Semiconductor Ceramics in Industrial Process Systems
Within semiconductor manufacturing, industrial ceramics function as stable interfaces between equipment, materials, and tightly controlled process conditions.
Across semiconductor ceramics applications, these components support heat exposure, electrical isolation, and chemical containment without introducing contamination risks.
As a result, advanced ceramics for semiconductor industry environments are widely adopted in chambers, furnaces, wafer handling, and packaging tools where metals or polymers fail.
Consequently, ceramics for semiconductor equipment become structural and functional elements rather than passive materials, directly influencing yield stability and process repeatability.
withstands sustained high temperature cycling
resists plasma and corrosive gases
maintains resistance under elevated voltage
preserves geometry under mechanical stress
ADCERAX® Material Properties of Semiconductor Ceramics
In semiconductor manufacturing, material choices are evaluated through quantifiable thermal, electrical, chemical, and mechanical behavior rather than nominal grades, allowing semiconductor ceramics to be compared and selected against real process constraints.
Thermal Properties
| Ceramic Material | Max Continuous Service Temp (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | CTE (×10⁻⁶/K, 20–800 °C) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃, 99.7%) | 1650 | 25–30 | 7.8 | Air, steady-state |
| ZTA | 1500 | 18–22 | 8.0 | Air, steady-state |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 1000 | 2.5–3.0 | 10.5 | Air, steady-state |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 1600 | 120–180 | 4.2 | Inert atmosphere |
| Boron Nitride (HPBN) | 1800 | 30–60 | 1.0 | Inert atmosphere |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | 1400 | 25–35 | 3.2 | Air, steady-state |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 1400 | 170–200 | 4.5 | Air, steady-state |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 1500 | 30–42 | 5.6 | Air, steady-state |
| Metallic Ceramics (Cermet) | 1000 | 20–50 | 6.0 | Air, steady-state |
| Sapphire (Al₂O₃ single crystal) | 1700 | 35 | 5.6 | Air, steady-state |
| Beryllium Oxide (BeO) | 1600 | 250–330 | 7.5 | Air, steady-state |
| Yttria (Y₂O₃) | 1700 | 12–15 | 8.1 | Plasma-compatible |
Electrical Properties of Semiconductor Ceramics
| Ceramic Material | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99.7%) | ≥10¹⁴ | 12–15 | 9.6 | 25 °C, dry |
| ZTA | ≥10¹³ | 10–12 | 10.0 | 25 °C, dry |
| Zirconia | ≥10¹² | 8–10 | 29 | 25 °C, dry |
| Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | 10⁵–10⁶ | 2–4 | 9.7 | 25 °C |
| Boron Nitride (HPBN) | ≥10¹⁵ | 3–4 | 4.0 | 25 °C |
| Silicon Nitride | ≥10¹⁴ | 12–14 | 7.8 | 25 °C |
| Aluminum Nitride | ≥10¹³ | 15–17 | 8.9 | 25 °C |
| Boron Carbide | 10²–10³ | 1–2 | 10.2 | 25 °C |
| Metallic Ceramics | 10⁶–10⁹ | 3–6 | 12–18 | 25 °C |
| Sapphire | ≥10¹⁵ | 15–18 | 9.4 | 25 °C |
| Beryllium Oxide | ≥10¹⁴ | 10–12 | 6.7 | 25 °C |
| Yttria | ≥10¹⁴ | 8–10 | 14–16 | 25 °C |
Chemical Stability of Semiconductor Ceramics
| Ceramic Material | Plasma Resistance | Acid Resistance (HF/HCl) | Alkali Resistance | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Medium | Limited / Good | Good | ICP plasma, 200 h |
| ZTA | Medium | Limited / Good | Good | ICP plasma, 200 h |
| Zirconia | Medium | Moderate / Good | Moderate | ICP plasma, 200 h |
| Silicon Carbide | High | Excellent / Excellent | Excellent | ICP plasma, 300 h |
| Boron Nitride | Medium | Excellent / Excellent | Good | Inert gas |
| Silicon Nitride | High | Good / Excellent | Good | ICP plasma |
| Aluminum Nitride | Medium | Limited / Good | Moderate | Dry plasma |
| Boron Carbide | High | Excellent / Excellent | Excellent | ICP plasma |
| Metallic Ceramics | Medium | Moderate / Moderate | Moderate | Process gas |
