When Metallurgical Ceramics Replace Metals
Metallurgical ceramics are purpose-built industrial ceramics selected for conditions where metal components soften, oxidize, or introduce contamination under sustained heat, abrasion, and reactive atmospheres.
As a result, they are widely applied in steelmaking, aluminum handling, and powder metallurgy as crucibles, liners, flow-path parts, kiln furniture, and wear modules that preserve both geometry and process chemistry.
Moreover, typical duty cycles often reach 800–1800 °C under continuous or repeated thermal cycling, which explains why ceramics are specified for metallurgy when uptime and output consistency are critical.
Consequently, because they remain electrically insulating and chemically inert in many furnace environments, metallurgical ceramics help reduce unplanned shutdowns caused by distortion, electrical shorting, and accelerated wear.
Holds shape through long hot cycles
Limits slag and melt contamination
Prevents arcing and stray currents
Resists erosion from particles
ADCERAX® Metallurgical Ceramics Properties
In real metallurgical systems, heat, electrical exposure, chemical contact, and mechanical load interact continuously, shaping how metallurgical ceramics perform over time.
Thermal Characteristics of Metallurgical Ceramics
| Material System | Continuous Service Temp (°C) | Thermal Shock ΔT (°C) | CTE (×10⁻⁶/K, 25–1000 °C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K @25 °C) | Test Conditions | Limiting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | 1600 | 250 | 7.8 | 25 | Air, slow heating | Thermal shock cracking |
| ZTA | 1550 | 350 | 7.5 | 20 | Air, cyclic heating | Phase mismatch stress |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂, YSZ) | 1400 | 400 | 10.5 | 2.5 | Air, rapid cycling | Low thermal conductivity |
| MSZ (Mg-PSZ) | 1700 | 300 | 10.2 | 3.0 | Long hold, oxidizing | Aging at mid-temperature |
| SiC (SSiC/RBSiC) | 1650 | 500 | 4.2 | 120 | Inert / reducing | Oxidation above 1400 °C |
| NBSiC | 1500 | 300 | 4.5 | 30 | Furnace atmosphere | Nitride oxidation |
| Boron Nitride (BN) | 1800 (inert) | >500 | 1.0 | 35 | Vacuum / inert gas | Oxidation in air |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | 1200 | 400 | 3.2 | 30 | Cyclic mechanical load | Oxidation over time |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 1400 | 300 | 4.5 | 170 | Dry, non-oxidizing | Hydrolysis sensitivity |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 2000 | 200 | 13.5 | 45 | Basic slag contact | Thermal cracking |
| Boron Carbide (B₄C) | 1500 | 250 | 5.6 | 30 | Abrasive heating | Brittleness |
Electrical Characteristics of Metallurgical Ceramics
| Material System | Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm @25 °C) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Dielectric Constant (1 MHz) | Test Conditions | Limiting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 10¹⁴ | 12 | 9.5 | Dry air | Resistivity drops with temperature |
| ZTA | 10¹³ | 10 | 10 | Dry air | Grain boundary conduction |
| Zirconia | 10⁸–10¹⁰ | 8 | 25 | Elevated temperature | Ionic conductivity |
| MSZ | 10⁹ | 7 | 22 | High temperature | Oxygen ion mobility |
| SiC | 10⁻²–10⁻¹ | — | — | Intrinsic semiconductive | Electrical conductivity |
| NBSiC | 10⁴ | — | — | Nitride bonded | Partial conductivity |
| Boron Nitride | 10¹⁵ | 9 | 4 | Inert environment | Oxidation limits |
| Silicon Nitride | 10¹⁴ | 10 | 8 | Dry condition | Surface oxidation |
| Aluminum Nitride | 10¹³ | 15 | 8.5 | Dry, low humidity | Moisture sensitivity |
| Magnesia | 10¹² | 9 | 9.8 | High temperature | Grain growth |
| Boron Carbide | 10⁻¹ | — | — | Semiconductive | Not insulating |
Chemical Characteristics of Metallurgical Ceramics
| Material System | Molten Metal Wettability (Contact Angle °) | Slag Resistance (pH Range) | Oxidation Resistance | Test Conditions | Limiting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 120–140 | 4–9 | Stable <1400 °C | Air, Al melt | Alkali attack |
| ZTA | 115–135 | 4–9 | Stable | Mixed slag | Phase corrosion |
| Zirconia | >140 | 3–10 | Stable | Steel melts | Reduction environments |
| MSZ | >145 | 3–11 | Stable | Long-term slag | Phase aging |
| SiC | >150 | 2–10 | Oxidizes >1400 °C | Reducing | Oxide scale |
| NBSiC | >140 | 3–9 | Limited | Furnace atmosphere | Nitride oxidation |
| Boron Nitride | >160 | 1–14 | Poor in air | Vacuum / inert | Oxidation |
| Silicon Nitride | >130 | 3–9 | Moderate | Gas furnaces | Oxidation |
| Aluminum Nitride | >140 | 3–9 | Moderate | Dry atmosphere | Hydrolysis |
| Magnesia | <90 | 9–14 | Stable | Basic slag | Acid dissolution |
| Boron Carbide | >150 | 3–10 | Stable | Abrasive melts | Brittleness |
Mechanical Characteristics of Metallurgical Ceramics
| Material System | Hardness (HV) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) | Test Conditions | Limiting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | 1500 | 350 | 3.5 | 3-point bend | Brittle fracture |
| ZTA | 1400 | 600 | 6.0 | Room temp | Thermal mismatch |
| Zirconia | 1200 | 900 | 8–10 | Transformation toughened | Low stiffness |
| MSZ | 1150 | 700 | 7.0 | Long-term load | Aging |
| SiC | 2500 | 450 | 4.0 | Abrasive load | Brittle |
| NBSiC | 2000 | 300 | 3.0 | Structural load | Porosity |
| Boron Nitride | 50 | 60 | 2.0 | Machinable grade | Low strength |
| Silicon Nitride | 1600 | 900 | 6.5 | Rolling contact | Cost |
| Aluminum Nitride | 1100 | 320 | 3.0 | Dry environment | Moisture |
| Magnesia | 900 | 150 | 2.0 | High temp load | Thermal cracking |
| Boron Carbide | 3000 | 350 | 2.8 | Abrasion | Extreme brittleness |
ADCERAX® Metallurgical Ceramics Across Core Industrial Functions
Within metallurgical production lines, ceramics are selected according to the functional roles they serve across heat exposure, material flow and structural support.

