Ceramic Foundations Within Photovoltaic Manufacturing
Photovoltaic ceramics are a class of industrial ceramics applied across solar manufacturing environments where heat exposure, mechanical contact, and process cleanliness must remain predictable over long production cycles.
In photovoltaic lines, these materials appear as ceramic components for photovoltaic manufacturing such as carriers, vacuum chucks, furnace fixtures, and wear interfaces that directly interact with wafers and cells.
Compared with metals or polymers, advanced ceramics for solar cell production maintain geometry and surface stability under repeated thermal and chemical stress.
Therefore, technical ceramics for PV equipment are widely adopted wherever process yield, equipment uptime, and batch consistency must be preserved.
retains shape under sustained high temperatures
prevents unintended current or charge leakage
withstands acids, alkalis, and cleaning agents
resists wear, deformation, and microcracking
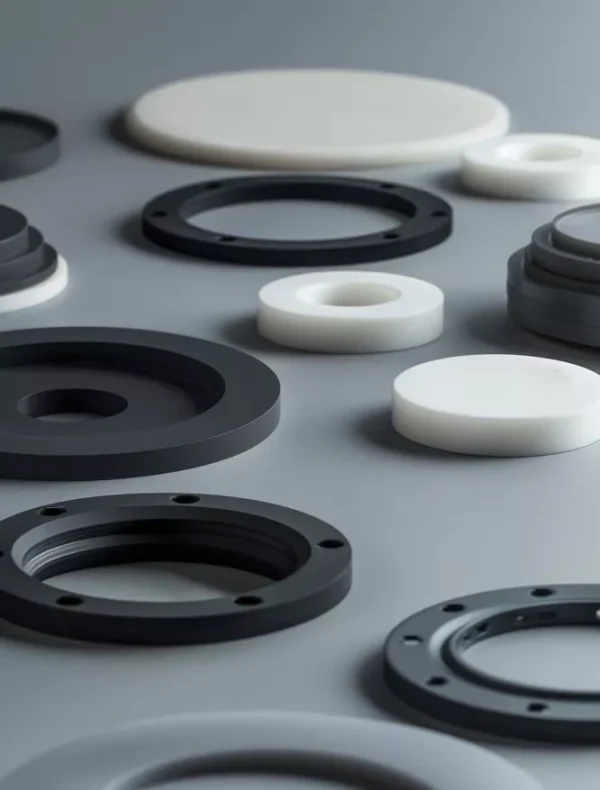

