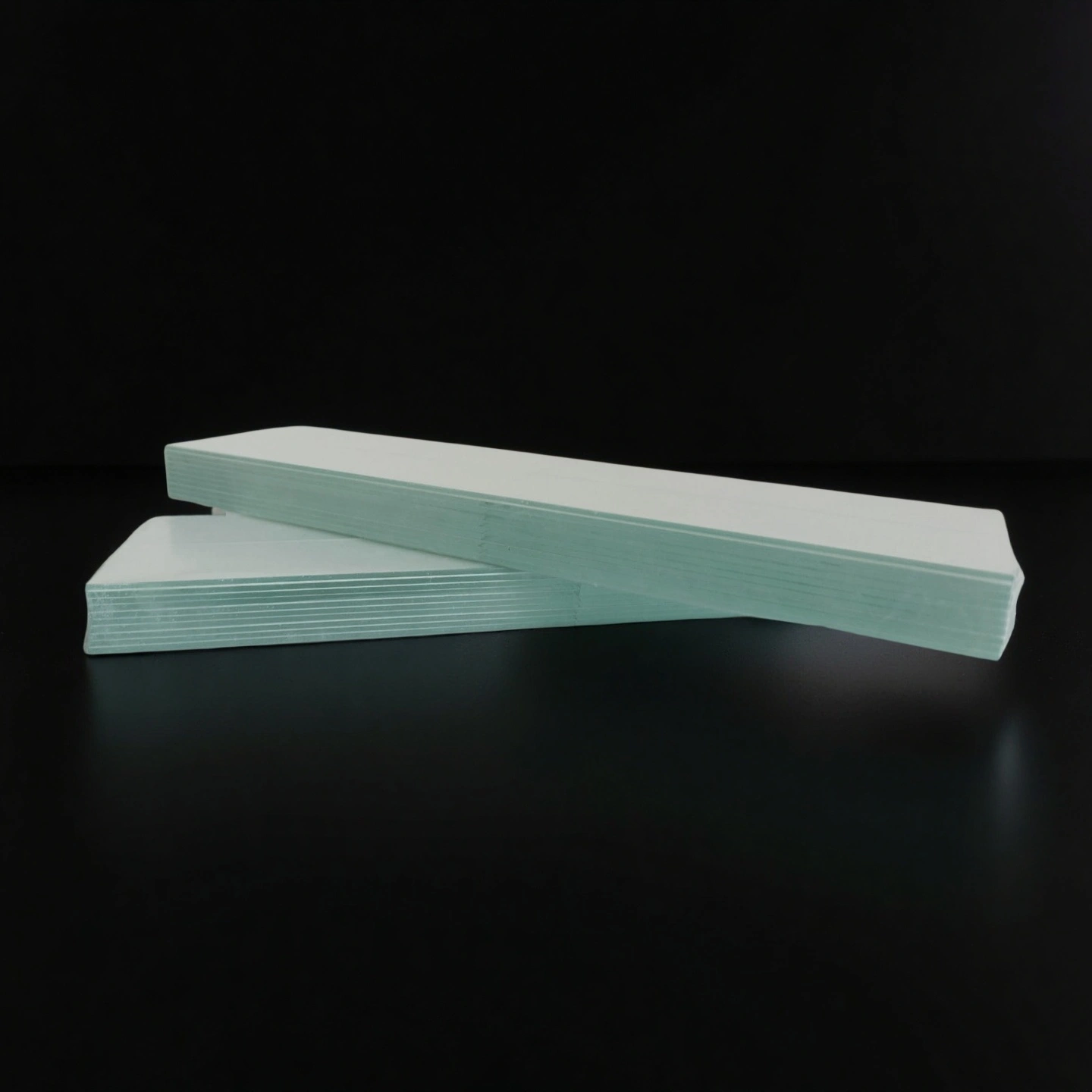

Ceramic TLC plate
Ceramic TLC plates provide a flat, chemically stable surface for thin-layer chromatography, supporting cleaner separations and repeatable runs.