Thermal Containment and High-Temperature Processing
In metallurgical production, components exposed to molten metals and sustained furnace heat must maintain shape, chemistry, and thermal balance over long operating cycles.
- High temperature metallurgical ceramics maintain dimensional stability during repeated heating and cooling, which is essential for consistent melting, sintering, and heat treatment workflows.
- By remaining chemically inert at elevated temperatures, ceramics for metallurgy help prevent contamination that can alter alloy composition or test accuracy.
- Their insulating behavior supports safer thermal control where metal containers would soften, oxidize, or deform.
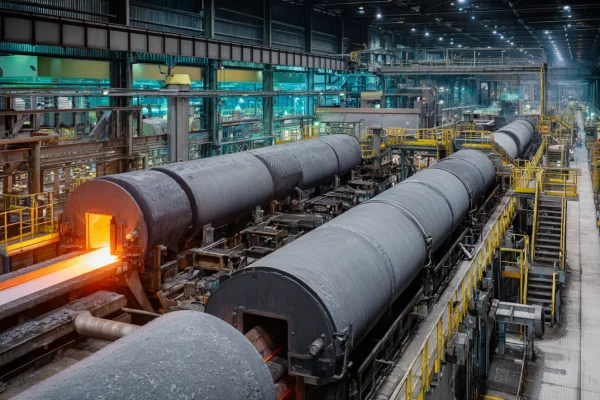

