Industrial Ceramics in Petrochemical Applications
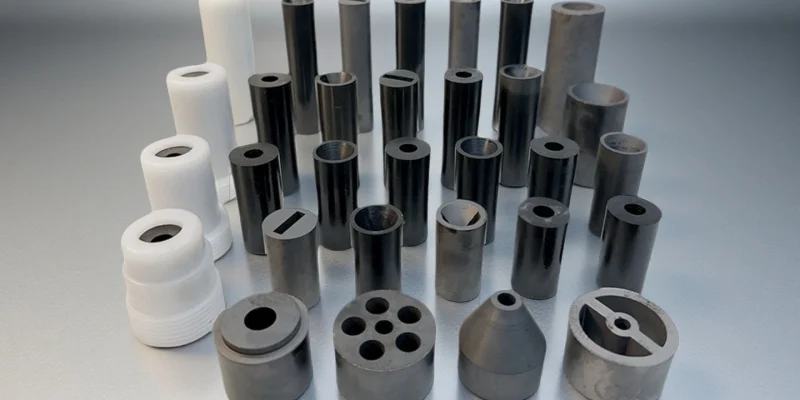
In petrochemical operations, industrial ceramics refer to engineered ceramic parts used where heat, pressure, and aggressive media exceed the limits of metals and polymers.
These components are commonly applied as liners, seals, tubes, bearings, and structural interfaces that must remain stable during long production cycles.
In contrast to metallic alloys, ceramic materials do not rely on surface coatings to resist attack, which reduces uncertainty in corrosive service.
As a result, ceramic components for petrochemical industry are selected to ensure predictable performance in critical process equipment.
maintains shape under sustained high temperatures
prevents current leakage in harsh environments
resists acids, alkalis, and reactive media
withstands wear, load, and cyclic stress

