
Ceramic Substrate for Electronics — Materials, Metallization & Custom Machining
ADCERAX is a factory-direct supplier of ceramic substrate blanks and build-to-print parts in Al₂O₃ (alumina), AlN, and Si₃N₄, helping prevent warpage-related assembly issues, thermal bottlenecks, and insulation failures through controlled material selection, flatness management, and critical tolerance control for ceramic PCB platforms, power electronics thermal paths, LED heat-spreader builds, and high-voltage insulation assemblies.
Send your drawing today—get a quote with DFM guidance, QC checkpoints, and lead-time options, so you can move from prototype to repeat supply with confidence.
What is Ceramic Substrate?
Ceramic Substrate Definition & Meaning
A ceramic substrate is an electrically insulating carrier made from engineering ceramics (such as Al₂O₃, AlN, or Si₃N₄) that supports circuits or devices while helping move heat away from the assembly. Compared with standard PCB materials, it is chosen when you need better heat handling, stronger electrical isolation, and more stable dimensions under temperature change for reliable industrial electronics builds.
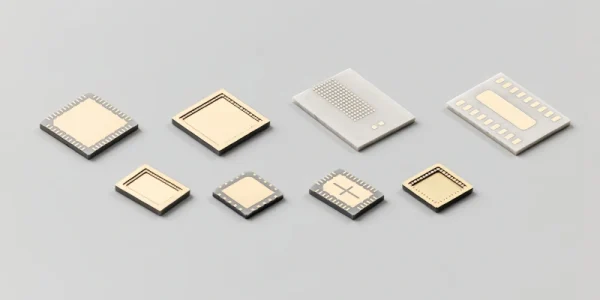
Advantages of Ceramic Substrate
Ceramic substrates are selected when you need stable electrical insulation and heat management without sacrificing geometry control in demanding assemblies.
Electrical Isolation You Can Trust
Ceramic substrates maintain reliable insulation performance in compact, high-voltage layouts where leakage risk must stay controlled.
Strong Chemical and Wear Resistance
They tolerate harsh environments better than many polymer-based materials, supporting longer service life in industrial conditions.
Built for Custom Geometries and Features
Holes, slots, profiles, and edge conditions can be specified to match fixtures, connectors, and thermal interfaces in build-to-print projects.
Flatness Supports Better Bonding and Yield
With controlled flatness/warpage targets, ceramic substrates help improve soldering, brazing, or metallization consistency and reduce rework.
Better Thermal Path, Lower Hot-Spot Risk
They move heat away from critical devices more efficiently than many organic boards, helping stabilize temperature rise under load.
Dimensional Stability Under Heat
Ceramic stays rigid and stable as temperature changes, reducing drift that can affect alignment, contact, and assembly repeatability.
Ceramic Substrate Properties
Ceramic substrates provide reliable electrical insulation, controlled flatness, and stable geometry under heat, reducing warpage-related assembly issues. They also support efficient heat spreading and consistent dielectric performance.
Alumina Ceramic Substrate
Alumina substrates (Al₂O₃) offer reliable electrical insulation, stable geometry at elevated temperatures, and cost-effective performance for ceramic PCBs, heater parts, and general electronic assemblies.
| Property | Unit | 96% Al₂O₃ | 99% Al₂O₃ | 99.5% Al₂O₃ | 99.6% Al₂O₃ | 99.7% Al₂O₃ | 99.8% Al₂O₃ | 99.9% Al₂O₃ | 99.99% Al₂O₃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina content | % | 96 | 99 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.99 |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.75 | 3.88 | 3.89 | 3.91 | 3.92 | 3.93 | 3.95 | 3.98 |
| Flexural strength | MPa | 330 | 360 | 379 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 320 |
| Hardness | GPa | 11.5 | 13.5 | 14.1 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m·K | 20–25 | 30–35 | 35 | 32–37 | 33–38 | 34–39 | 35–40 | 36–42 |
| Thermal shock resistance (ΔT) | °C | 150 | 200 | — | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 228 |
| Maximum use temperature (no load) | °C | ≤1600 | ≤1700 | ≤1750 | 1755 | 1760 | 1765 | 1770 | 1800 |
| Dielectric strength | kV/mm | 8–10 | 10–12 | 11–13 | 12–14 | 12–15 | 13–16 | 14–17 | 15–18 |
| Volume resistivity (25°C) | Ω·cm | ≥1×10¹³ | ≥1×10¹⁴ | ≥3×10¹⁴ | ≥5×10¹⁴ | ≥1×10¹⁵ | ≥3×10¹⁵ | ≥5×10¹⁵ | ≥1×10¹⁶ |
- This chart displays the typical properties of alumina (Al2O3) substrate used in our standard products. Please note: Customized parts may have adjusted characteristics depending on production methods, with specific parameters determined by the stabilizer type and formula chosen for your application.
Zirconia Toughened Alumina Ceramic Substrate
ZTA substrates combine alumina’s rigidity with zirconia toughening to improve fracture resistance, helping reduce edge chipping and cracking in fixtures and electronic assemblies under shock, vibration, or repeated handling.
| Property | Unit | Typical Range | Why Buyers Specify It |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | g/cm³ | 4.00 – 4.30 | Indicates densification and batch consistency |
| Flexural Strength | MPa | 700 – 1,200 | Impacts handling breakage risk and safety margin |
| Fracture Toughness | MPa·√m | 6 – 10 | Key ZTA advantage for edge-chipping and crack resistance |
| Hardness (Vickers) | GPa | 14 – 17 | Affects wear/scratch resistance and machinability |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m·K | 18 – 30 | Drives heat spreading performance (typically below AlN) |
| CTE (20–300°C) | ×10⁻⁶ /K | 8.0 – 9.5 | Influences thermal-cycling stress and material matching |
| Dielectric Strength | kV/mm | 10 – 15 | Determines insulation margin (depends on thickness/surface) |
| Volume Resistivity (25°C) | Ω·cm | 10¹² – 10¹⁴ | Indicates insulation stability and leakage risk |
- Values are typical ranges; they vary with ZrO₂ content, firing profile, and final density.