Key Properties of ADCERAX® Photovoltaics Ceramics
Across photovoltaic production lines, Photovoltaics Ceramics are selected not by material name alone but by how their physical and chemical properties behave under heat, electricity, chemicals, and mechanical load in real equipment conditions.
Thermal Properties
| Material | Max Continuous Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | CTE (×10⁻⁶/K) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99.5%) | 1650 | 25–30 | 7.5–8.0 | 25–1000 °C, air |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 1000 | 2.0–3.0 | 10.0–11.0 | 25–800 °C, air |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 1600 | 120–180 | 4.0–4.5 | 25–1200 °C, inert |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | 1200 | 20–30 | 3.0–3.3 | 25–1000 °C, air |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 1400 | 140–180 | 4.5–5.3 | 25–800 °C, inert |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 1400 | 30–42 | 5.0–5.5 | 25–800 °C, air |
| Fused Quartz (SiO₂) | 1100 | 1.3–1.5 | 0.5–0.6 | 25–800 °C, air |
| Glass-Ceramic | 900 | 1.5–2.5 | 0–2.0 | 25–700 °C, air |
Electrical Properties
| Material | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ≥10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 9.5–10.0 | 25 °C, dry |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | ≥10¹² | 8–10 | 25–30 | 25 °C, dry |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 10³–10⁵ | 2–3 | 9–10 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | ≥10¹³ | 10–12 | 7.5–8.5 | 25 °C |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | ≥10¹³ | 12–15 | 8.5–9.0 | 25 °C |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 10⁶–10⁸ | 4–6 | 6–7 | 25 °C |
| Fused Quartz | ≥10¹⁶ | 25–30 | 3.8–4.2 | 25 °C |
| Glass-Ceramic | ≥10¹² | 8–12 | 5–6 | 25 °C |
Chemical Resistance
| Material | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Oxidation Stability | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Stable in HCl/H₂SO₄ | Limited in strong alkali | Stable ≤1200 °C | pH 2–12, 25–80 °C |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | Stable in acids | Stable in alkali | Stable ≤1000 °C | pH 1–14, 25–80 °C |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | Stable except HF | Stable except molten alkali | Oxidizes >1000 °C | pH 1–13, 25–200 °C |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | Stable in acids | Limited in strong alkali | Stable ≤1100 °C | pH 2–11 |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | Hydrolyzes in moisture | Degrades in alkali | Stable in dry inert | Dry atmosphere |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | Stable in acids | Stable in alkali | Oxidizes >600 °C | pH 1–14 |
| Fused Quartz | Stable except HF | Limited in alkali | Stable ≤1100 °C | pH 2–10 |
| Glass-Ceramic | Stable in mild acids | Limited in alkali | Stable ≤900 °C | pH 3–10 |
Mechanical Properties
| Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | 300–380 | 1400–1800 | 3.5–4.5 | 25 °C |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 900–1200 | 1200–1300 | 7–10 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 400–450 | 2500–2800 | 3–4 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | 700–1000 | 1500–1700 | 5–7 | 25 °C |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 300–350 | 1100–1300 | 2.5–3.5 | 25 °C |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 350–450 | 3000–3800 | 2.5–3.0 | 25 °C |
| Fused Quartz | 50–70 | 550–600 | 0.7–0.8 | 25 °C |
| Glass-Ceramic | 120–200 | 700–900 | 1.5–2.0 | 25 °C |
Application Domains of ADCERAX® Photovoltaics Ceramics
In photovoltaic manufacturing, ceramic selection is guided by how different process zones impose distinct requirements on contact behavior, thermal stability, surface interaction, electrical isolation, and long-term wear performance.
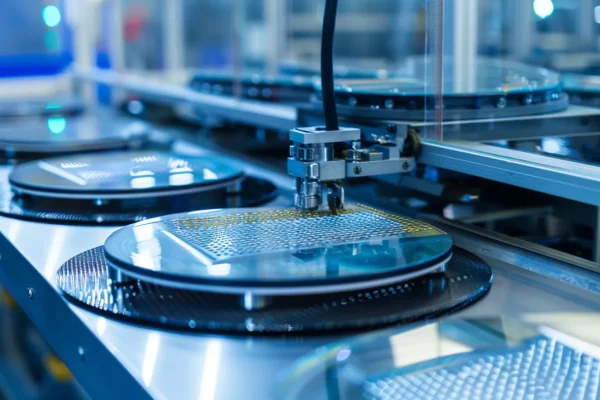

Wafer Handling and Precision Positioning
Photovoltaic production relies on controlled gripping, accurate placement, and low-particle contact during wafer and cell transfer, where photovoltaic ceramics reduce deformation and contamination risks.
- Uniform gripping minimizes micro-cracks during thin wafer handling.
- Low particle release supports stable yield in high-throughput lines.
- Dimensional stability preserves repeatable positioning accuracy.

High Temperature Furnace Processing
Thermal steps such as diffusion and oxidation demand ceramic components for photovoltaic manufacturing that maintain geometry and spacing through long heat cycles.
- Thermal stability preserves wafer spacing at elevated temperatures.
- Low creep prevents cumulative deformation over repeated cycles.
- Corrosion resistance extends service life in reactive atmospheres.
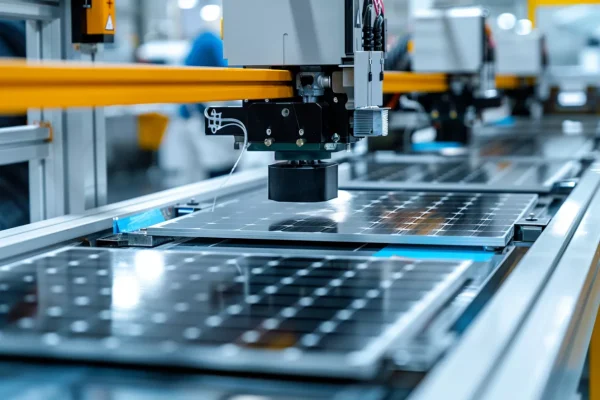

