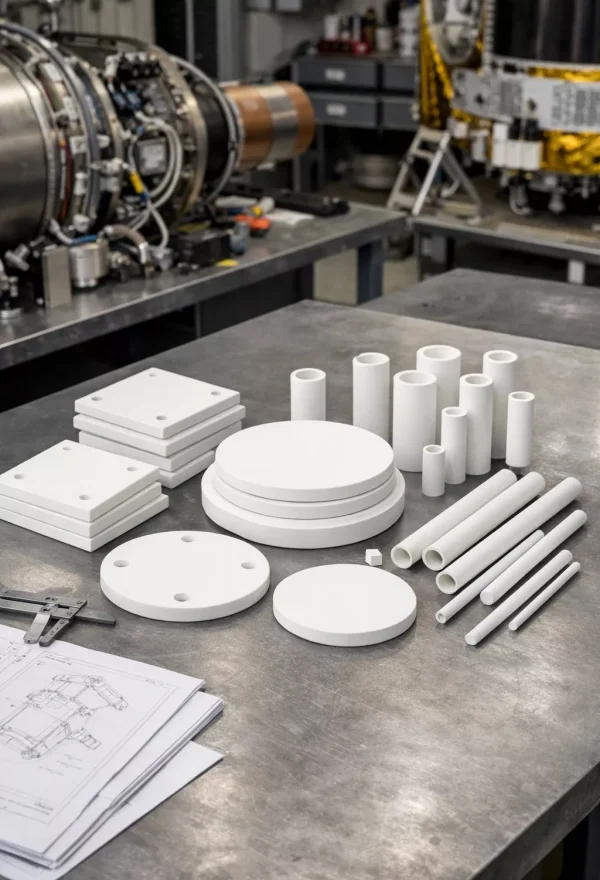
Ceramics Enabling Reliable Aerospace Systems
Industrial ceramics used in aerospace applications refer to advanced industrial ceramics engineered to operate where metals and polymers reach their physical limits.
In aerospace and aviation systems, these materials appear as bearings, washers, sleeves, substrates, tubes, and structural interfaces that must remain stable under heat, voltage, stress, and corrosive exposure.
As a result, Aerospace Ceramic solutions are widely adopted across Aerospace Industrial Ceramic assemblies that demand long service life and predictable behavior.
Moreover, Aerospace Engineering Ceramic components support system reliability by combining insulation, strength, and thermal balance within compact and weight-sensitive designs.
resists continuous heat and rapid cycling
withstands corrosive aerospace environments
maintains dielectric safety under voltage
supports load wear and vibration
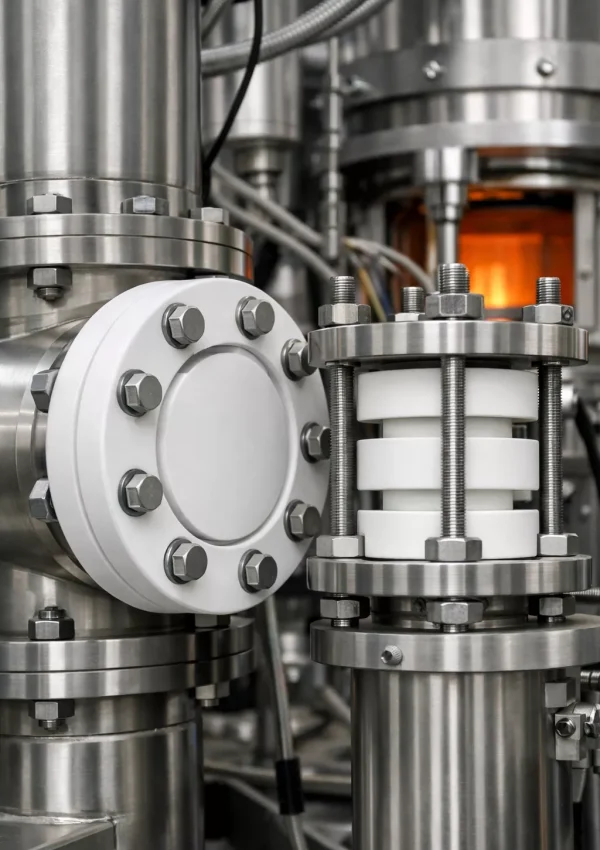
ADCERAX® Material Properties of Aerospace Ceramic
Material performance in aerospace systems is determined by how Aerospace Ceramic components respond to heat, electricity, chemical exposure, and mechanical load under defined operating conditions.
Thermal Properties
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Max Service Temperature (°C) | CTE (×10⁻⁶/K, 20–1000°C) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 95–99.5%) | 24–30 | 1500–1700 | 7.5–8.2 | Air, continuous thermal exposure |
| ZTA | 20–25 | 1400–1500 | 7.0–7.8 | Air, cyclic heating |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 2.5–3.0 | 1000–1200 | 10.0–10.5 | Air, thermal cycling |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 120–180 | 1600–1700 | 4.0–4.5 | Inert/oxidizing atmosphere |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | 20–35 | 1200–1400 | 3.0–3.3 | Air, rotating components |
| Boron Nitride (h-BN) | 30–60 (in-plane) | 1800 (inert) | 1.0–2.0 | Inert atmosphere |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 170–230 | 1400–1600 | 4.5–5.3 | Air, power electronics |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 30–42 | 1500–1600 | 4.5–5.0 | Air, abrasive environment |
| Glass Ceramic | 1.5–2.5 | 800–1000 | 0.0–2.0 | Air, thermal stability tests |
Electrical Properties
| Material | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | ≥10¹⁴ | 9–13 | 9.5–10 | Room temperature, dry |
| ZTA | ≥10¹³ | 8–12 | 9–10 | Room temperature |
| Zirconia | ≥10¹² | 7–10 | 25–30 | Room temperature |
| Silicon Carbide | 10²–10⁵ (semiconductive) | 2–4 | 9–10 | Controlled doping |
| Silicon Nitride | ≥10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 7–8 | Room temperature |
| Boron Nitride | ≥10¹⁵ | 3–4 | 4–5 | Inert atmosphere |
| Aluminum Nitride | ≥10¹³ | 10–15 | 8.5–9 | Power module conditions |
| Boron Carbide | 10²–10⁴ | 2–3 | 8–9 | High-load structures |
| Glass Ceramic | ≥10¹⁵ | 6–10 | 5–7 | Insulation components |
Chemical Stability
| Material | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Oxidation Behavior | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Stable to most acids | Limited in strong alkali | Stable up to 1000°C | Acid/alkali immersion |
| ZTA | Similar to alumina | Similar to alumina | Stable up to 1000°C | Chemical soak tests |
| Zirconia | Stable to acids | Moderate alkali attack | Stable up to 800°C | Aqueous corrosion |
| Silicon Carbide | Excellent | Excellent | Slow oxidation >1000°C | High-temp oxidation |
| Silicon Nitride | Good | Good | Oxidizes >1000°C | Moist air exposure |
| Boron Nitride | Inert to most chemicals | Alkali sensitive | Stable in inert gas | Chemical compatibility |
| Aluminum Nitride | Hydrolysis sensitive | Poor in water | Stable in dry air | Controlled humidity |
| Boron Carbide | Excellent | Excellent | Stable up to 1000°C | Abrasive slurry |
| Glass Ceramic | Good | Good | Stable below softening | Chemical durability |
Mechanical Properties
| Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 300–400 | 1200–1800 | 3.5–4.5 | 3-point bending |
| ZTA | 700–1000 | 1300–1600 | 6–8 | Impact and wear |
| Zirconia | 900–1200 | 1200–1300 | 7–10 | Room temperature |
| Silicon Carbide | 350–450 | 2500–2800 | 3–4 | Abrasive wear |
| Silicon Nitride | 800–1000 | 1500–1700 | 6–7 | Rotational stress |
| Boron Nitride | 20–50 | 30–50 | <1 | Machinability tests |
| Aluminum Nitride | 300–350 | 1100–1200 | 2.5–3.5 | Substrate loading |
| Boron Carbide | 300–400 | 3000–3800 | 2–3 | High-hardness testing |