Silicon Carbide Substrate
Silicon carbide substrates deliver high stiffness and chemical resistance, maintaining stable performance in corrosive, abrasive, or high-temperature electronic and thermal-duty environments.
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material System | RBSiC (80% SiC, 20% free Si) / SSiC (≥99% SiC) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | ≤1380°C (RBSiC) / ≤1600°C (SSiC) |
| Bulk Density | 3.02 g/cm³ (RBSiC) / 3.10 g/cm³ (SSiC) |
| Open Porosity | <0.1% |
| Flexural Strength (20°C) | 250 MPa (RBSiC) / 380 MPa (SSiC) |
| Flexural Strength (1200°C) | 280 MPa (RBSiC) / 400 MPa (SSiC) |
| Compressive Strength | 1000–2200 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 330 GPa (RBSiC) / 420 GPa (SSiC) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 45 W/m·K (RBSiC) / 74 W/m·K (SSiC) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 4.1–4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K |
| Hardness | 2600–2800 kg/mm² |
| Chemical Stability Range | pH 2–12 |
| Oxidation Stability | <1% microstructural oxidation after 50 cycles (1000°C → RT) |
- Please note: Customized parts may have adjusted characteristics depending on production methods, with specific parameters determined by the stabilizer type and formula chosen for your application.
Silicon Nitride Substrate
Silicon nitride substrates combine high strength with excellent thermal-shock and thermal-cycling stability, supporting reliable builds in mechanically stressed power and industrial electronics.
| SiN4 Type | Gas pressure sintering Si3N4 | Hot pressing sintering Si3N4 | High thermal conductivity Si3N4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.5 |
| Texture strength (MPa) | 300 | 300-320 | 300-320 |
| Young Modulus | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Hardness (GPa) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Maximum working temperature (°C) | 1100 | 1200 | 1200 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient (Mm/m·K) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Thermal shock resistance (ΔT °C) | 550 | 580 | 600 |
- Please note: Customized parts may have adjusted characteristics depending on production methods, with specific parameters determined by the stabilizer type and formula chosen for your application.
Ceramic Substrates and Components
Explore porcelain ceramic substrate and related components across common material systems and build types—from Al₂O₃, AlN, Si₃N₄ and ZTA to SiC, BeO, sapphire and YSZ—with options for standard blanks or build-to-print parts.

alumina ceramic substrate
Alumina (Al₂O₃) substrates deliver stable electrical insulation and cost-efficient strength, keeping geometry consistent for ceramic PCBs and general electronics.

zTA ceramic Substrates
ZTA ceramic substrates improve crack resistance and edge durability while maintaining rigidity, helping reduce chipping risk in machined and assembled parts.
aluminum nitride substrate
Aluminum nitride (AlN) substrates provide high thermal conductivity with strong dielectric isolation, helping pull heat from power devices and LED assemblies.

silicon nitride substrate
Silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) substrates offer high mechanical toughness and thermal-cycling stability, supporting reliable performance in stressed power module builds.
silicon carbide substrates
Silicon carbide (SiC) substrates deliver high stiffness and wear resistance, staying stable in corrosive or high-temperature electronics and thermal assemblies.

Beryllium Oxide Substrates
Beryllium oxide (BeO) substrates combine excellent thermal conductivity with strong electrical insulation, supporting compact layouts where heat dissipates fast.

Sapphire Substrate
Sapphire substrates provide optical-grade stability and dielectric strength, enabling durable windows, sensors, and specialized electronic or photonic packages.
YSZ Ceramic Substrate
YSZ ceramic substrates offer tough, thermally stable insulation with strong shock resistance, supporting fixtures and components in harsh thermal cycling.
HTCC Ceramic Substrate
HTCC ceramic substrates deliver strong insulation and structural stability at elevated temperatures, supporting reliable multilayer circuits and robust ceramic packages.
AMB Ceramic Substrate
AMB ceramic substrates provide high bond strength between metal and ceramic, improving thermal cycling reliability in power modules and harsh-duty assemblies.
Metallized Ceramic Substrates
Metallized ceramic substrates enable solderable, bondable conductor layers on ceramics, supporting precise interconnects, stable heat paths, and consistent assembly yield.
ceramic substrate circuit board
Ceramic substrate circuit boards provide stable insulation and heat spreading, supporting reliable traces and consistent performance in compact electronics.