Surface Finishing and Material Preparation
Before entering critical process steps, wafers and fixtures require controlled surface preparation using advanced ceramics for solar cell production.
- Wear resistance maintains flatness over extended grinding cycles.
- Thermal inertia reduces distortion during frictional heating.
- Consistent removal supports repeatable surface quality.
Electrical Isolation and Process Safety
Where voltage, heat, and mechanical stress overlap, insulation-grade ceramics stabilize equipment behavior and reduce unexpected electrical failure in PV tooling and fixtures.
- Electrical insulation prevents leakage in energized zones.
- Thermal shock resistance supports rapid heating cycles.
- Structural integrity maintains alignment under load.

Wear Protection and Mechanical Support
In continuous-motion zones and repetitive contact points, wear-focused ceramics protect geometry, edge condition, and alignment longer than metals or polymers in comparable duty cycles.
- Extreme hardness slows wear in repetitive contact points.
- Chemical stability tolerates cleaning and corrosive media.
- Long service life reduces replacement frequency.
Ceramic Components Matched to Photovoltaic Production Needs
Photovoltaic ceramics serve different roles across automation, high temperature equipment, finishing tools, and support structures.
ADCERAX® helps align ceramic materials and structures with production priorities such as consistency, cleanliness, and service life.
ADCERAX® Photovoltaic Ceramics by Material Systems
This classification organizes photovoltaic ceramic components by material system, allowing engineers and procurement teams to quickly navigate toward the ceramic properties most relevant to their process constraints and equipment platforms.

Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics remain the most widely adopted industrial ceramics for photovoltaic industry, balancing cost, stability, and scalability.
- Stable flatness under thermal cycling
- Reliable wear resistance for tooling
- Suitable for high-volume replacement

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are selected where wear life and positional accuracy directly affect equipment repeatability.
- Outstanding wear resistance lifetime
- Maintains sharp edges and tooth profiles
- Supports precision positioning interfaces
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide dominates high-temperature zones in ceramic components for photovoltaic manufacturing where deformation and lifetime drive cost.
- Minimal creep at elevated temperatures
- Long service life in furnace environments
- Compatible with corrosive atmospheres
Silicon Nitride Ceramics
Silicon nitride ceramics provide electrical insulation combined with thermal shock resistance in demanding equipment zones.
- Strong dielectric performance
- Resists rapid temperature changes
- Maintains structural integrity

AlN Ceramics
Aluminum nitride ceramics address thermal management challenges where heat transfer and electrical behavior intersect.
- High thermal conductivity control
- Stable electrical characteristics
- Suitable for precision thermal zones

Boron Carbide Ceramics
Boron carbide ceramics are applied in extreme wear and chemically aggressive contact zones.
- Exceptional hardness and wear resistance
- Strong chemical durability
- Extended replacement intervals

Fused Quartz Ceramics
Fused quartz ceramics are preferred where thermal shock resistance and cleanliness are critical.
- Low thermal expansion behavior
- High purity surface contact
- Stable under repeated heating

Glass-Ceramics
Glass-ceramic materials provide controlled thermal expansion for support and spacing functions.
- Predictable expansion characteristics
- Stable mechanical support geometry
- Suitable for cyclic thermal environments
One-Stop Ceramic Manufacturing Services for Photovoltaics Ceramics