| Glass Ceramic | 100–200 | 500–700 | 1.5–2.5 | Structural support |
ADCERAX® Ceramic Applications Across Aerospace Systems
Aerospace ceramic components are selected by application function first, with material behavior matched to mechanical load, thermal exposure, electrical demand, and environmental risk across flight and ground systems.
Power Electronics & Thermal Interfaces
Aerospace Ceramic materials enable reliable thermal transfer and electrical insulation within compact power assemblies.
- Alumina Aerospace Ceramic enables stable insulation while maintaining controlled heat transfer under continuous electrical load.
- Aluminum Nitride Aerospace Ceramic supports high thermal flux where power density and reliability must coexist.
- Aerospace Thermal Conductive Ceramic structures reduce thermal stress concentration at material interfaces.
Thermal transfer and electrical isolation maintained under cyclic power loading.
Provides rigid insulation interfaces for thermally stressed power assemblies.
High thermal conductivity substrate supporting compact aerospace power modules.
Rotating & Bearing Systems
Aerospace Ceramic solutions support high-speed rotation by combining low friction and structural stability.
- Silicon Nitride Bearing Ceramic reduces centrifugal stress through low density and high strength.
- Silicon Carbide Aerospace Ceramic resists abrasive wear and corrosion in aggressive operating media.
- Aerospace Wear Resistant Ceramic components extend maintenance intervals under continuous rotation.
Electrical insulation and dimensional stability ensured in auxiliary rotating systems.
Supports high rotational speed with reduced friction and thermal expansion.
Improves bearing life under high-speed aerospace operating conditions.
Maintains wear resistance under corrosive and particle-laden environments.
Protects rotating shafts from abrasion and chemical attack.
Structural Fastening & Positioning
Aerospace Ceramic components provide electrically insulated fastening and precise positioning under mechanical load.
- Zirconia Structural Ceramic delivers high fracture toughness for precision positioning.
- Alumina Structural Ceramic maintains stiffness and insulation under mechanical preload.
- Aerospace High Strength Ceramic fasteners reduce galvanic and thermal fatigue risks.
Enables rigid, insulated structural connections across aerospace systems.
Provides electrically insulating fastening under thermal cycling conditions.
High strength fastening suited for precision aerospace assemblies.
Maintains accurate alignment under temperature fluctuation and vibration.
Supports structural alignment within rotating or sliding interfaces.
Wear & Impact Protection Components
Aerospace Ceramic materials protect critical interfaces from abrasion, impact, and repetitive contact stress.
- ZTA Wear Resistant Ceramic absorbs impact while resisting abrasive degradation.
- Boron Carbide Structural Ceramic provides extreme hardness at reduced component weight.
- Aerospace Structural Ceramic solutions limit deformation under repetitive contact.
Wear-resistant interface supporting cyclic load and surface contact.
Lightweight wear surface for high-abrasion aerospace structures.
Maintains geometry under severe mechanical and abrasive stress.
High-Temperature Insulation & Protection
Aerospace Ceramic systems isolate heat and resist chemical attack in elevated temperature environments.
- Boron Nitride Insulation Ceramic offers thermal stability with non-wetting behavior.
- Glass Ceramic Insulation Ceramic maintains shape through repeated thermal cycling.
- Aerospace High Temperature Ceramic components reduce heat transfer to sensitive systems.
Provides high-temperature insulation and chemical inertness.
Machinable insulation component for controlled thermal environments.
Flat insulating structure maintaining stability under heat exposure.
Thermal isolation conduit for aerospace test and operating systems.
From Aerospace Application Conditions to Ceramic Solutions
Aerospace ceramic components are rarely selected by material name alone, but by operating limits and interface requirements.
As an Aerospace Engineering Ceramic Manufacturer, ADCERAX® supports material selection and machining decisions directly from real application conditions.
ADCERAX® Engineered Ceramic Categories Across Aerospace Applications
Material selection in aerospace systems is driven by operating conditions, functional loads, and verification requirements, leading industrial ceramics to be grouped primarily by material behavior rather than component geometry.