Key Properties of ADCERAX® Petrochemical Ceramics
This section translates how petrochemical ceramics behave under heat, electricity, chemistry, and mechanical load into measurable properties that guide material selection in real operating environments.
Thermal Properties of Petrochemical Ceramics
| Material | Max Continuous Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | CTE (×10⁻⁶ /K, 25–800 °C) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99%) | 1600 | 25–30 | 8.0 | Air, static |
| ZTA | 1550 | 18–22 | 8.5 | Air, static |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 1400 | 2.5–3.0 | 10.5 | Air, static |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 1650 | 120–150 | 4.2 | Inert, static |
| Boron Nitride (h-BN) | 900 | 30–60 (anisotropic) | 1.0–2.0 | Inert, static |
| Silicon Nitride | 1400 | 20–30 | 3.2 | Air, static |
| Aluminum Nitride | 1000 | 140–180 | 4.5 | Air, static |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 1700 | 40–60 | 13.0 | Air, static |
| Boron Carbide | 1600 | 30–40 | 5.6 | Inert, static |
| Transparent Ceramics (Sapphire) | 1700 | 30–35 | 7.5 | Air, static |
| Beryllium Oxide | 1000 | 250–300 | 7.0 | Air, static |
| Glass-Ceramics | 800 | 1.5–2.5 | 0–2.0 | Air, static |
Electrical Properties of Petrochemical Ceramics
| Material | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99%) | 10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 9.5 | 25 °C, dry |
| ZTA | 10¹³ | 10–12 | 10.0 | 25 °C, dry |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 10⁸–10⁹ | 8–10 | 25–30 | 25 °C, dry |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 10³–10⁵ | 3–5 | 9–10 | 25 °C, dry |
| Boron Nitride (h-BN) | 10¹³ | 6–8 | 4.0 | 25 °C, dry |
| Silicon Nitride | 10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 7.5 | 25 °C, dry |
| Aluminum Nitride | 10¹² | 15–18 | 8.5 | 25 °C, dry |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 9.8 | 25 °C, dry |
| Boron Carbide | 10²–10⁴ | 2–4 | 6–7 | 25 °C, dry |
| Transparent Ceramics (Sapphire) | 10¹⁴ | 13–16 | 9.4 | 25 °C, dry |
| Beryllium Oxide | 10¹³ | 10–12 | 6.8 | 25 °C, dry |
| Glass-Ceramics | 10¹⁰–10¹² | 6–10 | 4–6 | 25 °C, dry |
Chemical Properties of Petrochemical Ceramics
| Material | Acid Resistance (pH) | Alkali Resistance (pH) | Oxidation Stability (°C) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99%) | 1–14 (except HF) | 1–14 | 1200 | Aqueous |
| ZTA | 1–14 (except HF) | 1–14 | 1200 | Aqueous |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 1–14 | 1–14 | 1000 | Aqueous |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 1–14 | 1–14 | 1400 | Aqueous |
| Boron Nitride (h-BN) | 2–12 | 2–12 | 900 | Inert |
| Silicon Nitride | 2–12 | 2–12 | 1200 | Aqueous |
| Aluminum Nitride | 4–10 | 4–10 | 800 | Aqueous |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 7–14 | 7–14 | 1500 | Aqueous |
| Boron Carbide | 2–14 | 2–14 | 1200 | Aqueous |
| Transparent Ceramics (Sapphire) | 1–14 | 1–14 | 1400 | Aqueous |
| Beryllium Oxide | 2–12 | 2–12 | 1000 | Aqueous |
| Glass-Ceramics | 3–10 | 3–10 | 700 | Aqueous |
Mechanical Properties of Petrochemical Ceramics
| Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Hardness (HV) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99%) | 300–350 | 3.5–4.0 | 1500 | 25 °C |
| ZTA | 450–600 | 5.0–6.5 | 1400 | 25 °C |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 800–1000 | 7.0–10.0 | 1250 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 380–420 | 3.0–4.0 | 2500 | 25 °C |
| Boron Nitride (h-BN) | 30–60 | 2.0–3.0 | 100 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Nitride | 800–1000 | 6.0–7.5 | 1600 | 25 °C |
| Aluminum Nitride | 300–350 | 2.5–3.5 | 1100 | 25 °C |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 150–200 | 2.0–2.5 | 900 | 25 °C |
| Boron Carbide | 350–400 | 2.5–3.0 | 3000 | 25 °C |
| Transparent Ceramics (Sapphire) | 400–450 | 3.0–4.0 | 2000 | 25 °C |
| Beryllium Oxide | 250–300 | 2.5–3.0 | 1200 | 25 °C |
| Glass-Ceramics | 90–150 | 1.5–2.0 | 600 | 25 °C |
Functional Application Domains of ADCERAX® Petrochemical Ceramics
Petrochemical ceramics are deployed across industrial sectors according to dominant process risks such as heat, corrosion, abrasion, and chemical reactivity rather than by individual component forms.
High-Temperature Chemical Processing
Ceramic materials applied in high-temperature chemical processing maintain structural and chemical stability when prolonged heat exposure and reactive atmospheres exceed metallic limits.
- Alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide preserve dimensional stability during continuous thermal cycles, ensuring consistent reaction conditions.
- Chemical inertness of alumina- and zirconia-based ceramics prevents process contamination in high-temperature reactions and material handling stages.
- Resistance to thermal shock in silicon carbide and glass-ceramics reduces failure risk during startup and shutdown phases.
Corrosive Fluid Transport and Control
In corrosive fluid transport systems, ceramic materials protect equipment integrity where aggressive chemicals rapidly degrade metals and polymers.
- Alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide exhibit sustained corrosion resistance across acidic and alkaline process media.
- Stable ceramic geometries support flow consistency under combined pressure and temperature fluctuations.
- Wear-resistant ceramic surfaces extend service intervals in continuous petrochemical circulation systems.

Abrasive Slurry and Powder Handling
Ceramic materials used in abrasive slurry and powder handling environments resist mechanical degradation caused by particle impact and friction.
- High hardness in alumina, zirconia, and boron carbide minimizes abrasive wear during milling and dispersion processes.
- Stable microstructures in zirconia and silicon carbide support energy efficiency in grinding and mixing operations.
- Predictable wear behavior of ceramic media enables maintenance planning without unexpected shutdown events.

Structural Protection and Equipment Lining
Structural ceramic solutions reinforce petrochemical equipment exposed to combined mechanical load, heat, and chemical attack.
- Alumina, ZTA, and silicon carbide maintain geometric accuracy where metallic liners deform or corrode.
- High elastic modulus of structural ceramics supports load-bearing stability in reactors and furnaces.
- Long-term resistance to creep and deformation improves system reliability under continuous operation.