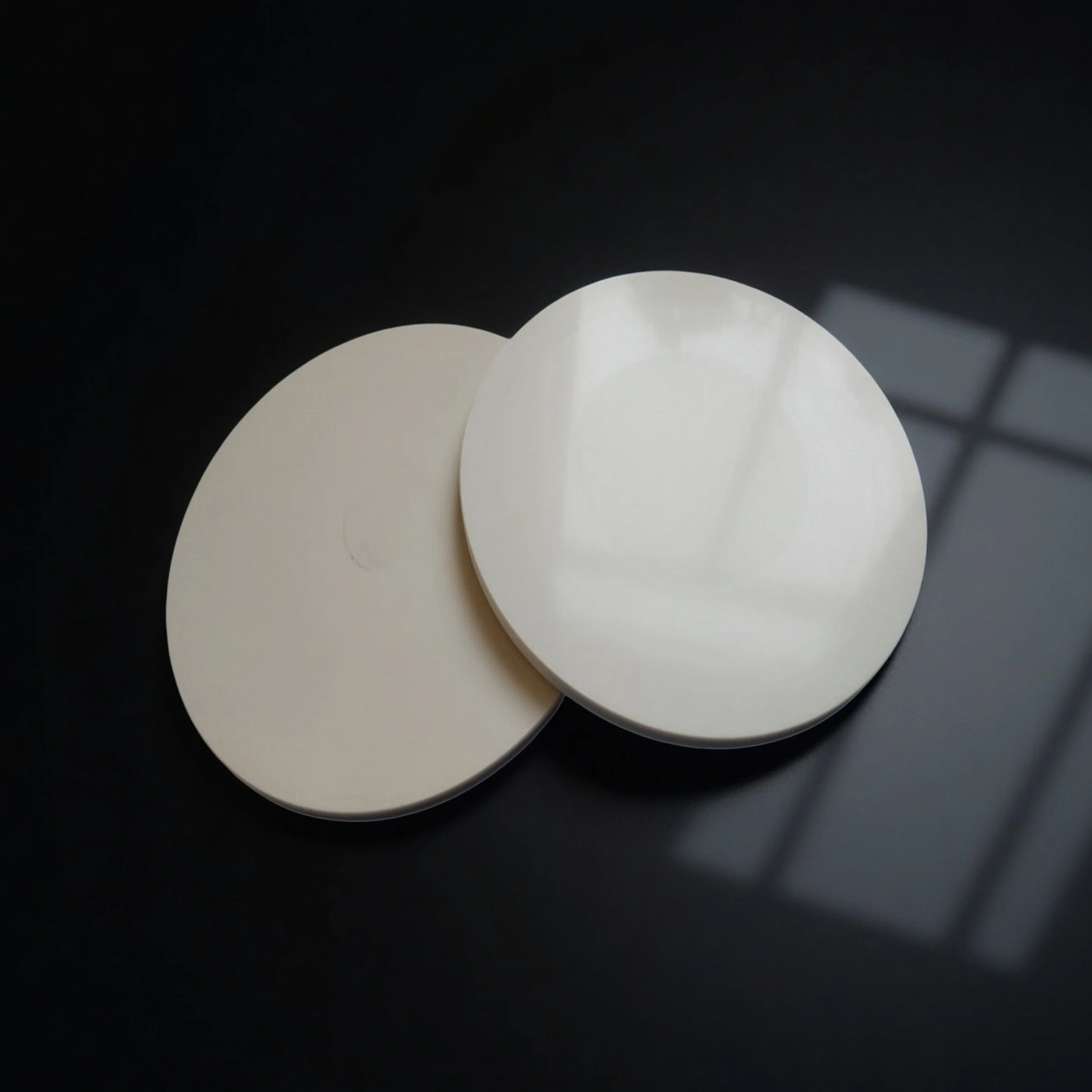

ceramic Polishing Plate
Ceramic polishing plates maintain stable flatness in fine finishing, supporting consistent surface quality and repeatable results across batches.
Industrial Ceramic Plates — Where Metal Distorts, Ceramics Stay Stable.
Control wear, deformation, and contamination in high-stress industrial environments.
Industrial Ceramic Plate Applications
Industrial ceramic plates are used wherever wear, heat, corrosion, or dimensional drift limit the service life of metal or polymer components. Different ceramic materials are selected based on operating temperature, mechanical load, and chemical exposure.