Alumina Ceramic
Alumina-based components are widely used where insulation, thermal balance, and dimensional stability must coexist.
- Electrical isolation under continuous operating voltage
-Stable heat transfer within compact assemblies
- Consistent tolerances for repeatable Aerospace Ceramic integration

ZTA Ceramic
ZTA ceramics are selected for load-bearing and wear-prone interfaces requiring impact tolerance.
- Enhanced toughness for structural contact zones
- Reliable wear resistance under cyclic loading
- Suitable for Aerospace Structural Ceramic applications

Zirconia Ceramic
Zirconia ceramics support precision positioning and strength-critical fastening tasks.
- High fracture toughness for assembly reliability
- Dimensional precision across temperature variation
- Used in Aerospace High Strength Ceramic structures
SiC Ceramic
Silicon carbide components address extreme wear, corrosion, and high-temperature exposure.
- Superior wear resistance in rotating systems
- Stable performance at elevated temperatures
- Common in Aerospace High Temperature Ceramic use
Si₃N₄ Ceramic
Silicon nitride ceramics are applied in high-speed and low-friction environments.
- Low density supporting high rotational speeds
- Reduced friction and long service life
- Preferred for Silicon Nitride Bearing Ceramic systems

Boron Nitride Ceramic
Boron nitride ceramics serve as insulation and protection in thermal zones.
- Excellent thermal insulation properties
- Chemical stability in reactive environments
- Used within Aerospace Insulation Ceramic assemblies

AlN Ceramic
Silicon carbide components address extreme wear, corrosion, and high-temperature exposure.
- High thermal conductivity with insulation
- Stable substrate for power electronics
- Typical Aerospace Thermal Conductive Ceramic material

B₄C Ceramic
Boron carbide ceramics are chosen for lightweight, high-hardness structural parts.
- Exceptional hardness with low density
- Resistance to abrasive wear conditions
- Applied in Aerospace Wear Resistant Ceramic designs