Process Monitoring and Functional Integration
Functional ceramics enable sensing, filtration, insulation, and observation within sealed petrochemical systems.
- Aluminum nitride and silicon nitride maintain signal stability under combined thermal and chemical stress.
- Porous alumina and silicon carbide structures allow controlled media interaction without compromising containment integrity.
- Sapphire and yttria-based transparent ceramics enable visual monitoring in pressurized and corrosive environments.
Align Ceramic Performance with Your Process Conditions
Petrochemical systems impose combined demands of temperature, corrosion, and mechanical stress that cannot be addressed by generic materials. ADCERAX® supports engineers in matching ceramic material behavior to real operating conditions before component selection.
ADCERAX® Ceramic Material Systems Serving Petrochemical Operations
Industrial ceramic components used in petrochemical systems are best understood when organized by material behavior rather than by individual shapes or parts.
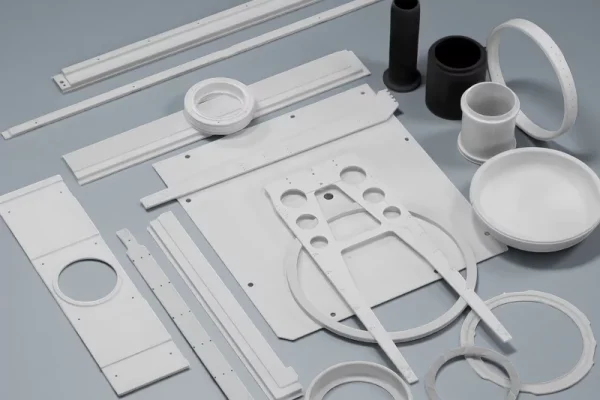

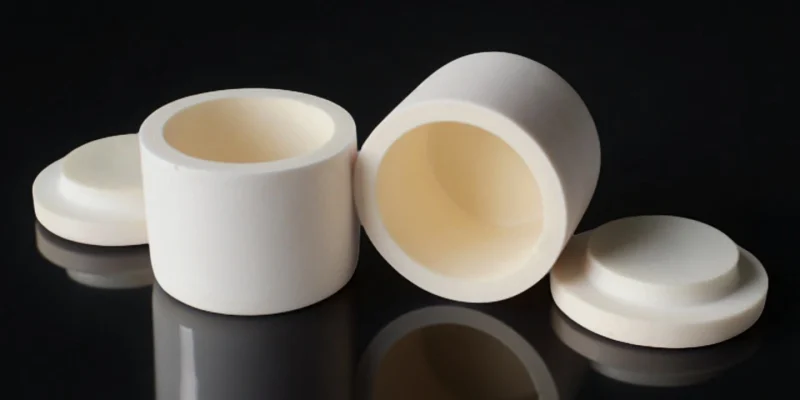
Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics serve as foundational industrial ceramic components chemical industry for petrochemical equipment.
- Stable under continuous thermal exposure
- Compatible with wide chemical media
- Cost-efficient for large-scale deployment
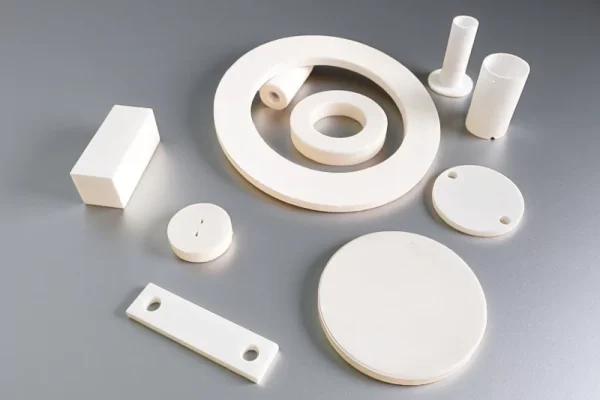

ZTA Ceramics
Zirconia Toughened Alumina improves fracture resistance in abrasive petrochemical environments.
- Enhanced wear resistance under slurry flow
- Improved impact tolerance over alumina
- Suitable for high-abrasion process zones
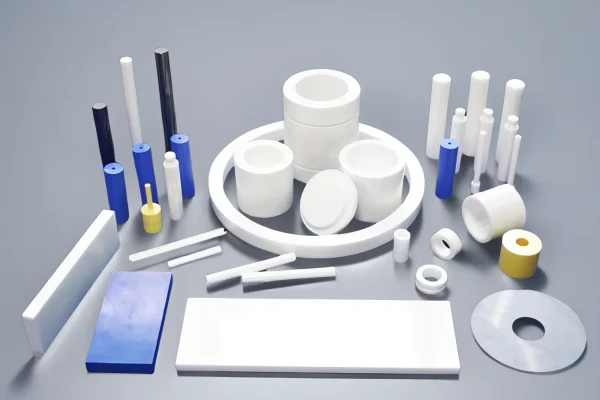