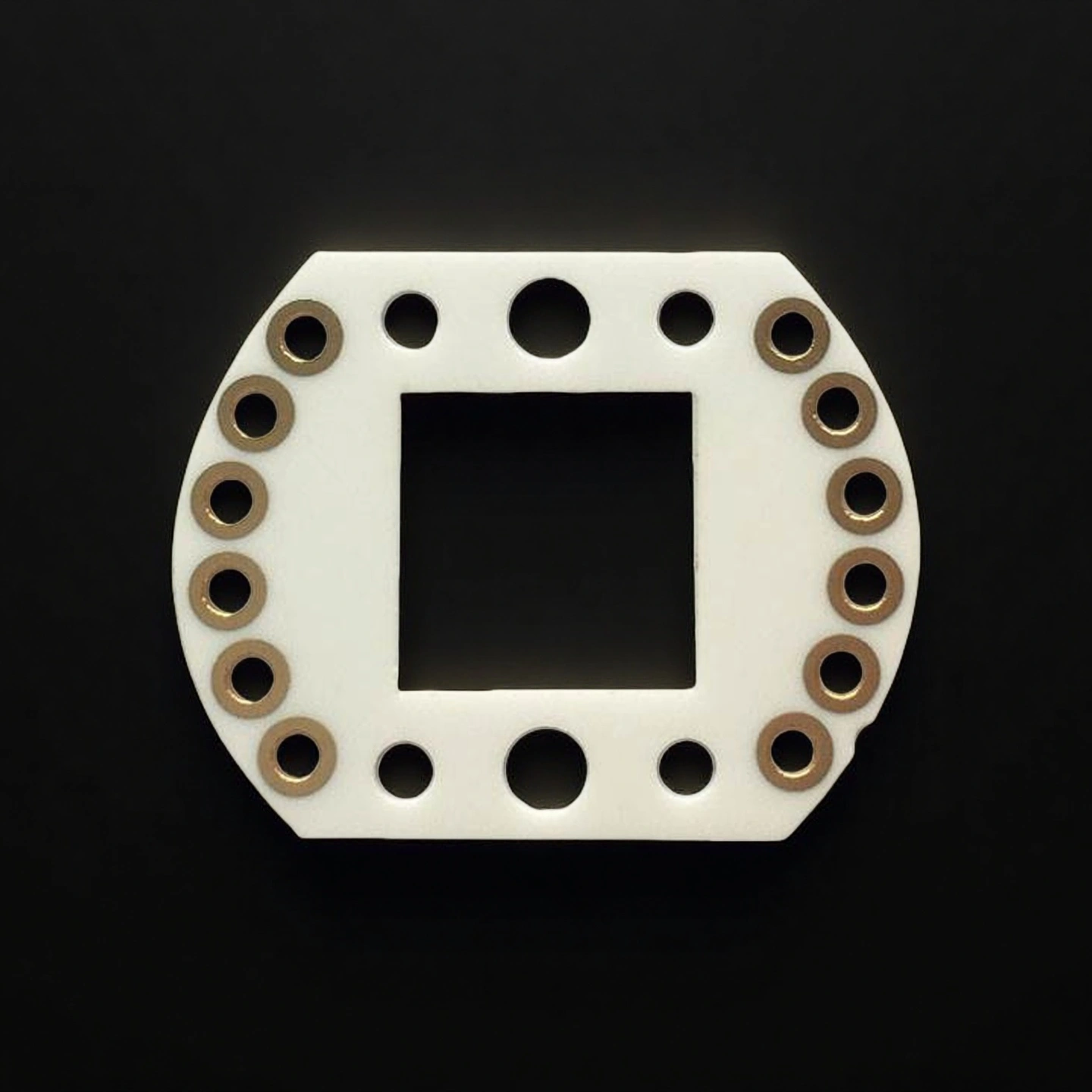
RF ceramic substrate
RF ceramic substrates offer controlled dielectric behavior and low loss, helping maintain signal integrity in microwave and high-frequency circuits.
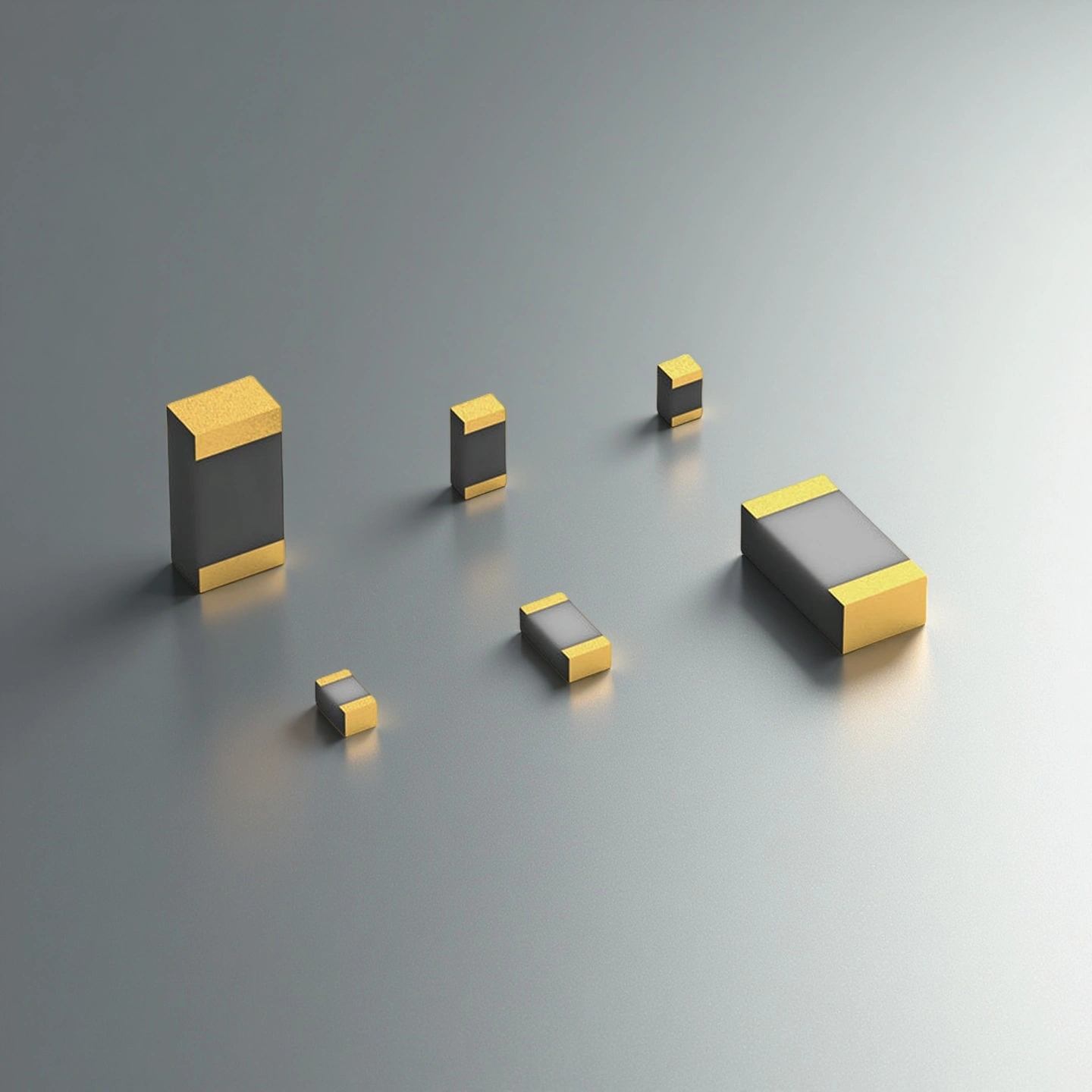
Heat Spreader Ceramic Substrate
Heat spreader ceramic substrates move heat efficiently while staying electrically insulating, reducing hot spots under power devices and LED modules.