Flow Control, Tubes, and Protective Pathways
Metallurgical systems rely on controlled flow of gases, melts, and thermal signals, where internal surfaces must resist erosion and chemical attack.
- Industrial ceramics for metallurgy preserve internal geometry in tubes and channels, ensuring predictable flow and measurement accuracy.
- Low reactivity and smooth surfaces reduce buildup and blockage during long production runs.
- Electrical insulation enables safe operation near heaters, sensors, and thermocouples.
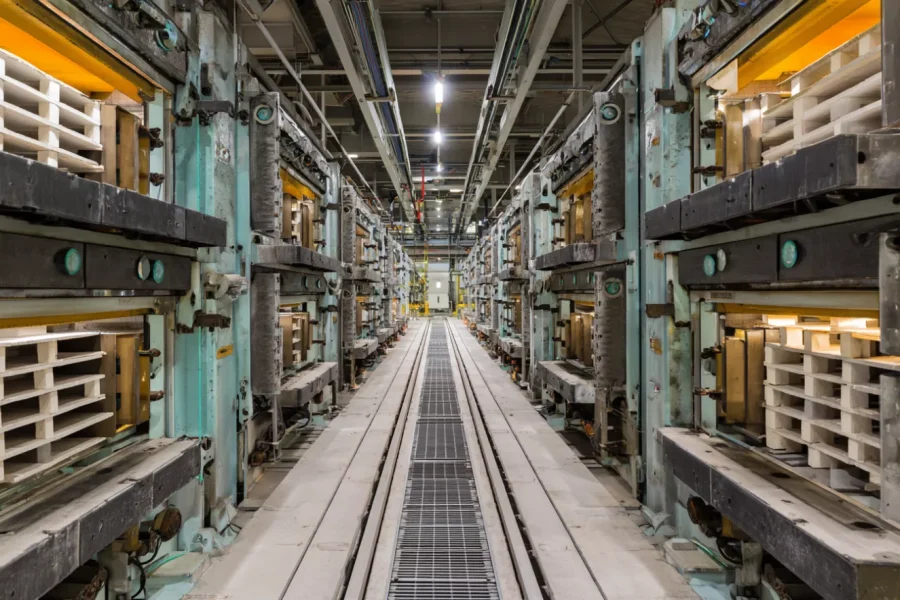

Structural Support and Furnace Furniture
Load-bearing and support ceramics define how reliably furnaces and kilns operate under continuous weight and heat.
- Engineering ceramics for metallurgy carry mechanical loads without creep, supporting repeatable furnace geometry.
- Thermal compatibility across large structures reduces stress accumulation and cracking.
- Stable support components improve batch consistency and extend furnace service life.
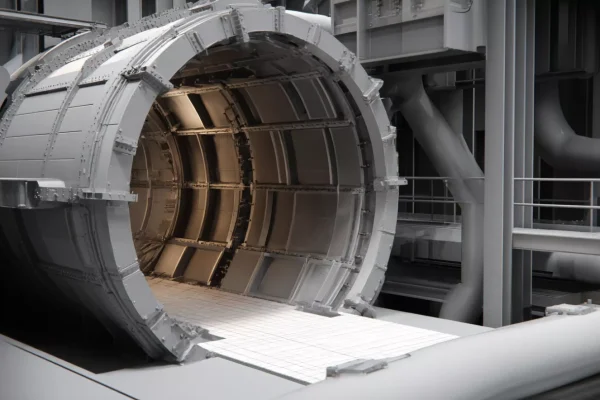

Wear Protection and Lining Systems
In abrasive and high-impact zones, ceramics act as sacrificial and protective layers that define maintenance cycles.
- Advanced ceramics for metallurgy reduce erosion in chutes, mills, and vessels exposed to continuous particle flow.
- High hardness and low wear rates help stabilize process efficiency over time.
- Modular ceramic linings simplify replacement and reduce downtime.
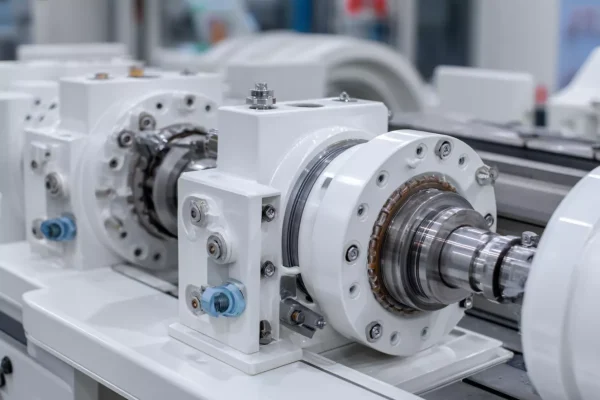

Precision Motion, Sealing, and Functional Components
Beyond static structures, metallurgical systems depend on ceramic components that move, seal, or rotate reliably at temperature.
- Technical ceramics for metallurgy enable precision motion where lubrication and metals fail.
- Electrical insulation and chemical stability support safe operation in mixed environments.
- Dimensional consistency ensures predictable sealing and alignment.
Ceramics Chosen by Metallurgical Function
Effective metallurgical ceramics are defined by where and how they function within the process, not by generic material labels. ADCERAX® works from application logic to deliver ceramics that match thermal load, wear mode, and service cycle.
Types of ADCERAX® Metallurgical Ceramics
To support fast specification and accurate selection, ADCERAX® organizes metallurgical ceramics by material systems that directly correspond to thermal load, wear mode, and chemical exposure.

Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics form the backbone of industrial ceramics for metallurgy where thermal stability and cost control must remain balanced.
- Stable dimensions under long furnace cycles
- Clean interaction with molten metals
- Wide availability for standard replacements

ZTA Ceramics
Zirconia Toughened Alumina combines alumina stability with enhanced fracture resistance for mechanically stressed zones.
- Improved crack resistance under thermal shock
- Higher wear tolerance than pure alumina
- Suitable for cyclic mechanical loading

Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are selected in metallurgy where extreme temperature gradients and dimensional precision are critical.
- Low thermal conductivity for insulation
-High fracture toughness under rapid cycling
- Stable geometry at elevated temperatures
Silicon Carbide Ceramics
Silicon carbide ceramics dominate high temperature metallurgical ceramics where abrasion, corrosion, and thermal conductivity intersect.
- Exceptional resistance to molten metal attack
-High thermal conductivity for heat control
- Long service life in abrasive flow

Boron Nitride Ceramics
Boron nitride ceramics enable non-wetting contact with molten metals and controlled release applications.
- Excellent non-wetting metal behavior
-Easy material release after processing
- Stable electrical insulation properties
Silicon Nitride Ceramics
Silicon nitride ceramics are used where mechanical strength and wear resistance must coexist with thermal cycling.
- High mechanical strength at temperature
-Excellent rolling and sliding wear resistance
- Reliable performance in moving assemblies
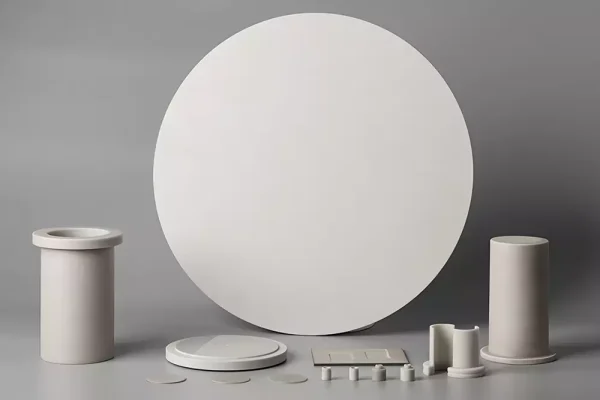

Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
Aluminum nitride ceramics support metallurgical systems requiring efficient heat dissipation with electrical insulation.
- High thermal conductivity ceramics
-Electrically insulating under heat
- Suitable for thermal management parts
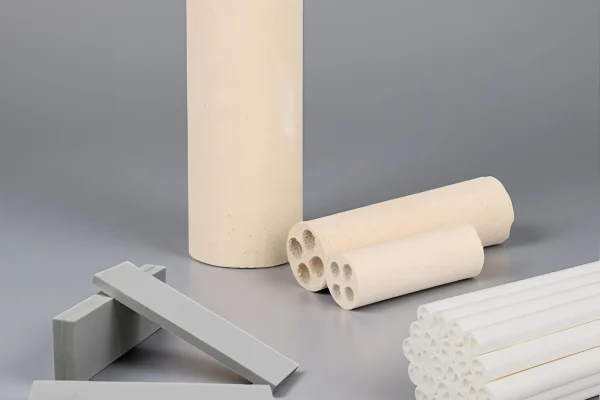

Magnesia Ceramics
Magnesia ceramics are applied in basic atmospheres and slag-rich metallurgical environments.
- Strong resistance to basic slags
-Stable chemical behavior at temperature
- Suitable for aggressive furnace media
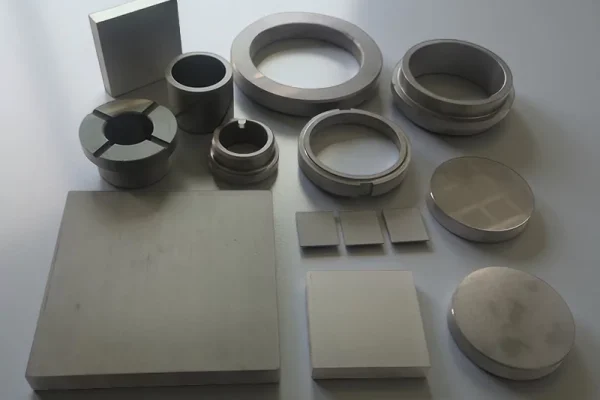