🛠Wear & Abrasion Protection
Typical environments:
chutes, hoppers, transfer points, sliding surfaces.
1. Protect equipment from abrasive solids and slurry erosion
2. Maintain flatness and surface integrity over long service cycles
3. Reduce downtime and replacement frequency
Typical products
Ceramic wear plates, ceramic lining plates, impact-resistant ceramic tiles
🧩Industrial ceramic plate examples
In a mineral handling system, ceramic wear plates replaced AR steel liners at a transfer chute handling silica-rich solids, extending wear life from about 6 months to over 24 months while reducing maintenance interventions by approximately 70%. Under continuous abrasion, thickness loss remained below 0.2 mm per year, resulting in more stable material flow and significantly lower unplanned downtime.

⚡Electrical Insulation & Thermal Isolation
Typical environments:power equipment, heating systems, process fixtures
1. Electrically insulating while maintaining mechanical strength
2. Reliable performance under combined heat and voltage stress
3. Low risk of tracking, leakage, or breakdown
Typical products
Electrical insulation plates, heater support plates, thermal isolation plates
🧩Industrial ceramic plate examples
In a high-temperature electrical heating assembly, alumina ceramic insulation plates replaced mica-based sheets, enabling stable continuous operation at approximately 900 °C with no recorded dielectric failures. Electrical leakage remained below 10⁻¹² A under rated voltage, extending insulation service intervals and improving overall system safety and reliability.

🧪Chemical & Corrosion-Resistant Linings
Typical environments:chemical processing, reactors, plating lines
1. Resist acids, alkalis, and corrosive media
2. Non-reactive surfaces help reduce contamination
3.Long-term chemical stability in harsh service
Typical products
Chemical lining plates, corrosion-resistant ceramic plates, reactor lining plates
🧩Industrial ceramic plate examples
In a chemical processing line exposed to mixed inorganic acids, ceramic lining plates were installed in place of stainless steel supports, showing less than 0.1% mass loss after 12 months of operation, while metal components exhibited visible corrosion within 8–10 weeks. Cleaning frequency was reduced by about 50%, helping stabilize process conditions and minimize contamination risk.
Precision Support & Structural Components
Typical environments:
semiconductor tools, industrial equipment fixtures
1. Tight dimensional control and surface stability
2. Support assemblies where repeatability matters more than cost
3. Compatible with custom machining and complex geometries
📍Typical materials
Precision ceramic plates, equipment support plates, custom machined ceramic plates
🧩Industrial ceramic plate examples
In a semiconductor tool fixture, precision ceramic plates were used as structural support components and maintained dimensional drift within 5 µm over six months of operation across repeated thermal cycles from 25 °C to 600 °C. The improved geometric stability contributed to a 2–3% yield increase by enhancing process repeatability and alignment accuracy.
Custom Industrial Ceramic Plates
ADCERAXcustom industrial ceramic panels are made to your drawing, including size/thickness, flatness, holes/slots, edge features, and surface finish. Typical lead time is 2–9 weeks, depending on material choice, tolerances, and machining complexity.
Customization Options
Define the dominant wear mechanism first—sliding abrasion, impact, particle erosion, or rubbing contact. Match plate thickness and wear margin to reduce fast thinning, edge breakage, and early changeouts in harsh-duty zones.
Share your drawing and fit points for reliable installation—plate size/thickness, flatness, holes/slots, countersinks, and edge chamfers. Controlled fit helps prevent gaps, vibration loosening, and premature cracking during service.
For hot zones, set the operating temperature and thermal cycling range to control warpage and thermal-stress cracking. Proper design maintains stable geometry and repeatable performance through repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles.
Specify the contact surface requirements—smoothness, sealing lands, or textured grip surfaces—based on how the plate interfaces with parts or media. The right surface finish helps reduce contamination, sticking, and uneven wear over time.
Customization Process
Send your application, operating temperature, wear/chemical exposure, and target service life. Include plate size/thickness, drawing (holes/slots/countersinks), quantity, and destination.
We confirm key specs: material grade, dimensions, flatness/tolerance, edge features, and surface finish. If needed, we recommend a plate design to reduce cracking, warpage, or wear.
We manufacture to spec and inspect critical dimensions and flatness. Inspection records, part ID/marking, and QC traceability are available for repeatable replacements.