ADCERAX® provides one-stop manufacturing support for photovoltaic ceramic components, covering the full path from material selection to finished part delivery.
This integrated approach helps align custom ceramic parts for solar manufacturing with real equipment interfaces, process windows, and delivery schedules.
choose alumina, zirconia, SiC, AlN grades
press, cast, extrude ceramic green bodies
achieve flatness, holes, slots tight tolerances
polish grind texture surfaces per application
sinter fire parts under controlled atmospheres
machine interfaces for equipment compatibility
ADCERAX® Photovoltaics Ceramics Manufacturing Capabilities
Large-Area Ceramic Flatness Control
Many photovoltaic fixtures and carriers fail not by material choice but by flatness drift after machining and thermal exposure.
process ceramic plates up to 800 mm
control residual stress after stock removal
achieve ≤0.03 mm across full surface
Precision Machining in Dense Ceramics
Vacuum chucks, wafer handling tools, and interface components require precise micro-features machined into high-density ceramics without inducing subsurface damage.
machine pores below 0.5 mm diameter
cut dense alumina SiC without cracking
maintain sharp geometry without chipping
Complex Geometry Machining
Photovoltaic ceramic parts often include compound geometries combining planes, slots, holes, and mating surfaces that must align with metal and polymer assemblies.
cut compound ceramic geometries accurately
hold ±0.02 mm on assembly features
machine geometry aligned with equipment motion
Technical Customization for Photovoltaic Ceramic Components
ADCERAX® provides structured customization for custom ceramic parts for solar manufacturing,
covering material selection, geometry definition, surface condition, and interface compatibility required by production equipment.
Based on drawings, samples, or functional specifications, ceramic parts for solar cell manufacturing equipment are developed to
integrate reliably into wafer handling, thermal processing, and finishing stages.
ADCERAX® Photovoltaics Ceramics FAQs
Material selection in Photovoltaics Ceramics depends on temperature exposure, contact mode, and cleanliness requirements rather than strength alone. Alumina is often chosen for dimensional stability and cost balance, while silicon carbide is preferred for high-temperature furnace zones. Zirconia and nitride ceramics are selected where wear resistance or electrical insulation is critical. ADCERAX® supports material comparison based on actual process conditions rather than generic datasheets.
Alumina offers stable geometry, good insulation, and predictable machining behavior in most photovoltaic tooling. Silicon carbide provides higher thermal conductivity and lower creep under sustained furnace temperatures. The choice depends on whether heat dissipation or dimensional stability dominates the process window. ADCERAX® evaluates both materials within the same Photovoltaics Ceramics framework to ensure compatibility with equipment interfaces.
Flatness directly influences contact pressure distribution during wafer gripping and transport. Even small deviations can introduce local stress points that affect yield consistency. High-precision flatness control allows Photovoltaics Ceramics to maintain repeatable positioning across automation cycles. ADCERAX® machines large-area ceramic parts to controlled flatness suitable for PV handling tools.
Vacuum chuck failure is often linked to uneven pore distribution, insufficient flatness, or surface particle release rather than material fracture. Microporous structure uniformity directly affects suction balance across thin wafers. Proper surface conditioning and pore geometry control reduce wafer distortion and handling instability. ADCERAX® addresses these risks through application-specific Photovoltaics Ceramics design.
Wear lifetime depends on hardness, microstructure stability, and surface finish under repetitive contact. Zirconia and boron carbide ceramics slow abrasion where metal alternatives degrade rapidly. Surface integrity after machining also plays a critical role in delaying crack initiation. ADCERAX® selects wear-focused Photovoltaics Ceramics based on actual contact mechanics.
Thermal deformation arises from creep, uneven heating, or residual machining stress. Materials like silicon carbide and high-purity alumina maintain geometry better under prolonged furnace exposure. Controlled sintering and post-machining stress management reduce long-term distortion. ADCERAX® designs Photovoltaics Ceramics to remain dimensionally stable throughout furnace cycles.
Surface roughness influences particle generation, friction, and contact repeatability. Excessively rough surfaces release loose grains, while overly smooth surfaces can affect suction or sliding behavior. Controlled surface finishes balance cleanliness and functional interaction. ADCERAX® tailors surface roughness of Photovoltaics Ceramics to the specific process role.
Higher ceramic purity reduces unwanted chemical interaction and contamination during processing. In photovoltaic environments, trace impurities can affect wafer surfaces or cleaning chemistry. Alumina and nitride ceramics with controlled purity provide more predictable behavior. ADCERAX® specifies purity grades aligned with Photovoltaics Ceramics application sensitivity.
Ceramics often replace metals where thermal stability, insulation, or wear resistance is required. Unlike metals, Photovoltaics Ceramics do not deform plastically or conduct unintended current. The transition requires careful interface and tolerance design. ADCERAX® supports ceramic substitution with application-level engineering review.
Thermal conductivity determines how quickly heat spreads or dissipates during processing. Aluminum nitride and silicon carbide are used where rapid heat transfer is beneficial. Lower-conductivity ceramics are selected to isolate heat-sensitive zones. ADCERAX® aligns Photovoltaics Ceramics selection with thermal management objectives.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.