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are chosen for precision and sealing reliability in dynamic systems.
- High strength under cyclic loading
- Excellent sealing performance in pumps
- Dimensional stability for control components
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide is a core ceramic solutions for corrosive environments in petrochemical systems.
- Exceptional corrosion resistance in aggressive media
- High thermal conductivity for heat transfer
- Structural stability at elevated temperatures
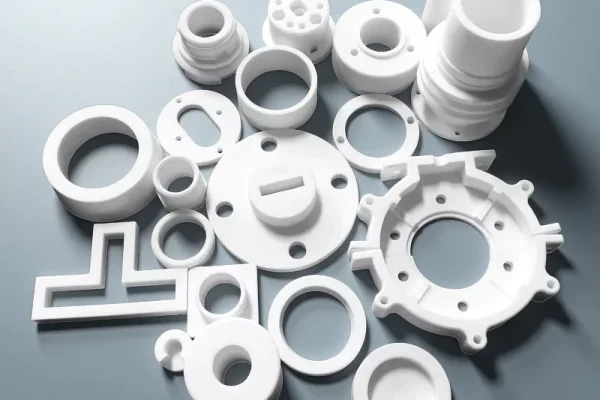

Boron Nitride Ceramics
Boron nitride ceramics provide non-wetting and insulating behavior in specialized equipment.
- Low adhesion to reactive melts
- High thermal shock resistance capability
- Stable electrical insulation at temperature
Silicon Nitride Ceramics
Silicon nitride ceramics support mechanically demanding petrochemical applications.
- High fracture toughness under load
- Reliable fatigue resistance in rotation
- Suitable for high-speed bearing systems
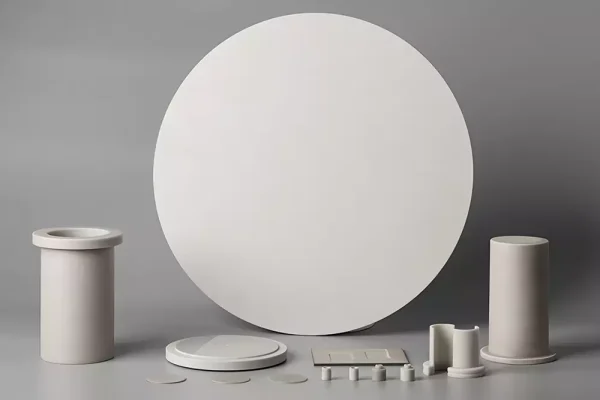

Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
Aluminum nitride ceramics combine thermal conductivity with electrical insulation.
- Efficient heat dissipation performance
- Electrical insulation under thermal stress
- Stable behavior in sensor systems
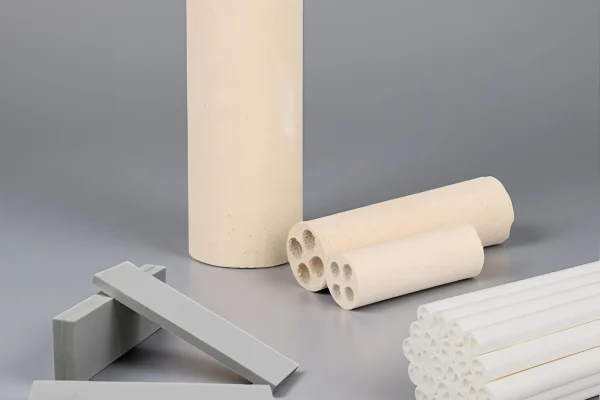

Magnesium Oxide Ceramics
Magnesia ceramics perform reliably in strongly alkaline petrochemical environments.
- Excellent resistance to alkaline corrosion
- Stable structure at elevated temperatures
- Suitable for refractory chemical contact

Boron Carbide Ceramics
Boron carbide ceramics address extreme wear in abrasive petrochemical processes.
- Exceptional hardness against particle erosion
- Lightweight structure under mechanical stress
- Extended service life in abrasion zones
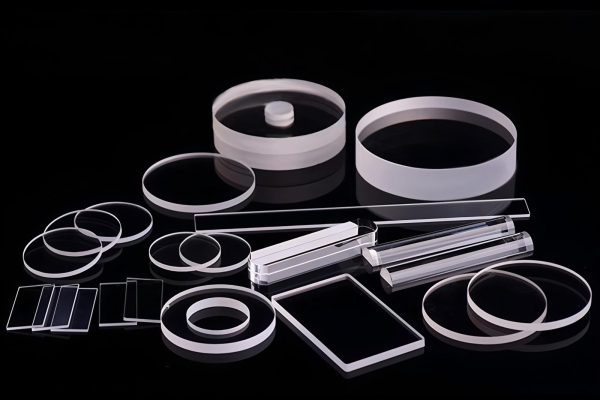

Transparent Ceramics
Transparent ceramics enable visual monitoring within harsh petrochemical systems.
- Optical clarity at high temperature
- Chemical resistance beyond glass materials
- Reliable sealing in pressurized observation

