Material Reliability Across Food Processing
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics refer to industrial ceramics applied as functional components within hygienic, thermal, and mechanically demanding food operations rather than as structural equipment shells.
In food plants, these food processing ceramic components are selected where metals or polymers struggle with wear, corrosion, or repeated CIP exposure under production conditions.
Moreover, ceramics for food processing equipment provide stable performance in filtration, pumping, valve control, heat exchange, grinding, and cutting, where dimensional stability and surface cleanliness directly affect yield and safety.
As a result, technical ceramics for food industry are increasingly used as critical contact and wear parts in modern food and beverage processing lines.
Withstands continuous heat and thermal cycling safely
Resists CIP acids alkalis and oxidizing agents
Prevents stray currents and electrochemical effects
Maintains precision under abrasion and pressure

Physicochemical Performance of ADCERAX® Food-Grade Ceramics
Material selection in Food Processing Engineering Ceramics is guided by measurable thermal, electrical, chemical, and mechanical limits that directly affect hygiene, reliability, and service life in food operations.
Thermal Properties
| Material | Maximum Continuous Service Temperature | Thermal Conductivity | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃ ≥99%) | 1,600 °C | 25–30 W/m·K | 7.5–8.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K | Air atmosphere, steady state |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 1,000 °C | 2.0–2.5 W/m·K | 10–11 × 10⁻⁶ /K | Air atmosphere, steady state |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1,650 °C | 120–160 W/m·K | 4.0–4.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K | Air atmosphere, steady state |
Electrical Properties
| Material | Volume Resistivity | Dielectric Strength | Relative Permittivity | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃ ≥99%) | ≥10¹⁴ Ω·cm | 12–15 kV/mm | 9.5–10 | 25 °C, dry |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | ≥10¹² Ω·cm | 8–10 kV/mm | 25–30 | 25 °C, dry |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 10³–10⁵ Ω·cm | 2–3 kV/mm | 9–10 | 25 °C, dry |
Chemical Stability
| Material | pH Resistance Range | Acid Resistance | Alkali Resistance | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃ ≥99%) | pH 1–13 | Stable in HNO₃, H₂SO₄ | Stable up to NaOH 10% | 80 °C immersion |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | pH 1–14 | Stable in most organic acids | Stable up to NaOH 10% | 80 °C immersion |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | pH 0–14 | Stable in strong acids | Stable in strong alkalis | 90 °C immersion |
Mechanical Properties
| Material | Flexural Strength | Compressive Strength | Hardness | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃ ≥99%) | 300–400 MPa | ≥2,000 MPa | 15–17 GPa | 3-point bending, RT |
| Zirconia (Y-TZP) | 900–1,200 MPa | ≥2,500 MPa | 12–13 GPa | 3-point bending, RT |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 350–450 MPa | ≥3,000 MPa | 22–25 GPa | 3-point bending, RT |
ADCERAX® Food Processing Engineering Ceramics Applications
Food processing operations rely on Food Processing Engineering Ceramics where hygiene, durability, and process stability must be maintained across continuous production cycles and repeated cleaning regimes.
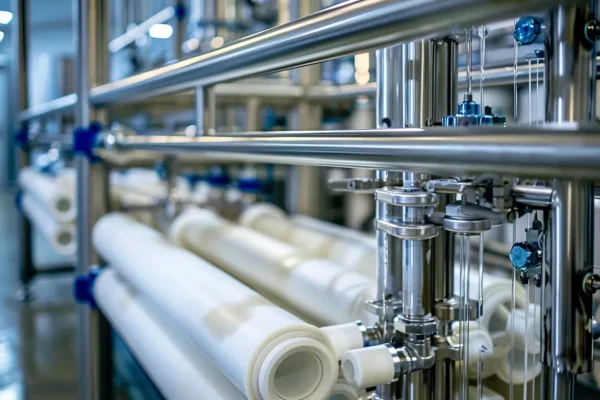