Plates are protected, labeled, and packed to prevent chipping and surface damage, then shipped with export-ready documentation.
Why Choose ADCERAX for Industrial Ceramic Plates?
ADCERAX supplies export-ready industrial ceramic plates with controlled manufacturing and batch inspection for consistent strength, flatness, and harsh-service stability. Fast engineering support helps confirm geometry, tolerances, surface finish, and lead time for reliable fit and repeatable replacements.
Competitive pricing with strict quality control from raw material sourcing to final delivery
Professional team providing comprehensive technical support and collaborative design
Small batch orders to large-scale production with complex geometries and tight tolerances
24-hour response and 24-hour dispatch for standard items, 3-7 weeks for custom orders.
China Industrial Ceramic Plate Manufacturers-ADCERAX

ADCERAX is a factory-direct industrial ceramic plate supplier with 20+ years of advanced ceramics experience, delivering wear-resistant, heat-stable, and corrosion-tolerant ceramic plates for harsh industrial service where uptime and dimensional stability matter.
Standard ceramic plates are available for fast replacement, and custom-to-drawing builds cover plate size/thickness, flatness, holes/slots, edge features, and surface finish. With batch inspection, traceable records, and protective packing, ADCERAX helps buyers keep performance consistent and maintenance cycles predictable.
Industrial Ceramic Plate Processing