Control Ceramic Substrate Cost — Clear Options for Price and Lead Time
Send your drawing or target specs to receive tiered quoting (standard vs enhanced QC), with practical lead-time routes to meet budget and schedule requirements.
Ceramic Substrate Applications
Ceramic substrate applications in industrial electronics focus on stable insulation and heat control where standard boards can drift, warp, or overheat. Below are four practical use blocks aligned with industrial-friendly sourcing paths.

Power Electronics & Industrial Drives
--reduce hotspot & insulation risk
Ceramic substrates support insulated thermal paths in inverters, converters, motor drives, welding power supplies, and induction systems. This is a common ceramic substrate electronics use case where heat spreading and electrical isolation must stay predictable across repeat builds.
🧩ADCERAX electronic ceramic substrate helps reduce hot-spot temperature rise and insulation breakdown risk by recommending the right ceramic system and locking critical thickness/flatness/tolerance targets early. For build-to-print parts, we control geometry and inspection points to cut rework caused by warpage, poor contact, or inconsistent fit-up.
LED / Lighting Thermal Substrate
--reduce thermal bottleneck & bonding variation
For ceramic substrate LED designs, ceramics provide a rigid, insulating base that helps pull heat away from LEDs to stabilize output and service life. Buyers often request led ceramic substrate options by material, thickness, and flatness target to match assembly yield needs.
🧩ADCERAX led ceramic substrate improves LED build stability by controlling flatness, surface quality, and edge condition, reducing voiding, uneven bonding, and yield loss during assembly. We support fast iteration from samples to batch supply so thermal path designs can be validated without long re-qualification loops.
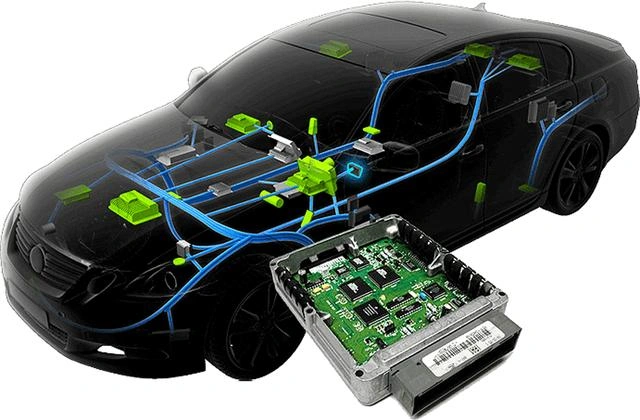
Automotive Electronics
--reduce cycling stress & fit-up rework
Ceramic substrates are used in automotive electronic modules that need reliable insulation and heat management under vibration and temperature cycling. This block targets ceramic substrate automotive for electronics—not honeycomb catalyst substrates—so inquiries stay aligned with electronic ceramic parts.
🧩ADCERAX ceramic substrate automotive supports automotive electronic modules by reducing failures linked to thermal cycling stress and dimension drift, using controlled material selection and consistent QC across batches. We also help prevent chipping-related scrap and handling damage through edge spec guidance and export-ready packaging.
Microwave / RF Electronics
--control dielectric behavior & keep signal integrityA
In microwave ceramic substrate and rf ceramic substrate applications, controlled dielectric behavior and geometry stability help maintain signal performance. An electronic ceramic substrate is typically selected when frequency stability and repeatable assembly matter more than standard PCB convenience.
🧩ADCERAX RF ceramic substrate helps minimize performance variation by supporting stable geometry control and predictable substrate build specs that protect signal integrity in RF layouts. We assist buyers in defining practical inspection items (dimensions, surface, flatness) to avoid lot-to-lot variation that can cause tuning shifts or unexpected loss.
Custom Ceramic Substrates — Options & Process
ADCERAX is a ceramic substrate manufacturer focused on custom ceramic substrates made to your drawing or sample. We offer custom sizes and thickness, tight tolerances, controlled flatness/warpage, holes/slots/profiling, edge chamfers, and QC checkpoints, with low-MOQ prototyping and repeatable supply.
Customization Options
Custom L×W, thickness, controlled flatness/warpage, and defined hole/slot positional tolerance.