Beryllium Oxide Ceramics
Beryllium oxide ceramics support high thermal conductivity applications with strict controls.
- Extremely high thermal conductivity capability
- Electrical insulation under heat load
- Used in specialized controlled environments

Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics provide dimensional stability under thermal cycling conditions.
- Low thermal expansion characteristics
- Excellent resistance to thermal shock
- Suitable for corrosive processing equipment
One-Stop Ceramic Manufacturing Services for Petrochemical Applications

ADCERAX® provides end-to-end manufacturing support for petrochemical ceramics, covering the full lifecycle from material selection to finished component delivery.
Each service stage is aligned with real petrochemical operating conditions to ensure performance consistency and dimensional reliability.
Defined according to petrochemical process conditions
Custom shaping for application-specific component geometry
Tight tolerance machining for complex ceramic parts
Controlled densification under high-temperature conditions
Dimensional verification and critical defect control
Functional surface preparation for service environments
ADCERAX® Petrochemical Ceramic Manufacturing Capabilities
Precision Green Machining
Green-state machining enables complex ceramic geometries to be formed efficiently before sintering, reducing scrap risk.
CNC green machining centers up to ±0.15 mm
Complex internal features formed before densification
Reduced post-sinter machining by 30–40%
Temperature Controlled Sintering
Controlled sintering determines final density, strength, and thermal stability of industrial ceramic components.
High-temperature furnaces operating up to 1800 °C
Density levels reaching ≥99.5% theoretical
Dimensional shrinkage controlled within ±0.8%
Diamond Precision Machining
Post-sinter diamond machining ensures tight tolerances and surface quality for advanced ceramic parts for chemical processing.
CNC diamond grinding achieving ±0.02 mm tolerances
Surface roughness controlled to Ra ≤0.4 μm
Reliable fitting in pumps, valves, and seals
Customized Ceramic Solutions for Petrochemical Operations
Petrochemical applications impose unique combinations of temperature, corrosion, and mechanical load that standard ceramic components rarely satisfy.
ADCERAX® supports application-specific ceramic customization by aligning material composition, geometry, and tolerance control with real operating conditions.
Begin a technical discussion with ADCERAX® engineers to define ceramic solutions aligned with your process.
ADCERAX® Petrochemical Ceramics FAQs
Petrochemical ceramics rely on strong ionic and covalent bonds that remain stable well above the operating limits of metallic alloys. High-purity alumina, silicon carbide, and zirconia retain mechanical strength and dimensional integrity during prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. This thermal stability prevents deformation that would otherwise cause sealing failure or misalignment in reactors and furnaces.
Petrochemical ceramics are chemically inert to most acids, alkalis, and reactive process media. Unlike metals, ceramic microstructures do not undergo electrochemical corrosion or ion leaching. This property directly extends component service life in corrosive fluid handling and chemical reaction systems.
High hardness is a defining property of petrochemical ceramics, often exceeding that of hardened steels. This hardness limits surface abrasion caused by solid particles in slurries or powders. As a result, ceramic components maintain dimensional accuracy and reduce unplanned shutdowns caused by excessive wear.
Many petrochemical ceramics, particularly silicon carbide and zirconia-based materials, exhibit controlled thermal expansion and high fracture toughness. These properties reduce internal stress during rapid heating or cooling cycles. This thermal shock resistance minimizes crack initiation during startup and shutdown operations.
Petrochemical ceramics provide smooth, hard sealing surfaces that resist wear and chemical attack. Stable surface geometry ensures consistent contact pressure at sealing interfaces. This directly reduces leakage risks in high-pressure and corrosive petrochemical systems.
Petrochemical processes often require tight tolerances to maintain flow control and mechanical alignment. Ceramics exhibit low creep and minimal thermal deformation compared with metals. This dimensional stability ensures long-term performance without frequent recalibration or replacement.
Petrochemical ceramics do not release metallic ions or organic contaminants into process media. This inert behavior protects catalyst performance and prevents downstream contamination. As a result, product consistency and reaction efficiency remain stable over extended operating periods.
High compressive strength is a key characteristic of advanced petrochemical ceramics. Dense ceramic microstructures withstand extreme internal pressures without plastic deformation. This property allows ceramics to be safely used in pressurized reactors, pipelines, and containment systems.
Resistance to heat, corrosion, and abrasion significantly slows degradation mechanisms. Petrochemical ceramics maintain functional surfaces longer than metallic alternatives. This directly reduces maintenance frequency and overall lifecycle costs.
Ceramics maintain stiffness and strength at temperatures where metals soften. This property prevents mechanical distortion under load during high-temperature operation. As a result, structural reliability is preserved in demanding petrochemical environments.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.