High temperature ceramic plates are built through controlled forming, high-temperature firing, and precision finishing to achieve stable flatness, strength, and repeatable performance. Below is a practical view of how plates are produced and what each step controls.
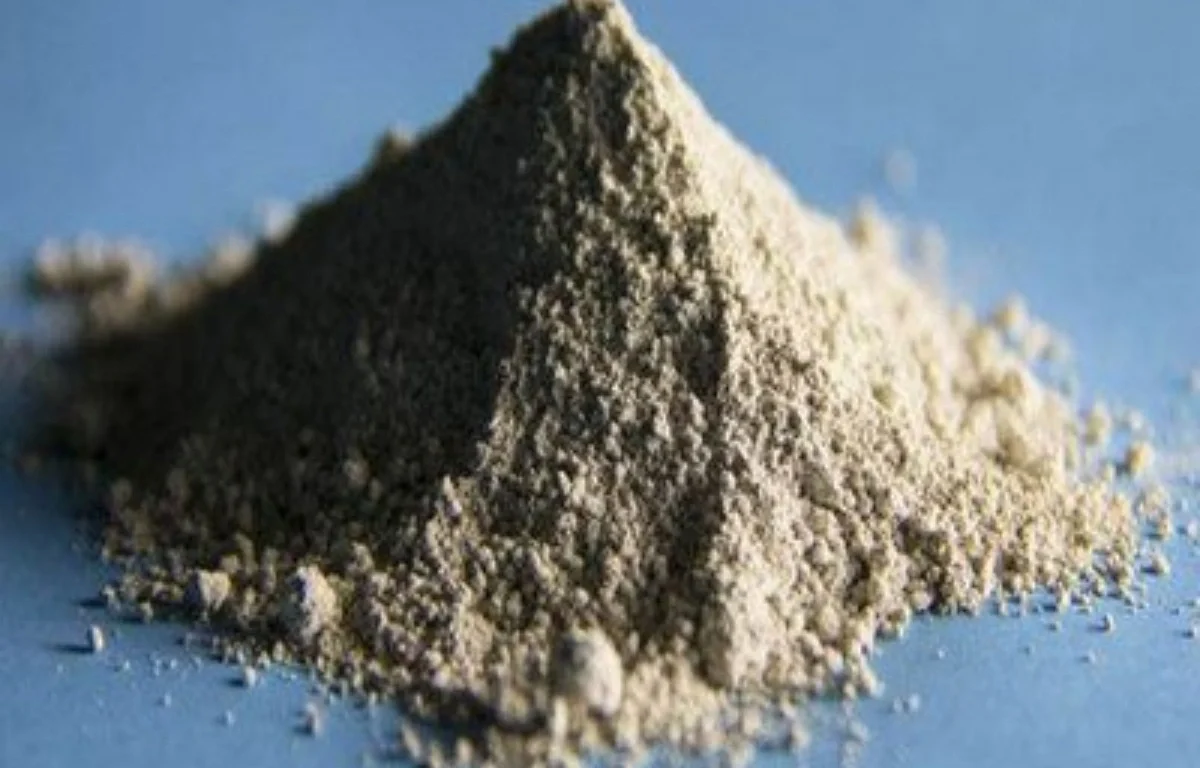

🧱 1)Material Preparation & Recipe Control
🔹Raw powder selection and batching to meet target purity and particle distribution
🔹 Binder addition and mixing for consistent green strength and forming stability
🔹Lot control to reduce variation between production batches
What it impacts: strength consistency, defect rate, warpage risk
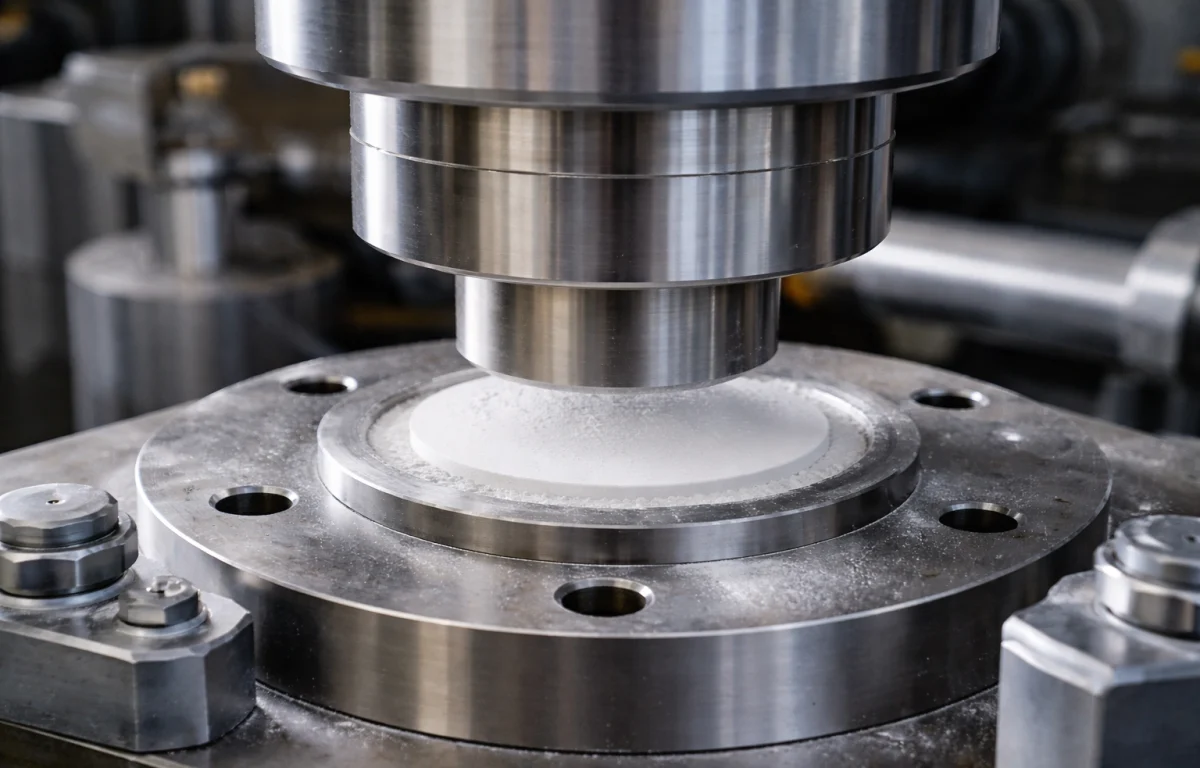

🧩 2)Forming & Green Machining
Choose the forming route based on plate size, thickness, and features:
🔹Dry pressing for dense, flat plates with stable thickness
🔹Tape casting for thinner plates and uniform surfaces
🔹Slip casting for complex geometries or special profiles
🔹 Green machining for holes/slots/windows when required
What it impacts: dimensional repeatability, feature accuracy, yield
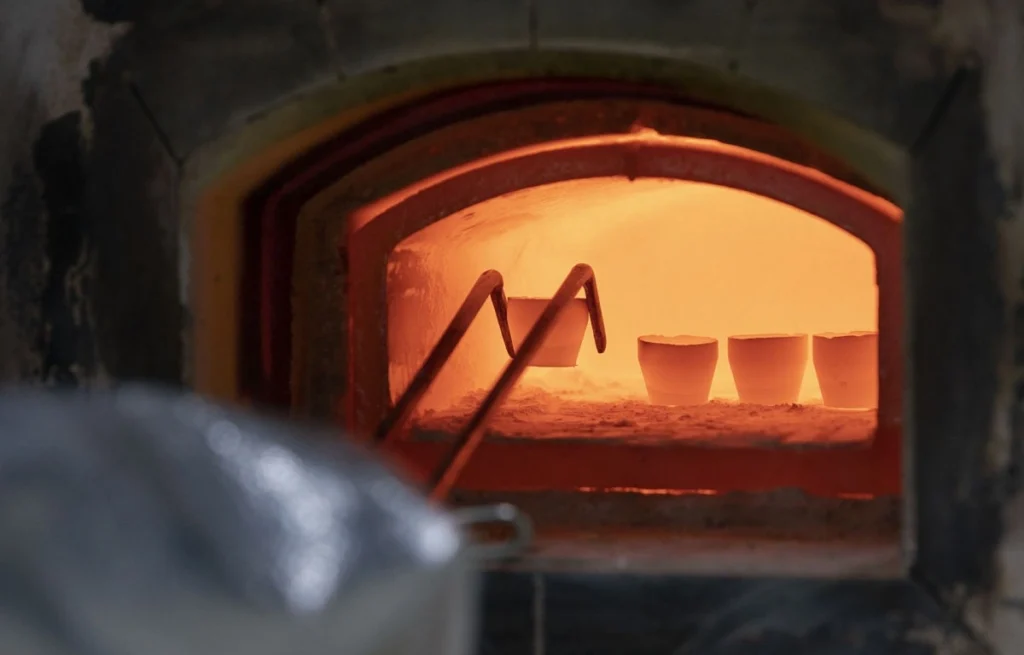

🔥3) Sintering / Firing & Dimensional Stabilization
🔹High-temperature firing matched to each ceramic system
🔹Controlled heating/cooling to reduce thermal stress and distortion
🔹Process tuning to achieve target density and stable microstructure
What it impacts: flatness stability, thermal performance, service life

🛠 4) Precision Finishing (Grinding / Lapping / Surface Control)
🔹Surface grinding for thickness control and parallelism
🔹Lapping for flatness and tighter surface finish requirements
🔹Edge finishing (chamfer/radius) to reduce chipping and stress.
🔹Machined holes/slots/countersinks for installation fit