Provide higher - level dimensional accuracy and concentricity control than the standard.
Flanges, steps, threads, drilling holes, grooves, etc.
Adjust the material according to the application requirements.
Polish and grind the surface to achieve a specific surface roughness.
Customization Process
Send us your drawing, CAD file, or physical sample with material grade, dimensions, tolerances, and quantity. Our engineers will evaluate the design and provide a detailed quotation with lead time and pricing.
Once the quote is approved, we proceed with sample prototyping (1–50 pcs) if needed, for testing and validation.
After sample approval or direct confirmation, we begin batch manufacturing using CNC machining, sintering, and polishing. All parts undergo dimensional checks, material purity testing, and surface finish inspection.
Finished products are securely packed and shipped via DHL/FedEx/UPS or your preferred method. We support global delivery with full documentation.
ADCERAX: A Trusted Ceramic Substrate Manufacturer
ADCERAX is a specialized ceramic substrate manufacturer, supplying standard blanks and build-to-print substrates with controlled material quality, flatness, and tight dimensional consistency. Our engineering support, sampling service, and export experience simplify global sourcing and reduce project risk.
Competitive pricing with strict quality control from raw material sourcing to final delivery
Professional team providing comprehensive technical support and collaborative design
Small batch orders to large-scale production with complex geometries and tight tolerances
24-hour response and 24-hour dispatch for standard items, 3-7 weeks for custom orders.
Ceramic Substrate Factory-ADCERAX

ADCERAX has been engaged in advanced ceramics for over 20 years and has developed 2,000+ types of precision components, including ceramic substrates made from alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlN), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), silicon carbide (SiC), ZTA, and other engineering ceramics.
We supply both standard substrate blanks and build-to-print ceramic substrates for ceramic PCB platforms, RF/microwave circuits, heat spreader assemblies, and ceramic heater structures, exporting to 50+ countries and supporting OEMs that require stable quality, controlled flatness, and repeatable dimensions for reliable production.
Ceramic Substrate Manufacturing Process
Our ceramic substrate manufacturing is designed to control the three things buyers care about most—material consistency, flatness/warpage, and dimensional repeatability from sample to batch supply.

Step 1 — Material Selection & Batch Control
We confirm your thermal load, voltage, and RF frequency (if needed), then select Al₂O₃, AlN, Si₃N₄, ZTA, or SiC. Powder batching is controlled for stable density and properties across lots.

Step 2 — Forming & Green Machining
Substrates are formed into plates/blanks, then green machining is used where applicable to create near-net shapes. This step reduces machining cost and helps maintain geometry consistency for build-to-print parts.
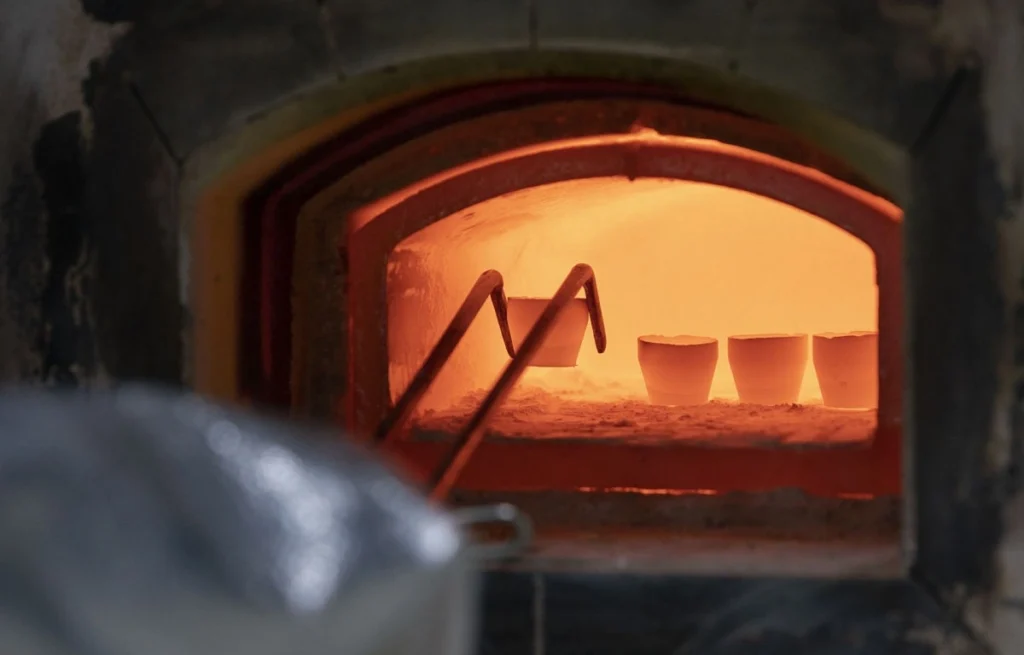

Step 3 — Sintering (Firing) for Density and Stability
The firing cycle is tuned for the selected material to reach target density and mechanical stability. Controlled sintering is a key driver of flatness stability and long-term reliability in service.