| Sapphire | Medium | Good / Excellent | Good | Wet chemical |
| Beryllium Oxide | Medium | Good / Good | Moderate | Wet chemical |
| Yttria | Very High | Excellent / Excellent | Excellent | Plasma etch |
Mechanical Properties of Semiconductor Ceramics
| Ceramic Material | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Hardness (HV) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (99.7%) | 320–380 | 1400–1600 | 3.5–4.0 | 4-point bend |
| ZTA | 450–650 | 1300–1500 | 6.0–7.0 | 4-point bend |
| Zirconia | 900–1200 | 1200–1300 | 7.0–10.0 | 4-point bend |
| Silicon Carbide | 400–450 | 2400–2800 | 3.5–4.5 | 4-point bend |
| Boron Nitride | 70–100 | 300–400 | 2.0–2.5 | 3-point bend |
| Silicon Nitride | 700–900 | 1500–1700 | 6.0–7.5 | 4-point bend |
| Aluminum Nitride | 300–350 | 1100–1200 | 2.5–3.0 | 4-point bend |
| Boron Carbide | 350–400 | 3000–3800 | 2.5–3.5 | 4-point bend |
| Metallic Ceramics | 500–800 | 900–1300 | 5.0–8.0 | 4-point bend |
| Sapphire | 400–500 | 2000 | 3.0–4.0 | 4-point bend |
| Beryllium Oxide | 300–350 | 1100 | 2.5–3.0 | 4-point bend |
| Yttria | 180–250 | 600–800 | 2.0–2.5 | 4-point bend |
Ceramic Functional Applications Across Semiconductor Manufacturing
Below, ADCERAX® groups semiconductor ceramics by real process functions rather than by material names, reflecting how engineers and buyers evaluate ceramics for semiconductor equipment in actual production lines.
Wafer Handling and Positioning
Semiconductor manufacturing relies on controlled wafer fixation and movement, where ceramic interfaces directly affect yield stability and contamination control.
- Dimensional stability supports repeatable wafer alignment during processing.
- Low particle generation reduces defect risks in high-value wafers.
- Thermal compatibility maintains accuracy across temperature transitions.
Thermal Processing and Furnace Systems
High-temperature process steps rely on ceramic components that remain chemically inert and dimensionally stable throughout extended furnace cycles.
- Thermal shock resistance enables repeated heating and cooling without structural failure.
- Chemical inertness limits ionic release and surface reactions at elevated temperatures.
- Creep stability preserves geometry during long-duration thermal exposure.
Substrates and Electrical Packaging
Electrical isolation and heat dissipation converge in ceramic substrates used for power devices and advanced packaging.
- Electrical insulation ensures stable signal separation at high voltages.
- Thermal conductivity supports efficient heat dissipation paths.
- Metallization compatibility enables reliable circuit integration.
Plasma Etching and Coating Chambers
Plasma-facing zones rely on ceramics that hold surface integrity under ion bombardment, reactive radicals, and long vacuum exposure.
- Plasma resistance reduces erosion and particle generation at the surface.
- Chemical stability withstands corrosive etch byproducts during chamber cycles.
- Electrical insulation supports repeatable bias control and uniform discharge.
Precision Tools and Wear Components
Localized contact, cutting, and bonding operations depend on ceramics with controlled wear and geometric accuracy.
- Wear resistance extends service life in repetitive motion.
- Edge integrity maintains consistent cutting and bonding quality.
- Mechanical strength supports micron-level precision operations.
From Application Needs to Ceramic Solutions
Each semiconductor process zone places distinct demands on ceramic performance and geometry control.
ADCERAX® translates application conditions into manufacturable ceramic solutions.
ADCERAX® Semiconductor Ceramics Portfolio Structure
This classification reflects how semiconductor ceramics are selected, qualified, and deployed across process tools rather than how they are manufactured.

Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics remain the most widely used semiconductor process ceramic parts due to balanced purity, insulation, and cost control.
- Stable electrical insulation in process environments
- Broad geometry coverage for tool integration
- Suitable for high volume repeat supply

ZTA Ceramics
Zirconia Toughened Alumina is applied where advanced ceramics for semiconductor industry demand higher fracture resistance.
- Improved crack resistance under mechanical load
- Better lifetime in repetitive motion zones
- Controlled wear in precision interfaces

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are selected for technical ceramics semiconductor applications requiring precision and wear stability.
- High strength in compact geometries
- Excellent dimensional retention
- Clean surface interaction with wafers
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide dominates high-temperature zones in ceramics for semiconductor equipment.
- Minimal deformation at elevated temperatures
- Low contamination during long thermal cycles
-Proven durability in diffusion furnaces

Boron Nitride Ceramics
Boron nitride supports custom semiconductor ceramic parts requiring thermal stability with easy release.
- Non-wetting behavior with molten materials
- Excellent thermal shock tolerance
- Stable performance in inert atmospheres
Silicon Nitride Ceramics
Silicon nitride ceramics serve moving or load-bearing roles in semiconductor ceramics systems.
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Low friction under dynamic conditions
- Long service life in mechanical assemblies

AlN Ceramics
Aluminum nitride is chosen for high purity ceramic parts for semiconductor thermal management.
- High thermal conductivity performance
- Reliable electrical insulation
- Stable behavior under power cycling

Boron Carbide Ceramics
Boron carbide is applied in semiconductor process ceramic components exposed to extreme wear.
- Exceptional hardness performance
- Long-term abrasion resistance
-Stable geometry under repeated contact
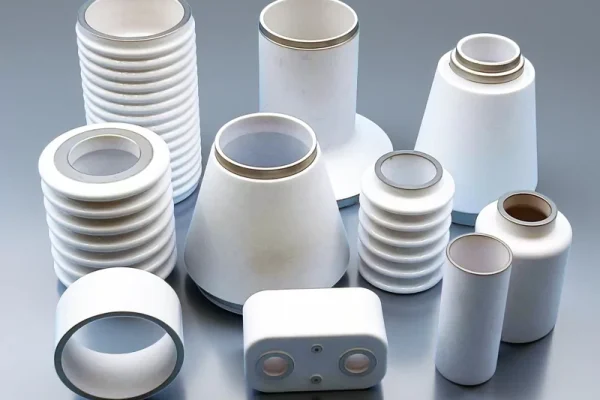

Metallized Ceramics
Metal–ceramic composites combine mechanical strength with functional stability in ceramics for semiconductor equipment.
- Controlled conductivity characteristics
- Improved impact tolerance
- Stable interface with metal assemblies
Transparent Ceramics
Transparent ceramics support optical and inspection-related technical ceramics semiconductor applications.
- Optical clarity under harsh conditions
- Stable transmission properties
- Resistant to thermal and chemical stress
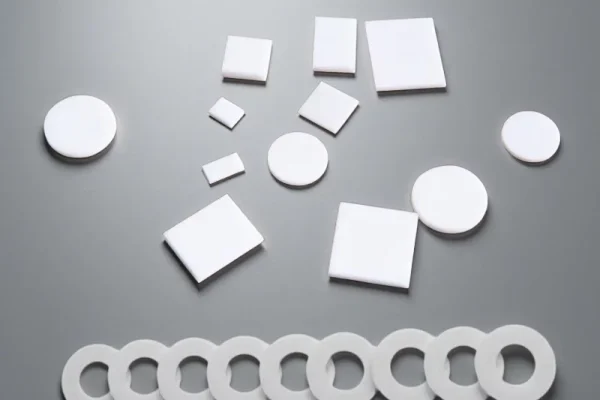

BeO Ceramics
Beryllium oxide ceramics are applied where high purity ceramic parts for semiconductor require maximum heat dissipation.
- Extremely high thermal conductivity
- Stable electrical insulation
- Compact thermal management capability
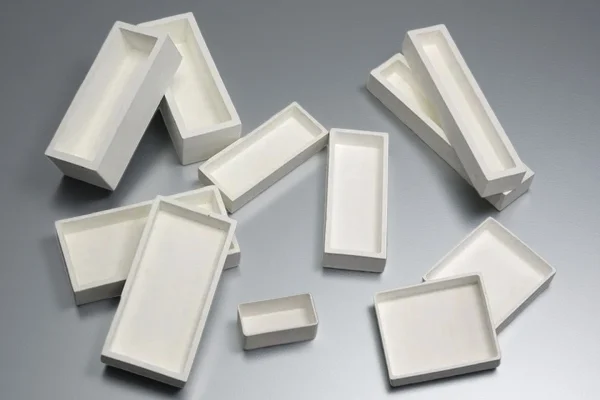