Boron Carbide Ceramics
Boron carbide ceramics serve extreme wear zones where hardness dominates material selection.
- Exceptional hardness against abrasion
-Lightweight structure for rotating systems
- Long service life in blasting media
End-to-End Processing Support for Metallurgical Ceramics

ADCERAX® provides a single, integrated workflow for metallurgical ceramic components, covering every stage from material selection to final delivery.
This one-stop approach reduces coordination risk and ensures metallurgical ceramics remain consistent with real operating conditions rather than isolated specifications.
consistent composition across production batches
stable shapes before high temperature firing
predictable densification under controlled temperatures
tight tolerances for functional assemblies
interfaces optimized for contact performance
measured compliance with engineering drawings
ADCERAX® Manufacturing Metallurgical Ceramics with Process-Level Control
High-Temperature Sintering
Controlled sintering defines the final density, grain structure, and service stability of metallurgical ceramic components.
Tunnel and box kilns up to 1800 °C
Density control within ±0.5% variation
Stable grain growth across long firing cycles
Precision Ceramic Machining
Post-sintering machining ensures metallurgical ceramics meet functional fit and assembly requirements in real equipment.
CNC grinding centers with diamond tooling
Dimensional tolerances down to ±0.02 mm
Consistent surface finish for mating interfaces
Complex Ceramic Forming
It determines whether metallurgical ceramics can be adapted to real furnace geometries, flow paths, and load-bearing structures.
Multi-axis extrusion and isostatic pressing
Thin-wall structures down to 2–3 mm
Large-format parts up to 1200 mm
Advanced Manufacturing Processes for ADCERAX® Labware Ceramics
Custom Metallurgical Ceramics for Process-Specific Demands
Every metallurgical system presents unique thermal profiles, chemical exposure, and mechanical loading conditions that standard ceramic parts cannot fully address.
ADCERAX® works directly from drawings, samples, or operating parameters to deliver custom metallurgical ceramics that align with real furnace geometry, flow paths, and service cycles.
Contact ADCERAX® to discuss your operating conditions and receive a ceramic solution matched to your metallurgical process.
ADCERAX® Metallurgical Ceramics FAQs
Metals gradually creep, oxidize, or soften under sustained high temperatures, which leads to dimensional drift and premature failure. Metallurgical ceramics maintain stable crystal structures and elastic modulus even during continuous operation above 1000 °C. This stability allows furnace components to retain geometry and alignment throughout long production cycles.
Downtime often results from unpredictable component degradation rather than sudden failure. Metallurgical ceramics exhibit slow, predictable wear mechanisms instead of rapid deformation or oxidation. This allows maintenance teams to plan replacement intervals more accurately and avoid emergency shutdowns.
Thermal shock resistance depends on material selection rather than ceramics as a broad category. Properly engineered metallurgical ceramics, such as zirconia- or SiC-based systems, combine low thermal expansion with sufficient fracture toughness. This balance reduces crack initiation during repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Molten metals aggressively attack metallic alloys through dissolution and diffusion. Metallurgical ceramics remain chemically inert in contact with aluminum, steel, and specialty alloys. This prevents contamination of the melt while extending component service life.
Particle impact and abrasion rapidly erode metal liners and chutes. Wear-resistant metallurgical ceramics distribute contact stress across hard, stable surfaces. This significantly slows material loss and reduces liner replacement frequency.
Large components introduce risks of deformation and creep under load. Materials such as NBSiC and silicon carbide-based metallurgical ceramics retain mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. This makes them suitable for beams, shelves, and load-bearing furnace furniture.
Energy loss often occurs through uncontrolled heat transfer and structural distortion. Low thermal expansion and controlled conductivity allow metallurgical ceramics to maintain uniform heat zones. As a result, furnaces operate closer to target temperatures with reduced energy waste.
Small dimensional changes can disrupt alignment, flow paths, or sealing interfaces. Metallurgical ceramics resist creep and plastic deformation under thermal and mechanical load. This preserves functional geometry throughout the component’s service life.
Metallic components can introduce trace elements into melts or powders. High-purity metallurgical ceramics minimize ionic diffusion and surface reactions. This makes them suitable for specialty alloys, analytical melting, and controlled-atmosphere processing.
In metallurgical environments, corrosion and wear often occur simultaneously. Metallurgical ceramics resist chemical attack while maintaining surface hardness. This dual resistance prevents accelerated failure common in coated metal solutions.
Get in touch with us
We believe that Adcerax will become your best partner!
Please fill in your contact information in the form or call us.

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.