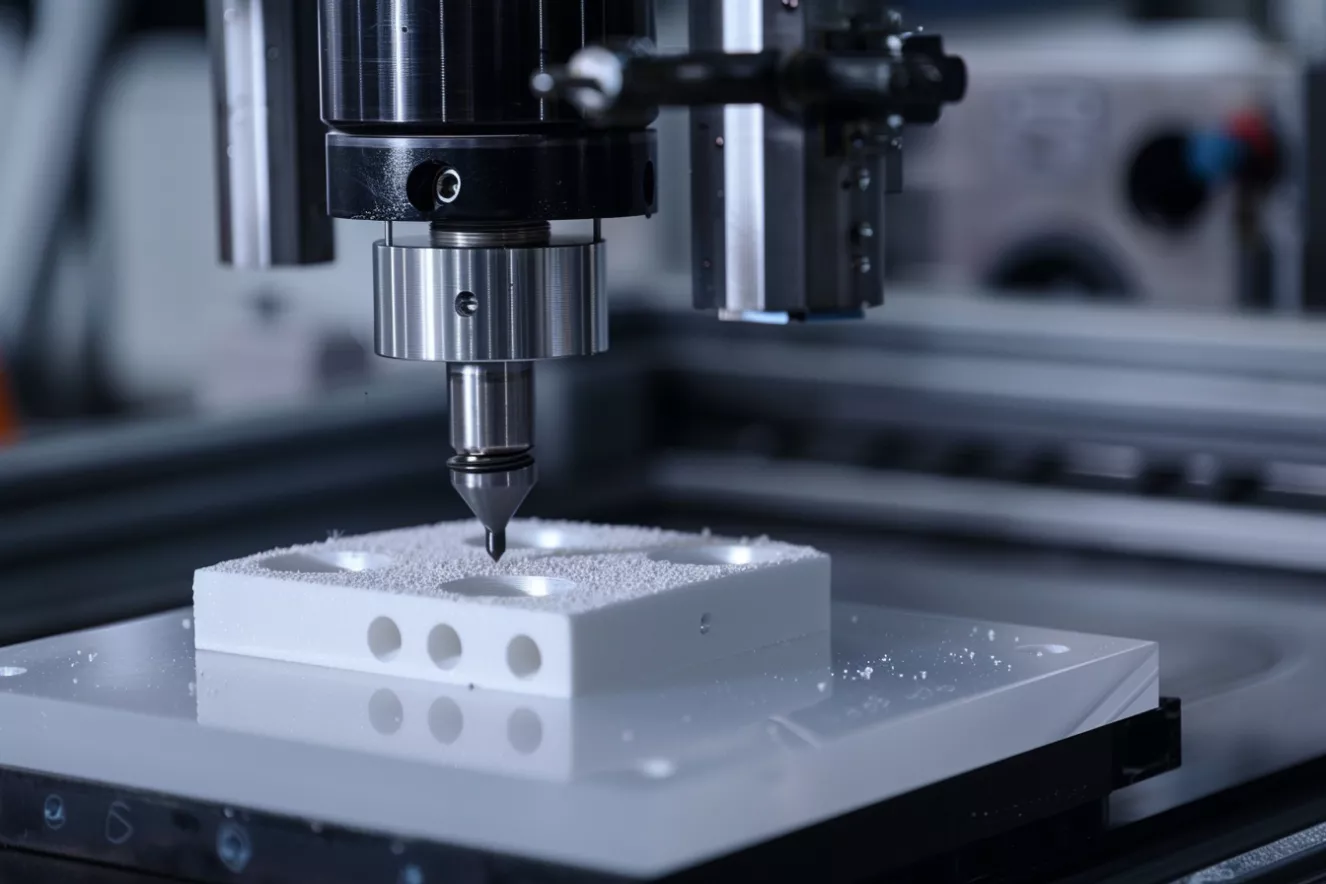

Step 4 — Precision Machining (to Print)
CNC grinding and finishing bring the substrate to final size, thickness tolerance, and edge condition. Common features include holes, slots, profiles, and chamfers, with attention to chipping control.
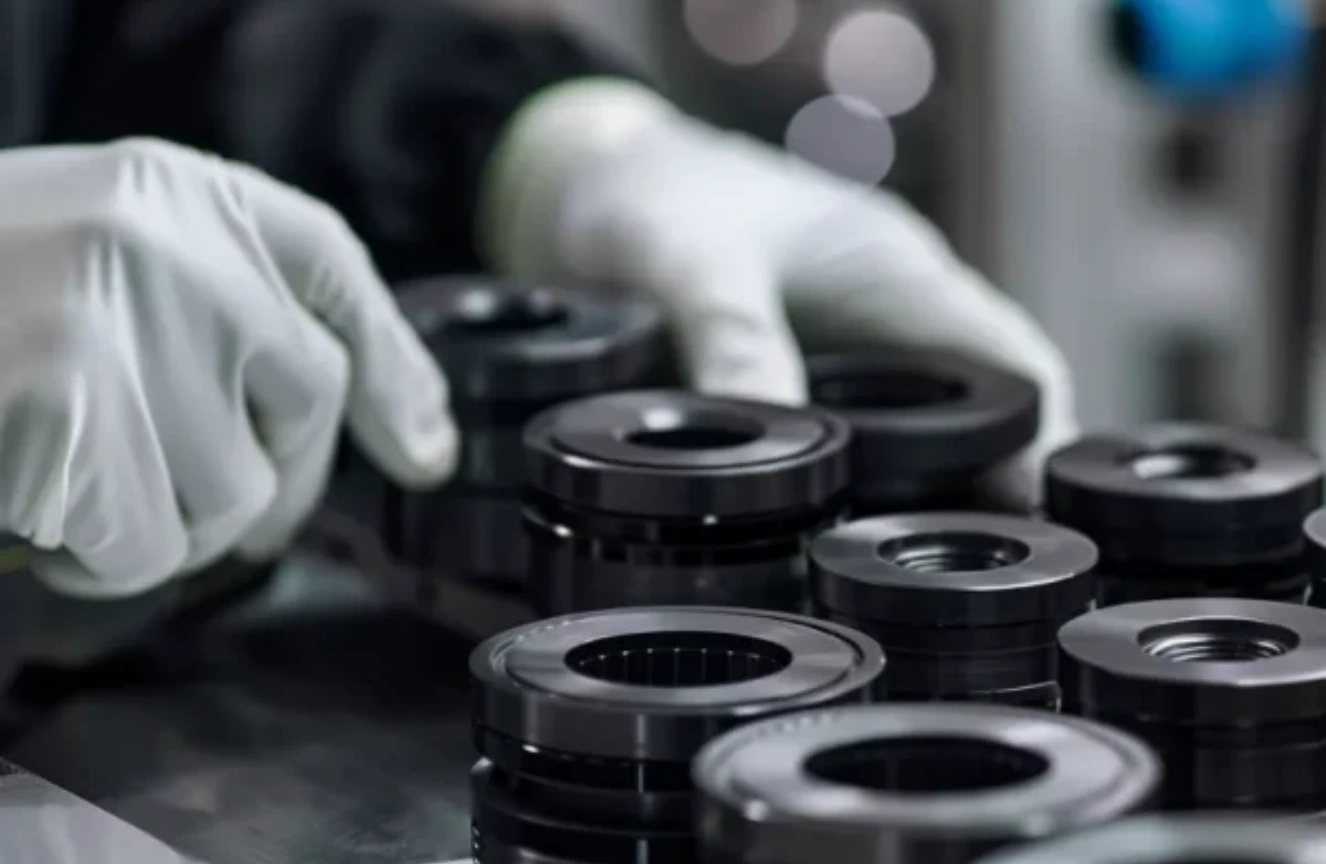

Step 5 — Surface Finish & Flatness Control
Surface condition and flatness are managed to match the assembly method (bonding, soldering, brazing, clamping). This step is where many yield issues are prevented, especially for tight-contact thermal interfaces.
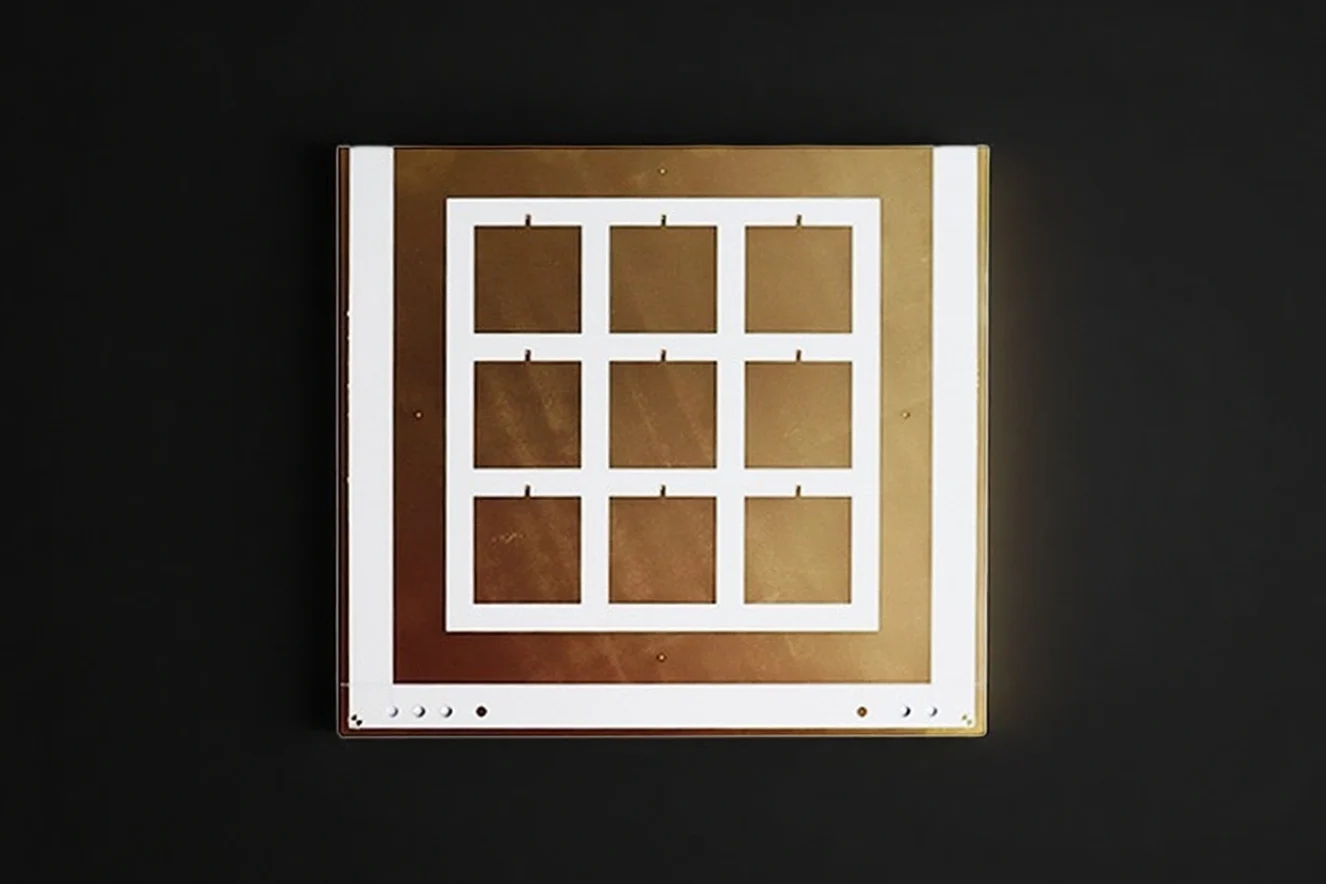

Step 6 — Metallization / Coating (Optional)
If your design needs conductive patterns or solderable areas, we support metallization options as specified (based on your application and drawing requirements), with inspection checkpoints defined upfront.