Yttria Ceramics
Yttria ceramics are widely used in plasma-facing semiconductor ceramics.
- Strong plasma erosion resistance
- Low particle generation
- Long service life in coating chambers
Integrated Manufacturing Support for Semiconductor Ceramics
ADCERAX® provides coordinated manufacturing workflows for semiconductor ceramics, covering material preparation, precision forming, finishing, and verification within a single supply chain.
Each process stage is aligned with equipment requirements to support reliable delivery of ceramics for semiconductor equipment without fragmented sourcing.
match ceramic grades to process environments
press, cast, or extrude complex ceramic geometries
achieve tight tolerances on functional ceramic parts
control roughness and edge integrity consistently
apply DBC DPC or HTCC conductive layers
verify interfaces with metal or composite components
ADCERAX® Machining Capabilities for Semiconductor Ceramics
Precision Ceramic Sintering Control
Controlled sintering defines final density, grain structure, and dimensional stability for semiconductor ceramics used in thermal and plasma processes.
stable firing up to 1700 °C ±5 °C
oxygen nitrogen vacuum selectable per material
≥99.5% theoretical density across batches
Accurate CNC Ceramic Machining
Post-sinter machining enables custom semiconductor ceramic parts to meet strict assembly and alignment requirements.
complex geometries without stress concentration
dimensional accuracy down to ±0.01 mm
Ra ≤0.4 µm on functional interfaces
Metallization & Interface Processing
Metallized ceramics support electrical and thermal integration in ceramics for semiconductor equipment, especially packaging and power modules.
copper thickness 0.2–0.8 mm selectable
peel strength ≥6 N/mm verified
flatness ≤0.15% after metallization
Custom Semiconductor Ceramics Built Around Your Process
ADCERAX® supports custom semiconductor ceramic development by translating application conditions, drawings, and tolerance requirements into manufacturable ceramic solutions.
From geometry optimization to material selection, each customization step focuses on fit, consistency, and integration with semiconductor equipment environments.
Start a technical discussion with ADCERAX® to align your ceramic design with real process conditions.
FAQs About ADCERAX® Semiconductor Ceramics
Semiconductor Ceramics are selected primarily for low outgassing, chemical inertness, and stable surface chemistry under vacuum and plasma exposure.
These properties prevent ionic release and particle generation that could directly impact wafer yield.
ADCERAX® controls raw material purity and sintering density to ensure Semiconductor Ceramics remain stable throughout long process cycles.
Unlike metals, Semiconductor Ceramics maintain dimensional stability and mechanical strength at temperatures exceeding 1000 °C.
This stability prevents creep, warpage, and alignment drift during diffusion, oxidation, and annealing steps.
ADCERAX® Semiconductor Ceramics are engineered to sustain repeated thermal cycling without structural degradation.
Plasma-facing Semiconductor Ceramics resist erosion, sputtering, and surface roughening under ion bombardment.
This resistance minimizes particle shedding that could otherwise cause defect formation on wafers.
ADCERAX® applies material selection and surface finishing strategies specifically for plasma-exposed ceramic components.
Semiconductor Ceramics combine high stiffness with low thermal expansion, ensuring precise wafer positioning.
These characteristics prevent deformation during temperature changes and mechanical loading.
ADCERAX® supplies Semiconductor Ceramics that support repeatable wafer handling without inducing stress or misalignment.
High dielectric strength and volume resistivity allow Semiconductor Ceramics to isolate electrical fields reliably.
This insulation stability is essential in electrostatic chucks, heaters, and chamber assemblies.
ADCERAX® verifies electrical performance to ensure Semiconductor Ceramics remain insulating under elevated temperature and voltage.
In applications such as heater plates and substrates, efficient heat transfer is critical for temperature uniformity.
Materials like aluminum nitride ceramics balance insulation with high thermal conductivity.
ADCERAX® selects Semiconductor Ceramics that manage heat flow without sacrificing electrical isolation.
Surface roughness directly influences particle adhesion and cleaning efficiency.
A controlled finish minimizes contamination risks in wafer-facing applications.
ADCERAX® manages surface finishing to meet functional requirements for Semiconductor Ceramics.
Ceramic substrates provide electrical insulation, thermal management, and mechanical support simultaneously.
This multifunctional performance enables reliable power and signal integration.
ADCERAX® develops Semiconductor Ceramics aligned with DBC, DPC, and HTCC packaging needs.
Impurities can migrate under heat or plasma exposure, affecting device yield.
High-purity Semiconductor Ceramics reduce this risk by maintaining chemical stability.
ADCERAX® controls raw materials and processing to meet purity expectations.
Stable ceramic components reduce unexpected failures caused by thermal shock or chemical attack.
This reliability lowers maintenance interventions and unplanned stoppages.
ADCERAX® Semiconductor Ceramics are designed for predictable performance across production cycles.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.