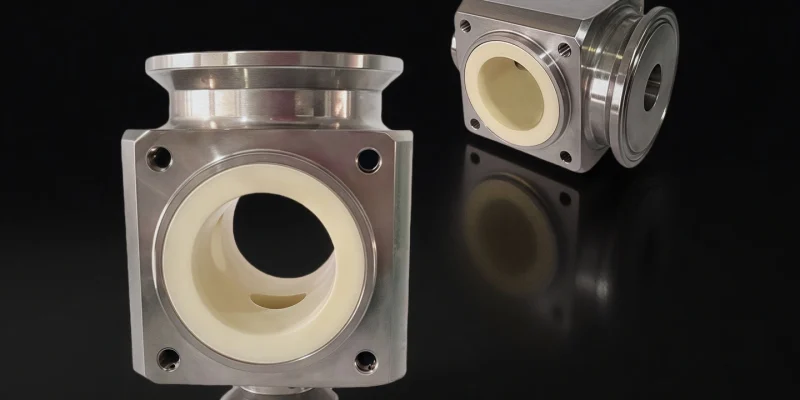
Filtration and Separation Systems
Ceramic filtration plays a central role in liquid clarification, particle removal, and process stabilization across food and beverage production lines.
- Chemical inertness allows stable operation under aggressive CIP cleaning agents and elevated temperatures.
- Pore structure consistency supports predictable filtration performance and reproducible product quality.
- Long service life reduces consumable replacement frequency and operating cost volatility.

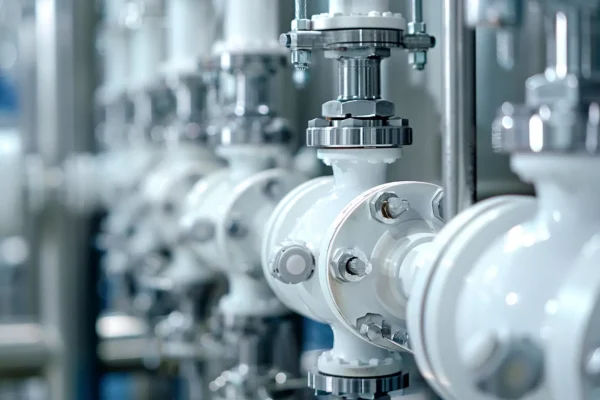
Pumping and Metering Units
Ceramic pump components support stable flow control and precise dosing in food processes involving abrasion, viscosity variation, and frequent sanitation.
- Wear resistance maintains dimensional accuracy under continuous reciprocating motion.
- Low contamination risk minimizes metal ion release into sensitive food products.
- Surface stability enables consistent sealing during long-term operation.