What it impacts: fit reliability, sealing/contact performance, crack resistance
FAQs About Industrial Ceramic Plate
Choose ceramics when failure is driven by abrasion/erosion, corrosion, heat distortion, electrical leakage, or contamination. Ceramics typically win when uptime, dimensional stability, and cleanliness matter more than impact tolerance or low initial cost.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is the most widely used industrial ceramic for wear, heat stability, and electrical insulation. It is commonly used for wear plates, insulation parts, and furnace fixtures.
Choose it when… you need a reliable all-round ceramic for wear/heat/insulation with strong value and repeatable supply. - Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Zirconia is chosen for higher toughness and better crack resistance in fit-critical or shock-prone parts. It helps reduce chipping and fracture under vibration or assembly stress.
Choose it when… impact, vibration, or mounting stress is the main risk and you need stronger crack resistance. - Silicon Carbide (SiC)
SiC is used for severe wear and corrosive service that also needs high stiffness and thermal stability. It performs well in high-load, high-temperature environments.
Choose it when… abrasion/erosion is heavy and you need maximum rigidity and long service life. - Boron Nitride (BN)
BN is selected for high-temperature electrical insulation with easy machining and clean contact behavior. It is often used in controlled atmospheres or vacuum conditions.
Choose it when… you need a machinable high-temp insulator with low sticking, especially in inert or vacuum environments.