Glass Ceramic
Glass ceramics provide machinability and thermal stability in insulating structures.
- Controlled expansion under thermal cycling
- Good electrical insulation performance
- Used as Glass Ceramic Aerospace Ceramic components
Integrated Manufacturing Services for Aerospace Ceramic Components

ADCERAX® delivers an integrated manufacturing pathway for aerospace ceramic components, aligning material behavior, geometry control, and process execution into a single, coherent workflow.
As an Aerospace Ceramic Manufacturer serving demanding industrial systems, this one-stop service is structured to translate operating conditions and drawings directly into manufacturable, repeatable ceramic parts.
application conditions mapped to alumina, zirconia, SiC, Si₃N₄, AlN systems
dry pressing, isostatic pressing up to 300 MPa
high-temperature firing controlled to ±5 °C stability
diamond machining achieving ±0.01 mm critical tolerances
grinding and lapping to Ra ≤0.4 µm surfaces
chamfering, interface control, fit-ready ceramic components
ADCERAX® Advanced Ceramic Manufacturing Processes for Aerospace Ceramic
High-Pressure
Ceramic Forming
High-pressure forming establishes the internal density and geometric foundation required for Aerospace Industrial Ceramic reliability.
uniform compaction up to 300 MPa pressure
green body deviation limited within ±0.3 %
relative density exceeding 98 % before sintering
High-Temperature
Controlled Sintering
Sintering defines the final microstructure that governs Aerospace High Temperature Ceramic stability and strength.
sintering temperatures up to 1,800 °C controlled
temperature variation maintained within ±5 °C
grain growth regulated for strength retention
Precision
Diamond Machining
Post-sinter machining transforms dense ceramic bodies into Aerospace Precision Ceramic components with functional accuracy.
dimensional tolerances achieved within ±0.01 mm
surface roughness refined to Ra ≤ 0.4 µm
controlled chamfers reduce stress concentration
ADCERAX® Custom Aerospace Ceramic Solutions Aligned With Real Operating Conditions
ADCERAX® provides Aerospace Custom Ceramic solutions developed directly from drawings, interface constraints, and operating limits rather than catalog assumptions.
As an Aerospace Engineering Ceramic Manufacturer, customization focuses on precision geometry, material behavior, and manufacturability across non-standard aerospace applications.
FAQs about Industrial Ceramic for Aerospace System
Silicon nitride bearings offer low density and high fracture toughness, reducing centrifugal stress at high RPM. Thermal shock resistance supports rapid temperature changes during operation. Lower friction coefficients reduce heat generation inside sealed aerospace housings. These properties stabilize long-term rotational performance.
Alumina washers provide electrical insulation while allowing controlled heat transfer between power devices and heat sinks. High dielectric strength prevents breakdown under high voltage. Stable thermal conductivity reduces hotspot formation. This balance protects sensitive power modules during continuous operation.
Zirconia bolts maintain preload stability without creep at elevated temperatures. High fracture strength supports structural fastening under vibration. Corrosion resistance prevents degradation in aggressive aerospace environments. These properties improve joint reliability in long-life assemblies.
Alumina flanges resist thermal deformation where metal flanges may warp. Chemical inertness protects sealing interfaces from combustion byproducts. Dimensional stability preserves flatness across thermal cycles. This ensures consistent sealing performance over extended service periods.
Silicon carbide shaft sleeves exhibit exceptional wear and corrosion resistance. High thermal conductivity dissipates frictional heat efficiently. Structural rigidity prevents deformation under load. These attributes extend service life in aerospace rotating equipment.
Silicon carbide bearings retain mechanical strength at temperatures exceeding metal limits. Low thermal expansion reduces internal stress during heating. Chemical stability prevents oxidation and corrosion. This ensures consistent bearing performance in aerospace thermal systems.
Boron nitride tubes provide electrical insulation combined with thermal shock resistance. Low wettability prevents adhesion of molten metals or contaminants. Stable structure supports use near heat sources. These properties protect surrounding components in aerospace thermal zones.
Boron carbide plates offer extremely high hardness and low density. Impact resistance protects critical surfaces from particle erosion. Structural stability is maintained under mechanical stress. This makes them effective for aerospace wear and impact shielding.
Glass ceramic insulation components provide low thermal conductivity with controlled expansion. Electrical insulation remains stable over long service life. Smooth surfaces support clean integration into assemblies. These properties suit insulation and separation roles in aerospace environments.
Ceramic components resist simultaneous chemical attack and mechanical abrasion. This prevents gradual wall thinning and pore deformation. Filtration performance remains consistent over extended service periods.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.