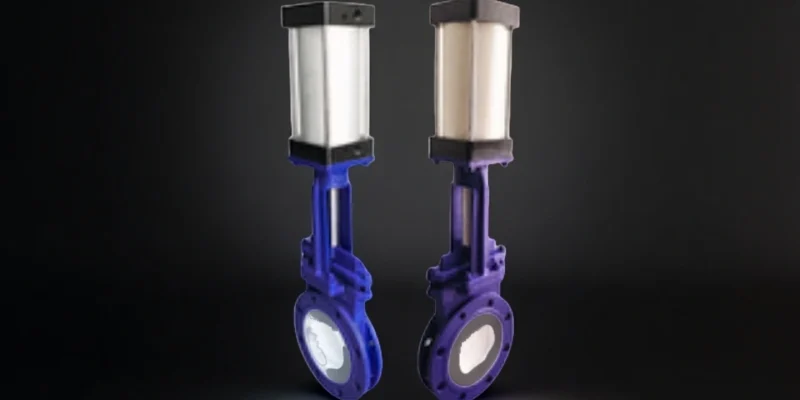
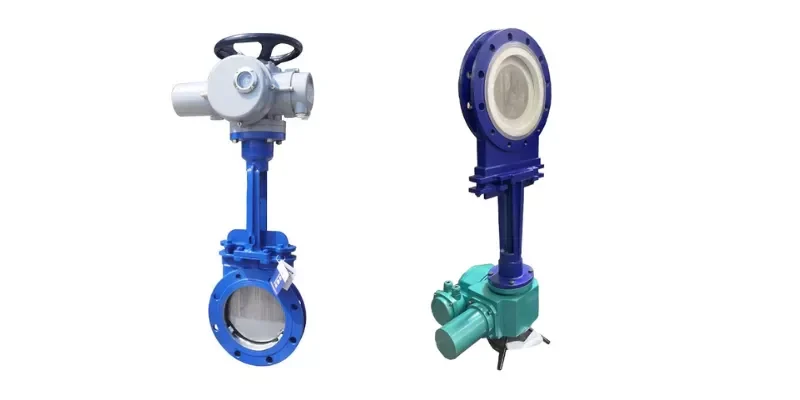
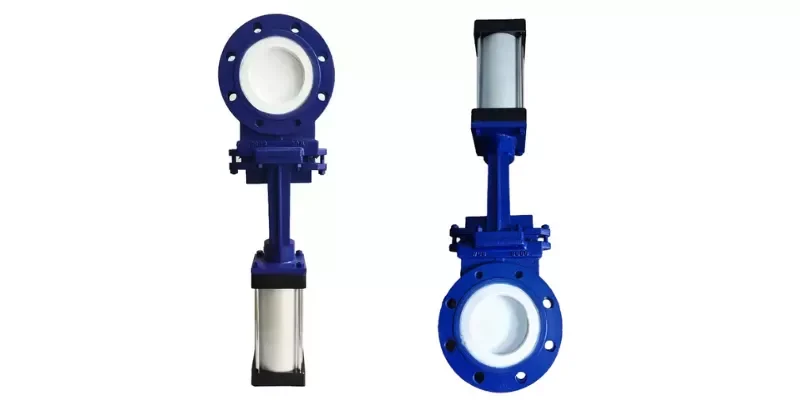
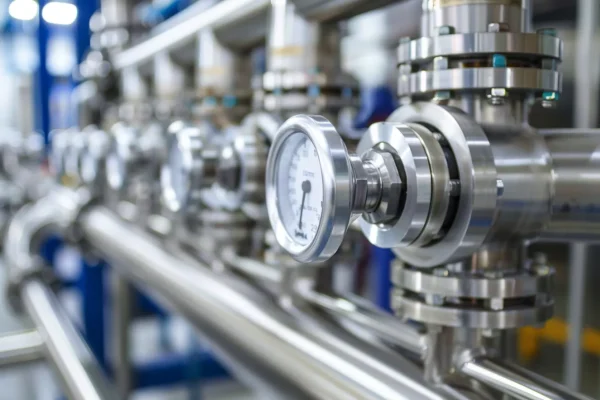
Valve and Flow Control Assemblies
Ceramic valve components are applied where hygienic flow regulation, repeatable sealing, and resistance to aggressive cleaning cycles are required in food processing lines.
- Dimensional stability ensures sealing accuracy under frequent opening and closing cycles.
- Chemical resistance maintains integrity during alkaline and acidic CIP cleaning.
- Wear durability extends service life in particulate or high-viscosity media.
Balanced sealing under high differential pressure
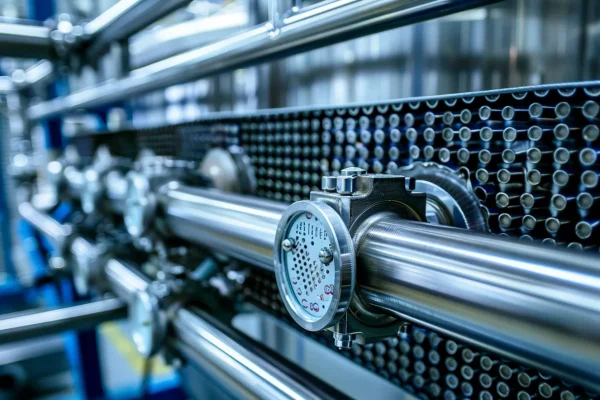

Heat Exchange and Thermal Control
Ceramic heat exchange components manage thermal transfer in food processes where corrosion, fouling, and temperature cycling limit metallic solutions.
- High thermal conductivity supports efficient heat transfer with compact designs.
- Corrosion resistance ensures compatibility with acidic and alkaline media.
- Thermal shock tolerance maintains integrity during rapid temperature changes.
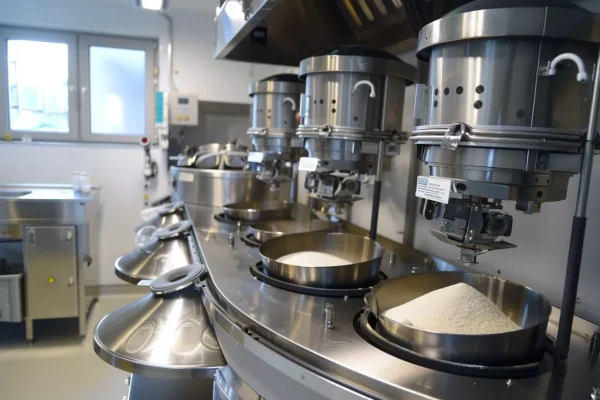