Ceramic Substrates Cutting
Ceramic substrates cutting is used to achieve clean outlines, tight dimensions, and repeatable features on Al₂O₃, AlN, Si₃N₄, ZTA, and SiC substrates—while minimizing chipping and scrap.
📌 Laser Cutting
Fast for profiles and complex shapes; ideal for prototypes and small-to-mid batches.
Choose it when you need clean panel singulation for fragile substrates, and want higher throughput with lower edge-chipping risk than full cutting.
📌 Laser Scribing
Controlled scoring for panel separation; helps improve throughput and consistency.
Choose it when you need clean panel singulation for fragile substrates, and want higher throughput with lower edge-chipping risk than full cutting.
📌Laser Drilling
Micro-holes and dense patterns when mechanical drilling risks chipping or tool wear.
Choose it when you need micro-holes, dense via patterns, or tight pitch features where mechanical drilling may crack edges or wear tools fast.
📌Laser Profiling
Contoured outlines, windows, and internal cutouts with stable repeatability.
Choose it when you need tight-tolerance contours and internal windows on thicker or harder ceramics, where repeatable geometry matters most.
FAQs About Ceramic Substrate
No. Ceramic substrates are electrically insulating (dielectric) structural materials, not semiconductors. Their main role is to support circuits or devices, provide electrical isolation, and help manage heat and dimensional stability in an assembly.
Ceramic Substrates offer significant advantages over FR4, including much higher thermal conductivity for better heat dissipation, superior performance at high temperatures, a lower coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) for better compatibility with semiconductor chips, excellent electrical insulation at high voltages, and greater mechanical stability and hermeticity. This makes Advanced Ceramic Substrates ideal for high-power, high-frequency, and harsh environment applications.
Absolutely. We specialize in providing Custom Ceramic Substrates. You can specify dimensions, thickness, material type, surface finish, machined features (like holes, slots, and scoring), and metallization patterns. Our engineering team can work with you to develop the perfect Ceramic Substrate solution for your unique application.
We offer various metallization options to transform your Ceramic Substrate into a functional circuit board. Common methods include Thick Film printing (using pastes like Silver, Gold, Platinum), Thin Film sputtering/evaporation (for high-precision traces), Direct Plated Copper (DPC), and Direct Bonded Copper (DBC). The choice depends on your circuit's complexity, current carrying requirements, and operating frequency for your Metallized Ceramic Substrate.
A: Selecting the right Ceramic Substrate material depends on several factors:
- Thermal Management Needs: For high heat dissipation, Aluminum Nitride is preferred; Alumina is suitable for moderate needs.
- Operating Temperature: All our Ceramic Substrates perform well at high temperatures.
- Electrical Requirements: Consider dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation strength.
- Mechanical Properties: Strength, CTE compatibility with attached components.
- Cost: Alumina is generally more cost-effective than AlN. Our technical team can help you evaluate these factors to choose the optimal Ceramic Substrate.
Yes, our Ceramic Substrates, when appropriately metallized, are fully compatible with standard microelectronic assembly processes. This includes reflow soldering, die attach, wire bonding (gold or aluminum), and encapsulation, allowing for seamless integration into your manufacturing workflow.
Ceramic substrates are used for pressure sensors because they provide a stable, electrically insulating, and chemically resistant platform that helps the sensing element stay accurate and reliable over time.
Reduce cost by simplifying geometry, relaxing non-critical tolerances, defining flatness only on functional zones, using standard thickness/blank sizes where possible, and selecting material based on the real bottleneck (thermal vs mechanical vs electrical). Cost usually spikes when you combine tight tolerances, complex features, and strict inspection scope on every piece.
Choose based on the dominant risk. Al₂O₃ is the cost-effective baseline for insulation and general electronics; AlN is selected when heat spreading is the bottleneck; Si₃N₄ is chosen when thermal cycling and mechanical stress drive failures; ZTA is preferred when edge-chipping/crack resistance matters; SiC fits harsh chemical/high-temperature duty where stiffness and chemical resistance are critical.
Metallic substrate uses a metal foil honeycomb; ceramic honeycomb uses a ceramic monolith (often cordierite).
Heat-up: Metallic warms faster and spreads heat better; ceramic is slightly slower but very stable at high temperatures.
Durability: Metallic handles vibration/shock better; ceramic offers strong corrosion and thermal-aging resistance.
Best choice: Pick metallic for fast light-off and high vibration duty; pick ceramic honeycomb for long-life high-temperature catalyst service.
Ceramic substrates (Al₂O₃, AlN, Si₃N₄) are rigid dielectrics used when heat, voltage, and stability drive reliability. Organic substrates (FR-4, polyimide, BT) are polymer laminates optimized for cost and high-volume PCB routing.
Heat & temperature: Ceramics manage hot spots and high temperatures better; organics can become the bottleneck in high-power builds.
Insulation & stability: Ceramics keep insulation and geometry more stable; organics are more sensitive to heat, moisture, and creep.
Cost & complexity: Organics win on low cost and complex multilayers; ceramics cost more per piece but often reduce rework and failure risk.
Choose ceramic for power/LED/HV/high-temp or flatness-sensitive assemblies; choose organic for mainstream PCBs with moderate thermal and voltage demands.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.
info@adcerax.com
Telephone: +(86) 0731-74427743
WhatsApp: +(86) 19311583352
Within 24 hours
*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