Start with the failure mode: wear (hardness, microstructure), heat (max use temp, creep/warpage), chemicals (compatibility), electrical need (resistivity/dielectric), and mechanical load (flexural strength, design safety factor). Then confirm geometry sensitivity: flatness, sealing lands, holes/slots, edge conditions, and mounting method.
Ceramics are strong in compression but more sensitive to tensile stress and edge chips than metals. Most “brittleness problems” are design or mounting problems—sharp corners, point loads, uneven clamping, thermal gradients, or impact—rather than a material defect.
Common causes include stress concentration at sharp corners/holes, uneven support causing bending, overtightened bolts, thermal shock from fast quenching, and local hot spots. Good fixes are chamfers/radii, compliant pads, controlled clamping, and layouts that avoid point loading.
Avoid placing holes too close to edges, use generous corner radii on slots, and keep adequate ligament width around cutouts. Where possible, use countersinks carefully and control torque to prevent bending stress; design the fixture so the plate sits flat and supported.
Specify finish based on the interface: sealing or flat support needs tighter flatness and smoother finish; wear liners may benefit from controlled texture to reduce slip or control flow behavior. Over-specifying finish increases cost without improving performance, so link finish to function.
Yes, but most dense ceramics are hard and require diamond machining or grinding. It is typically more cost-effective to form near-net shapes and then finish critical features; tight tolerances, thin walls, and deep slots increase cycle time and risk.
At minimum: dimensions, thickness, flatness (if required), edge quality, and visual checks for chips or micro-cracks. For critical parts, add traceability marking, inspection records, and sampling plans that match your risk level and replacement strategy.
Alumina (Al₂O₃): Typically ≤1700–1800 °C (no-load conditions). Real service limits drop if the plate is clamped, heavily loaded, or exposed to fast heat-up/cool-down.
Zirconia (ZrO₂): Commonly ~1500 °C continuous use for stable service, especially where insulation and toughness are valued.
Reaction-Bonded SiC (RB-SiC): Typically ≤1380 °C for structural use, with good rigidity and thermal performance.
Sintered SiC (SSiC): Typically ≤1600 °C for harsher furnace duty where higher temperature capability is required.
Boron Nitride (BN): Often ~900–1000 °C in air, but can reach much higher in vacuum/inert atmosphere (commonly ~1850–2300 °C, depending on grade), since oxidation in air is the main limiter.
Tip: If your process includes rapid thermal cycling, prioritize the heating/cooling rate and fixture design as much as the headline temperature rating.
Proper care helps industrial ceramic plates maintain flatness, strength, and service life in harsh conditions. Follow these best practices:
Handle carefully: Avoid impacts on edges and corners, which are the most chip-sensitive areas. Use padded supports and do not place ceramic plates directly on hard metal surfaces.
Install with uniform support: Ensure full, even contact with the fixture or backing surface. Avoid point loads, uneven clamping, or over-tightening bolts that can introduce bending stress.
Control thermal cycling: Heat up and cool down gradually whenever possible. Sudden temperature changes can create thermal stress and lead to cracking, especially in thick plates.
Keep surfaces clean: Remove abrasive debris, metal fragments, or chemical residues that can cause localized wear or contamination during operation.
Inspect periodically: Check for edge chips, surface cracks, or flatness changes and replace plates before damage propagates into functional failure.
Use proper storage and transport: Store plates flat with protective spacing, and use shock-resistant packaging during transport to prevent chipping.
With correct handling, installation, and thermal management, industrial ceramic plates can deliver long, predictable service life with minimal maintenance.
Yes. ADCERAX customizes industrial ceramic plates to your drawing and operating conditions, including size/thickness, flatness, holes/slots, edge features, and surface finish. Share your application details and a sketch/CAD, and we’ll confirm the best design and lead time (typically 2–9 weeks, depending on complexity).
You can buy corrosion-resistant ceramic plates from a factory-direct industrial ceramic plate supplier that supports wholesale orders, custom machining, and global export. ADCERAX offers standard plates for quick replacement and custom-to-drawing options (size/thickness, holes/slots, edge features, surface finish) to match your chemical environment and operating conditions, with factory pricing for international buyers.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
info@adcerax.com
Telephone: +(86) 0731-74427743
WhatsApp: +(86) 19311583352
Within 24 hours
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