Grinding, Mixing and Cutting Operations
Ceramic grinding and cutting components enable precise size reduction and material handling while limiting wear debris and contamination.
- Hardness stability preserves cutting edges and grinding efficiency.
- Low wear debris protects product purity in sensitive formulations.
- Mechanical reliability supports consistent batch-to-batch processing.
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics for Critical Process Zones
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics are applied in zones exposed to abrasion, corrosion, and repeated sanitation cycles.
These ceramic solutions maintain structural stability and surface integrity across demanding food processing operations.
ADCERAX® Ceramic Categories for Hygienic Food Processing Systems
These categories organize food processing ceramics by material behavior, helping engineers quickly match performance characteristics with specific process units and hygiene requirements.
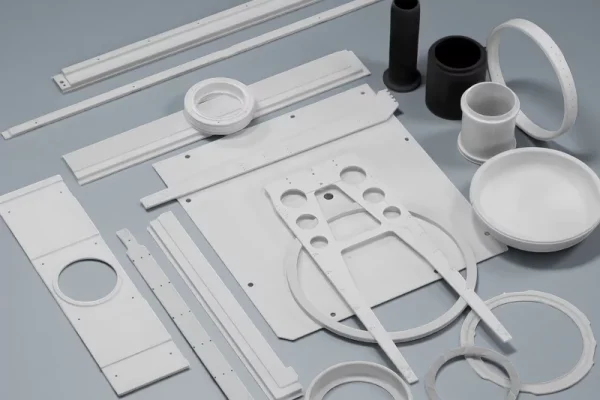

Alumina Ceramics
Alumina-based components serve as stable, cost-effective solutions for wear, filtration, cutting, and pumping tasks in food operations.
- Consistent wear resistance in abrasive media
- Stable surfaces under frequent CIP cycles
- Suitable for high-volume standardized components
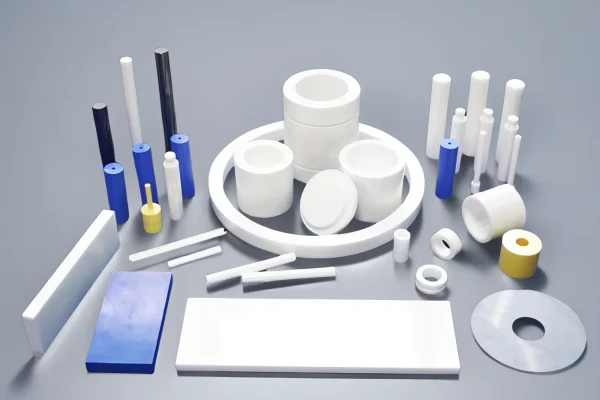

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are applied where higher toughness, impact resistance, and precision control are required in hygienic environments.
- Enhanced fracture toughness for dynamic loads
- Smooth surfaces for hygienic sealing interfaces
- Extended service life in precision components
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide ceramics address extreme thermal and chemical demands within heat exchange and filtration systems.
- Exceptional corrosion resistance in aggressive fluids
- High thermal conductivity for efficient heat transfer
- Structural stability under pressure and temperature
Integrated Manufacturing Services for Food Processing Ceramics
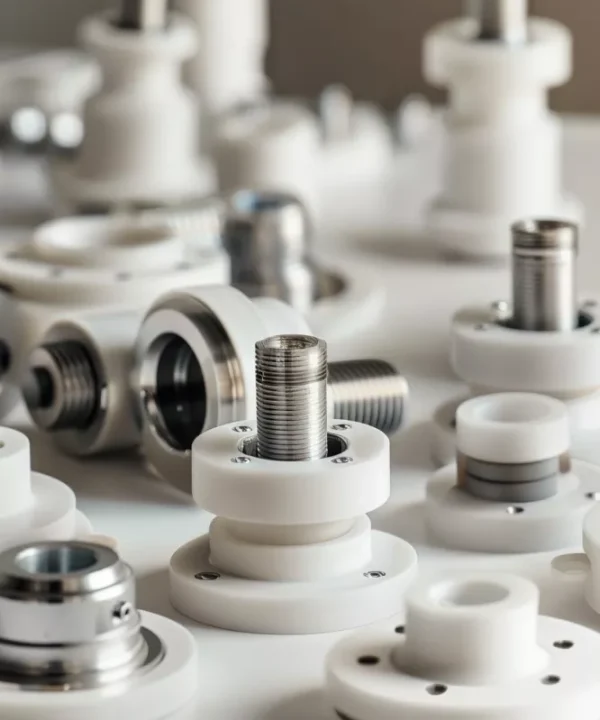

ADCERAX® provides a unified manufacturing workflow covering material shaping, precision machining, and functional finishing for ceramic components used in food processing equipment.
As a ceramic parts manufacturer for food industry, ADCERAX® focuses on machining accuracy, material control, and process reproducibility rather than generic outsourcing steps.
dry pressing or extrusion forming up to ±0.5% dimensional repeatability
CNC shaping on unfired bodies reducing post-sinter tolerance loss
controlled firing up to 1,650 °C for alumina and SiC
final tolerances down to ±0.01 mm on functional surfaces
Ra 0.4–0.8 µm achievable for hygienic contact areas
ceramic-to-metal or ceramic-to-ceramic fit verification on request
ADCERAX® Precision Ceramic Processing Capabilities for Food Industry Applications
High-Temperature Sintering Control
Controlled sintering defines final density, grain structure, and chemical stability for food-grade ceramics.
temperature uniformity within ±5 °C across load
sustained sintering up to 1,650 °C
bulk density exceeding 99.5% theoretical
CNC Grinding and Finishing
Post-sinter grinding ensures functional tolerances and hygienic surface performance in critical contact areas.
dimensional tolerances down to ±0.01 mm
Ra 0.4–0.8 µm on sealing faces
roundness and flatness below 0.005 mm
Green Body Machining
Green machining enables complex geometries while minimizing stress and material loss after firing.
machining efficiency improved by over 30%
shrinkage deviation limited within ±0.3%
internal channels and thin walls achievable
Custom Ceramic Solutions for Food Processing Equipment
ADCERAX® addresses common food processing pain points such as rapid wear, CIP-related corrosion, and non-standard interfaces by delivering custom ceramic components for food processing matched to real operating conditions.
As an experienced ceramic parts manufacturer, ADCERAX® translates drawings or samples into reliable ceramic solutions that reduce replacement frequency and process risk.
ADCERAX® Technical FAQs for Food Processing Engineering Ceramics
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics outperform stainless steel in abrasion, corrosion, and chemical stability under repeated CIP cycles.
Ceramic surfaces do not suffer from pitting or ion leaching when exposed to alkaline or acidic cleaning agents.
This stability reduces contamination risk and extends service life in filtration, pumping, and valve systems.
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics maintain structural integrity across wide pH ranges and elevated cleaning temperatures.
Unlike metals, ceramic materials do not form corrosion products after repeated CIP exposure.
This property allows predictable cleaning cycles without progressive material degradation.
High hardness and microstructural stability give Food Processing Engineering Ceramics superior resistance to abrasive particles.
Wear rates remain low even in slurry transport, dosing pumps, and valve sealing surfaces.
This reduces dimensional drift that commonly causes leakage or metering inaccuracies.
Ceramic membranes used in Food Processing Engineering Ceramics retain pore geometry under thermal and chemical stress.
Unlike polymer membranes, pore collapse and swelling are minimized.
This ensures consistent flux and separation efficiency across long operating cycles.
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics combine hardness with smooth surface finishes.
This reduces particle embedding and abrasive scoring common in metal components.
As a result, flow stability and sealing performance are preserved under challenging media conditions.
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics remain stable in oxidizing, acidic, and alkaline environments.
Material properties do not degrade under standard CIP formulations.
This ensures long-term compatibility with modern sanitation protocols.
Yes, Food Processing Engineering Ceramics provide smooth, non-reactive sealing surfaces.
This limits residue adhesion and microbial retention at valve interfaces.
The result is improved hygienic reliability compared to metallic sealing materials.
Silicon carbide components within Food Processing Engineering Ceramics offer high thermal conductivity with corrosion resistance.
Heat transfer efficiency remains stable even under aggressive cleaning conditions.
This prevents efficiency loss caused by scaling or chemical attack on metal exchangers.
Food Processing Engineering Ceramics exhibit high hardness with low wear debris generation.
This prevents metal contamination during grinding or dispersion of food ingredients.
Particle size consistency is easier to maintain across batches.
Many Food Processing Engineering Ceramics tolerate rapid temperature changes without cracking.
Controlled microstructures reduce thermal stress accumulation.
This is critical in systems combining hot processing and cold CIP rinsing.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.